Are you trying to decide between a managed vs unmanaged switch for your network? Managed switches offer extensive configuration options, advanced security, and performance optimization tailored for complex networks. In contrast, unmanaged switches provide a simple, plug-and-play solution ideal for smaller setups.
Read on to understand these differences in detail and make an informed choice.
Managed vs Unmanaged Switch
| Feature | Managed Switch | Unmanaged Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Extensive configuration options via CLI or web GUI | Fixed configuration, no management interface |
| Security | Advanced features like ACLs, 802.1X authentication, and VLANs | Minimal security features |
| Performance | Supports QoS for traffic prioritization and application optimization | Treats all traffic equally |
| Monitoring | SNMP, port mirroring, and other tools for monitoring and troubleshooting | Limited visibility into network issues |
| Scalability | Supports large, complex networks with high traffic volumes | Best suited for small, simple networks |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost and requires more IT expertise | Lower cost and easier to deploy and maintain |
| Ideal Use Cases | Enterprises, data centers, industrial environments, healthcare | Homes, small offices, basic connectivity needs |
| VLANs | Supports virtual LANs for network segmentation and security | No VLAN support |
| Redundancy | Supports protocols like STP and RSTP for high-availability | No redundancy features |
| PoE Support | Often available on managed switches | Available on some unmanaged switches |
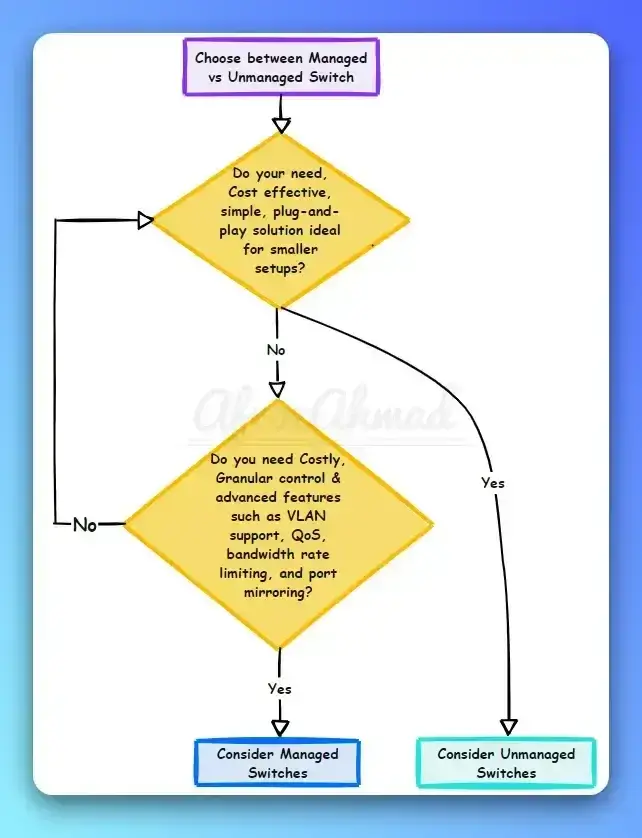
Unmanaged vs Managed Switch Decision Flowchart
Network Switches 101: The Brain of Your LAN
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, let’s cover some basics. A network switch is like the central nervous system of your Local Area Network (LAN). It connects all your devices – computers, servers, printers, you name it – allowing them to communicate with each other seamlessly. Think of it as a traffic controller directing data packets to their intended destinations.
Under the hood, a switch has three main components:
- Ports: Where you plug in your Ethernet cables
- MAC address table: A directory of connected devices
- Forwarding plane: The decision-maker that determines where to send data
Now that we’ve got the fundamentals down, let’s explore the two main types of switches: unmanaged and managed.
Unmanaged Switches: Plug, Play, and Forget
An unmanaged switch is like a straightforward, no-frills appliance. You take it out of the box, plug in your devices, and voila – you’re ready to go! These switches automatically negotiate settings like data rate and duplex mode, making setup a breeze.
Key Characteristics of Unmanaged Switches
- Plug-and-play operation
- Fixed configuration (can’t be modified)
- No management or security features
- Ideal for small, simple networks
Unmanaged switches are perfect for homes, small offices, or any environment where you need basic connectivity without the bells and whistles. They’re affordable, easy to use, and require minimal IT expertise.
Below are some of my favorite unmanaged switches.





Managed Switches: Unleash the Power of Customization
On the other hand, a managed switch is like a high-performance sports car with all the extras. It gives you complete control over your network, allowing you to configure, monitor, and optimize every aspect of its performance.
Key Characteristics of Managed Switches
- Granular control over network traffic and access
- Advanced features like VLANs, QoS, SNMP, and port mirroring
- Robust security and access control capabilities
- Ideal for larger, complex networks with demanding requirements
Managed switches are the go-to choice for enterprises, data centers, and any network that demands high performance, security, and reliability. They offer a wealth of features that empower you to tailor your network to your exact specifications.
Below are some of my favorite managed switches.
![Zyxel Multi-Gig 12-Port Web Managed Switch with 2-Port 2.5G/2-Port 10G SFP+ Desktop/Wallmount, 5-Years Warranty [XGS1210-12]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41u++vnt4qL._SS520_.jpg)



The Great Divide: Managed vs Unmanaged Switches
So, what sets managed and unmanaged switches apart? Let’s break it down:
- Configuration Options: Managed switches offer extensive configuration options, while unmanaged switches have a fixed configuration.
- Security Features: Managed switches provide advanced security features like access control lists and 802.1X authentication, whereas unmanaged switches have minimal security.
- Performance Optimization: With managed switches, you can prioritize traffic and optimize application performance using Quality of Service (QoS). Unmanaged switches treat all traffic equally.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Managed switches offer powerful monitoring and troubleshooting tools, such as SNMP and port mirroring. Unmanaged switches have limited visibility into network issues.
- Cost and Complexity: Managed switches are more expensive and require more IT expertise to set up and maintain compared to unmanaged switches.
Choosing the Right Switch for Your Network
Now that you understand the key differences between managed and unmanaged switches, how do you choose the right one for your network? Consider the following factors:
- Network Size and Complexity: The larger and more complex your network, the more likely you’ll need a managed switch.
- Application Criticality: If you have mission-critical applications that demand high performance and reliability, a managed switch is a must.
- Security Requirements: If your network handles sensitive data or must comply with stringent security regulations, a managed switch is essential.
- Scalability: If you anticipate significant growth in the future, a managed switch will provide the flexibility and features to support that growth.
- Budget and IT Resources: Managed switches are more expensive and require more IT expertise. Make sure you have the budget and staff to support your choice.
Real-World Scenarios: Matching Switches to Networks
Let’s look at some common use cases and the type of switch that’s best suited for each:
- Home or Small Office: An unmanaged switch is usually sufficient for basic connectivity needs.
- Small to Medium Business: A smart managed switch offers a good balance of features and affordability.
- Enterprise or Data Center: Fully managed switches are critical for handling high traffic volumes, ensuring security, and maintaining uptime.
- Industrial or Healthcare: Managed switches with industrial-grade durability and reliability are essential for harsh environments and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
Managed Switch Features: A Closer Look
If you’ve determined that a managed switch is right for your network, let’s explore some of its key features in more detail:
- VLANs: Virtual LANs allow you to segment your network into smaller, isolated subnetworks for improved security and performance.
- QoS: Quality of Service lets you prioritize critical traffic (like voice or video) over less sensitive data, ensuring optimal application performance.
- Port Mirroring: This feature allows you to mirror traffic from one or more ports to another for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
- Redundancy Protocols: Managed switches support protocols like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) to prevent network loops and ensure high availability.
- Access Control Lists: ACLs allow you to filter traffic based on IP addresses, MAC addresses, or other criteria, enhancing network security.
- CLI and Web GUI: Managed switches offer both command-line and web-based interfaces for configuration and management, catering to different skill levels and preferences.
Conclusion: Making the Smart Switch Choice
Choosing the right Ethernet switch is crucial for building a high-performance, secure, and reliable network. By understanding the differences between managed and unmanaged switches and assessing your specific needs, you can make an informed decision that will serve your organization well into the future.
Remember, while managed switches offer advanced features and benefits, they also come with higher costs and complexity. If you’re unsure which type of switch is best for your environment, consult with a network professional who can guide you through the selection process.
We hope this article has demystified the world of Ethernet switches and empowered you to make the best choice for your network. Remember, investing in the right switch today can pay dividends in performance, security, and reliability for years to come.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a managed switch in an unmanaged mode?
A: Yes, most managed switches can function as unmanaged switches if you choose not to configure their advanced features. However, you’ll be paying for features you’re not using.
Q: Do I need a managed switch for Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices?
A: Not necessarily. While many managed switches support PoE, there are also unmanaged PoE switches available. The choice depends on your other network requirements.
Q: Can I mix managed and unmanaged switches in the same network?
A: Yes, you can mix managed and unmanaged switches in a network. However, the unmanaged switches will not be able to take advantage of the advanced features of the managed switches.
Q: How do I access the management interface of a managed switch?
A: Most managed switches offer both a command-line interface (CLI) accessible via Telnet or SSH and a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) accessible through a browser.
Q: What’s the difference between a managed switch and a smart switch?
A: A smart switch is a type of managed switch that offers a subset of the features of a fully managed switch. It’s a good middle ground between unmanaged and fully managed switches in terms of cost and complexity.
- Epson EpiqVision Flex CO-W01 Projector Review - February 21, 2025
- How to Log in to Your Netgear Router - January 17, 2025
- Gaimoo GM200 Mini Projector Review - January 12, 2025



