- OSPF Link State Advertisements – All 11 OSPF LSA Types Explained
- What is OSPF Link State Advertisement(LSA)?
- OSPF LSA Types Explained – 11 Types of LSA
- 1. What is a Type 1 LSA or OSPF Router LSA?
- 2. What is a Type 2 LSA or OSPF Network LSA?
- 3. What is a Type 3 LSA or OSPF Network Summary LSA?
- 4. What is a Type 4 LSA or OSPF ASBR Summary LSA?
- 5. What is a Type 5 LSA or OSPF AS External LSAs?
- 6. What is a Type 6 LSA or OSPF MOSPF LSA?
- 7. What is a Type 7 LSA or OSPF NSSA External LSAs?
- 8. What is type 8 LSA?
- 9. What is an Opaque LSA – Type 9,10 and 11?
- How to protect OSPF link-state Database from overload?
- How can you slow down OSPF LSA updates during times of network instability?
- What are different OSPF LSA types? -OSPF LSA Types Summary
- Conclusion
OSPF Link State Advertisements – All 11 OSPF LSA Types Explained
An important part of OSPF is the Link State Advertisements (LSAs). LSAs are generated by every router in the AS and contain information about the router’s links and connected networks. Other routers then use this information to calculate the best route to a destination. There are different OSPF LSA types, each with a different purpose and function. In this blog post, I will dig deep into all LSA types, explaining what they do and how to use appropriate commands to check them.
A Quick Recap on OSPF:
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is an Internet Protocol (IP) based network dynamic routing protocol. It is categorized as an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) because of its application within a single autonomous system (AS) and its usage of a link state routing (LSR) algorithm to calculate the shortest paths to a destination.
Check out my previous article about OSPF states.
What is OSPF Link State Advertisement(LSA)?
Link State Advertisement (LSA) is the basic building block that makes up the link state database in OSPF. Every OSPF-enabled router generates LSA, which contains information about the bandwidth, link’s cost, MTU, ip subnet details, link color, etc., of the router’s links and neighbors. The router uses this information to calculate the best path to each destination in the network.
LSAs are flooded throughout the OSPF network, so all routers can view the network topology consistently. When a router receives an LSA, it updates its link state database with the new information.
The router will add this information to its database if the LSA contains information about a new link or neighbor. Likewise, if the LSA contains updated information about an existing link or neighbor, the router will update its database accordingly.
The OSPF routing protocol uses a link state database (LSDB) to store LSAs. The OSPF routing algorithm uses the link state information contained within LSAs to calculate the shortest path to each reachable destination.
Because LSAs age over time, they are stored for a certain amount of time (Max-age 1 hour) before being removed from the link state databases.
Refreshing the LSA (LSRefresh Time) with an increased sequence number and an age of zero is performed every 30 minutes by the router that created the LSA.
OSPF LSA Types Explained – 11 Types of LSA
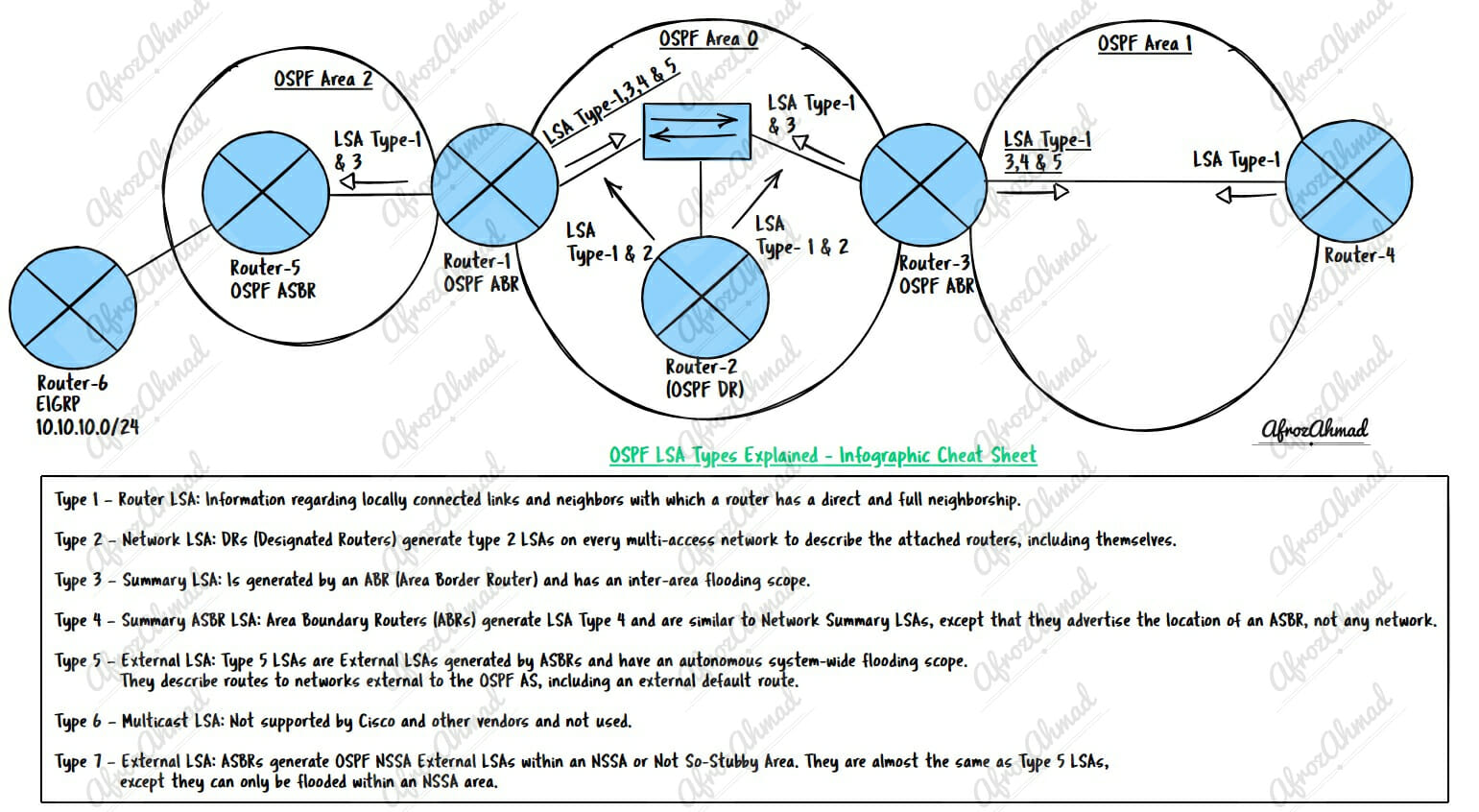
There are 11 types of LSA in OSPF, as described in RFC 2328, and we will dive deep into each type of LSA.
There are 11 different OSPF LSA types:
- LSA Type 1 – Router LSA
- LSA Type 2 – Network LSA
- LSA Type 3 – Summary LSA
- LSA Type 4 – ASBR Summary LSA
- LSA Type 5 – External LSA
- LSA Type 6 – Multicast LSA
- LSA Type 7 – NSSA External LSA
- LSA Type 8 – Link-local LSA
- LSA Type 9 – Opaque LSA
- LSA Type 10 – Opaque LSA
- LSA Type 11 – Opaque LSA
1. What is a Type 1 LSA or OSPF Router LSA?
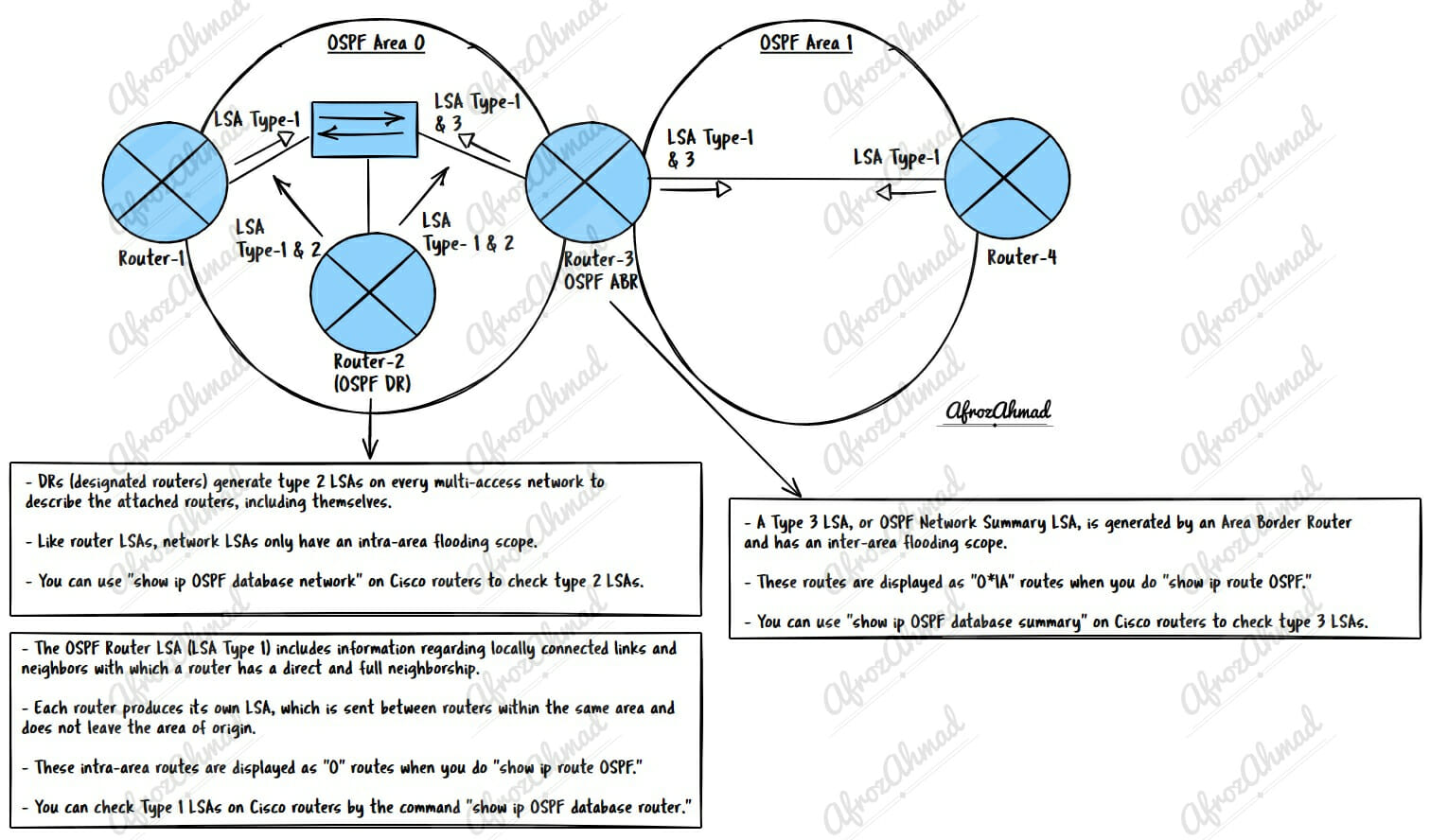
The OSPF Router LSA (LSA Type 1) includes information regarding locally connected links and neighbors with which a router has a direct and full neighborship.
Each router produces its own LSA, which is sent between routers within the same area and does not leave the area of origin.
These intra-area routes are displayed as “O” routes when you do “show ip route OSPF.”
This information includes the router’s ID, the cost of the links connected to the router, the router’s neighbors, and other information. Other routers use this network information to build their routing tables.
You can check Type 1 LSAs on Cisco routers by the command “show ip OSPF database router.”
2. What is a Type 2 LSA or OSPF Network LSA?
DRs (Designated Routers) generate type 2 LSAs on every multi-access network to describe the attached routers, including themselves.
Like router LSAs, network LSAs only have an intra-area flooding scope.
You can use “show ip OSPF database network” on Cisco routers to check type 2 LSAs.
3. What is a Type 3 LSA or OSPF Network Summary LSA?
A Type 3 LSA, or OSPF Network Summary LSA, is generated by an Area Border Router and has an inter-area flooding scope.
The OSPF network summary LSAs are transmitted to a single area to advertise destinations (including a default route, if configured) outside that area but remain within the OSPF autonomous system.
LSA Type 3 packets are sent to multiple areas in the network by using summary prefixes. This makes OSPF more scalable.
These routes are displayed as “O*IA” routes when you do “show ip route OSPF.”
You can use “show ip OSPF database summary” on Cisco routers to check type 3 LSAs.
4. What is a Type 4 LSA or OSPF ASBR Summary LSA?
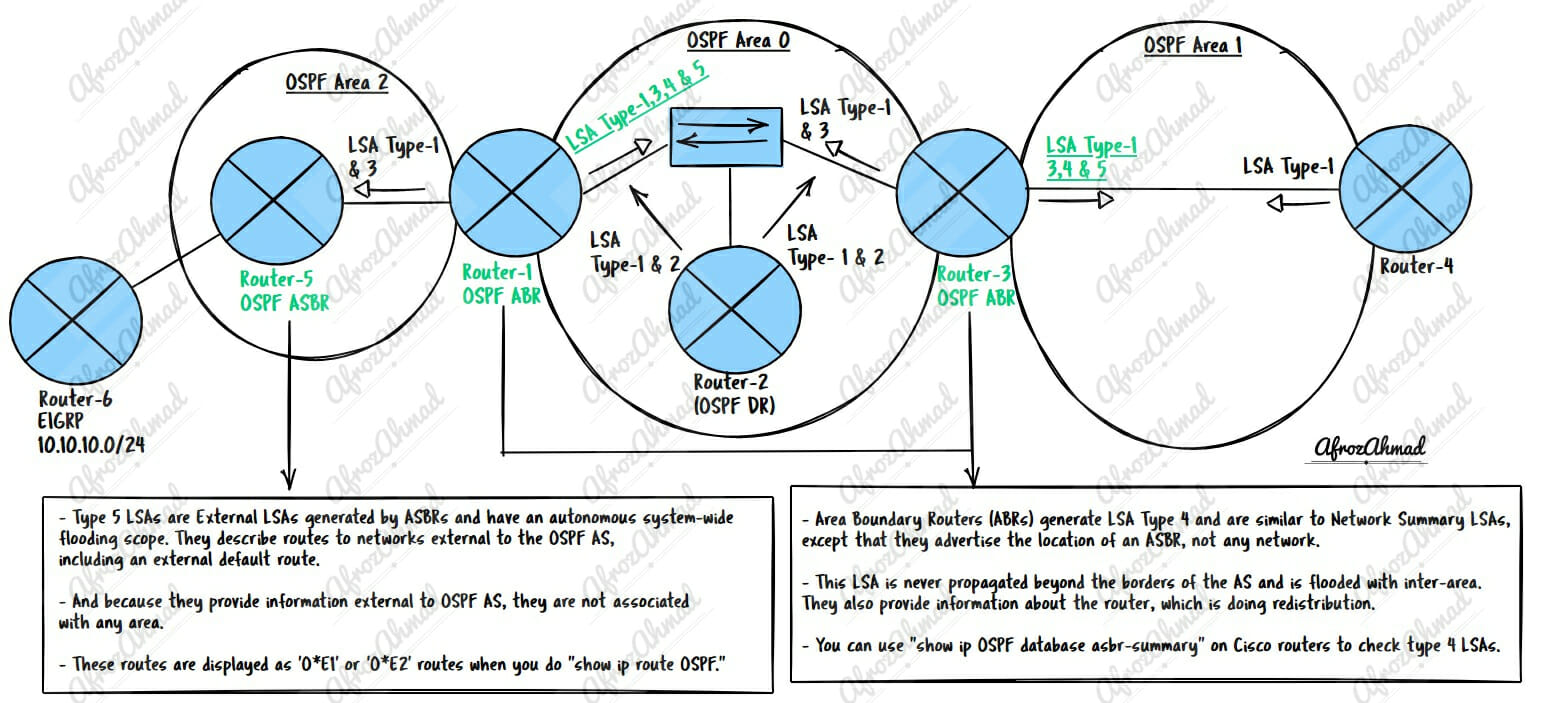
Area Boundary Routers (ABRs) generate LSA Type 4 and are similar to Network Summary LSAs, except that they advertise the location of an ASBR, not any network.
This LSA is never propagated beyond the borders of the AS and is flooded with inter-area. They also provide information about the router, which is doing redistribution.
You can use “show ip OSPF database asbr-summary” on Cisco routers to check type 4 LSAs.
5. What is a Type 5 LSA or OSPF AS External LSAs?
Type 5 LSAs are External LSAs generated by ASBRs and have an autonomous system-wide flooding scope. They describe routes to networks external to the OSPF AS, including an external default route.
And because they provide information external to OSPF AS, they are not associated with any area.
These routes are displayed as ‘O*E1’ or ‘O*E2’ routes when you do “show ip route OSPF.”
You can use the show command “show ip OSPF database external” on Cisco routers to check type 5 LSAs.
An important thing to note for this LSA is that an OSPF external route cannot be the next hop of another OSPF external route.
6. What is a Type 6 LSA or OSPF MOSPF LSA?
The Multicast Open Shortest Path First (MOSPF) protocol generates Type 6 LSAs. MOSPF is an extension to the OSPF routing protocol that allows it to support multicast routing.
Type 6 LSAs contain information about the multicast capabilities of the router that generated them.
Cisco and other network vendors no longer support MOSPF.
It is rarely used and will likely be phased out soon.
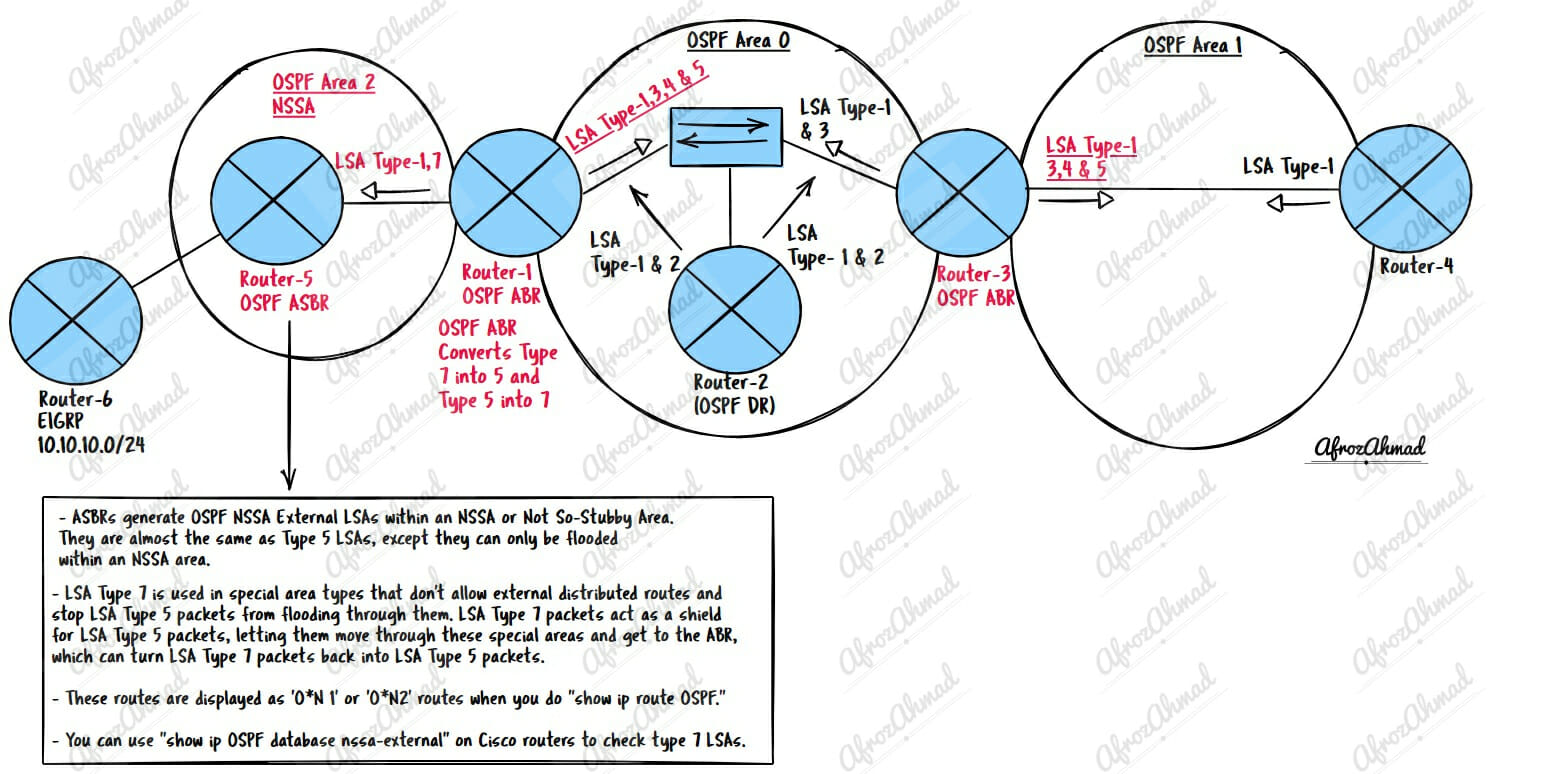
7. What is a Type 7 LSA or OSPF NSSA External LSAs?
ASBRs generate OSPF NSSA External LSAs within an NSSA or Not So-Stubby Area. They are almost the same as Type 5 LSAs, except they can only be flooded within an NSSA area.
LSA Type 7 is used in special area types that don’t allow external distributed routes and stop LSA Type 5 packets from flooding through them. LSA Type 7 packets act as a shield for LSA Type 5 packets, letting them move through these special areas and get to the ABR, which can turn LSA Type 7 packets back into LSA Type 5 packets.
These routes are displayed as ‘O*N 1’ or ‘O*N2’ routes when you do “show ip route OSPF.”
You can use “show ip OSPF database nssa-external” on Cisco routers to check type 7 LSAs.
8. What is type 8 LSA?
A Type 8 LSA is used to deliver information about link-local addresses and a list of IPv6 addresses on the link.
It was originally intended for transit AS(Autonomous Systems), where OSPFv2 may take the role of the internal Border Gateway Protocol to be utilized as an “External-Attributes-LSA” in OSPFv2 (iBGP).
LSA Type 5 carries BGP destinations, and their BGP characteristics are added in LSA Type 8 in these networks. Unfortunately, it was never standardized for OSPFv2 and was never supported by most OSPFv2 implementations.
9. What is an Opaque LSA – Type 9,10 and 11?
An Opaque LSA (Type 9, 10, or 11) is used to carry extra information about OSPF upgrades for application-specific use cases. The information carried in an Opaque LSA is dependent on the Opaque type.
The Type 9 LSA is used for two purposes: to advertise prefixes for stub and transit networks and to support IETF NSF (Non-Stop Forwarding).
Type 10 Opaque LSAs contain extended information that should be flooded by other routers, even if the router cannot understand the extended information itself.
Typically, 10 LSAs are used for traffic engineering (MPLS-TE) extensions to OSPF for creating the Traffic Engineering Database (TED). This allows for more accurate routing by flooding extra information about links beyond just their metric, such as link bandwidth and color.
Type 11 packets do the same thing as LSA Type 10 packets but are not flooded into special area types (Stub areas). This makes it easier to make better use of network resources.
How to protect OSPF link-state Database from overload?
You can use the “max-lsa” command to limit the number of non-self-generated LSAs for a given OSPF process, preventing excessive LSAs generated by other routers in the OSPF domain from draining the CPU and memory resources of a router.
Use caution as this might cause issues in the OSPF process.
Configured under router OSPF.
Router OSPF 1
max-lsa –>>type ? to check all the options available.
How can you slow down OSPF LSA updates during times of network instability?
You can use OSPF LSA throttling (configured with “timers throttle lsa all”) to slow down LSA updates during times of network instability. It also allows for faster OSPF convergence by providing LSA rate limiting in milliseconds.
Use caution as this might cause issues in the OSPF process.
Configured under router OSPF.
Router OSPF 1
timers throttle lsa all –>>type ? to check all the options available.

What are different OSPF LSA types? -OSPF LSA Types Summary
Let us recap.
- Type 1 – Router LSA: Information regarding locally connected links and neighbors with which a router has a direct and full neighborship.
- Type 2 – Network LSA: DRs (Designated Routers) generate type 2 LSAs on every multi-access network to describe the attached routers, including themselves.
- Type 3 – Summary LSA: Is generated by an ABR (Area Border Router) and has an inter-area flooding scope.
- Type 4 – Summary ASBR LSA: Area Boundary Routers (ABRs) generate LSA Type 4 and are similar to Network Summary LSAs, except that they advertise the location of an ASBR, not any network.
- Type 5 – External LSA: Type 5 LSAs are External LSAs generated by ASBRs and have an autonomous system-wide flooding scope. They describe routes to networks external to the OSPF AS, including an external default route.
- Type 6 – Multicast LSA: Not supported by Cisco and other vendors and not used.
- Type 7 – External LSA: ASBRs generate OSPF NSSA External LSAs within an NSSA or Not So-Stubby Area. They are almost the same as Type 5 LSAs, except they can only be flooded within an NSSA area.
Conclusion
We have discussed different OSPF LSA types in this article, used to share different types of routing information between OSPF-enabled devices. Ensure you understand all the types thoroughly, as the OSPF routing process depends highly on LSA propagation, generation, and reception.
We will put the knowledge from this article into practical use in the upcoming OSPF area configuration article. If you want to get this content ahead of time, subscribe to one of our free newsletters.
Further Study:-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Link-state_advertisement
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025