An ethernet switch or network switch is an essential device for connecting multiple devices together on a local area network (LAN).
This comprehensive guide will explain what is an ethernet switch, what do it do , how it works, and its key benefits.
What is an Ethernet or Network Switch?
An ethernet switch or network switch is a networking device that connects multiple devices on a computer network. It works on the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model and uses MAC addresses to forward data packets to the correct destination device.
Some key things about ethernet switches:
- Forwards data frames based on MAC addresses
- Operates at layer 2 (data link layer) of the OSI model
- A plug-and-play device with no configuration required
- Creates a collision domain per port
- Supports full-duplex communication for increased speed
How Does an Ethernet Switch Work?
Ethernet switches use packet switching to receive, process, and forward data. The key steps are:
- Receiving: The switch receives an incoming ethernet frame on one of its ports.
- Learning: It examines the source MAC address and adds it to the MAC address table along with the associated port.
- Forwarding: It looks up the destination MAC address in the table to find the correct outgoing port.
- Filtering: It forwards the frame only to the destination port, filtering it from other ports.
- Flooding: If the destination MAC address isn’t found, the frame is flooded out to all ports.
This selective forwarding allows the switch to filter data traffic and prevent unnecessary broadcasting across the network.
What do ethernet switches do?
Here are the key things that ethernet switches do:
In summary, the main job of an ethernet switch is to intelligently forward frames between devices to enable local communication using MAC address lookups. This makes them a core component of Ethernet based networks.
Ethernet switches send frames only to specific devices having specific mac addresses and only intended to receive that frame.
So now the question comes:-
How does the switch decide where to send the frames transmitted from different devices on the network?
Every frame has a source and destination MAC address field, and a switch opens up (if it needs to) that frame and looks at that information. Then, it cross-verifies that source MAC address in its table. If the source MAC address is not present in the table, it adds the MAC address and the port into the table. This table is referred to as the content-addressable memory table ( CAM table) in CatOS and the MAC address table in IOS holds a map of which MAC addresses have been detected on which ports and is used to identify which ports have been discovered.
The switch then identifies the destination MAC address of the frame and examines the table to see whether there is a match. If there is a match, that frame is only forwarded to that port. The frame is transmitted to all ports if a match is not found.
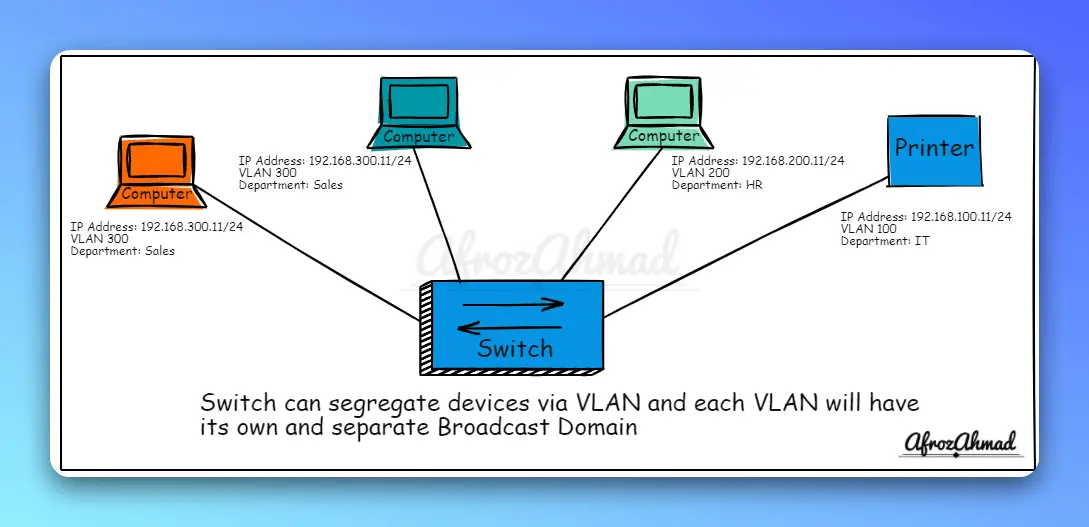
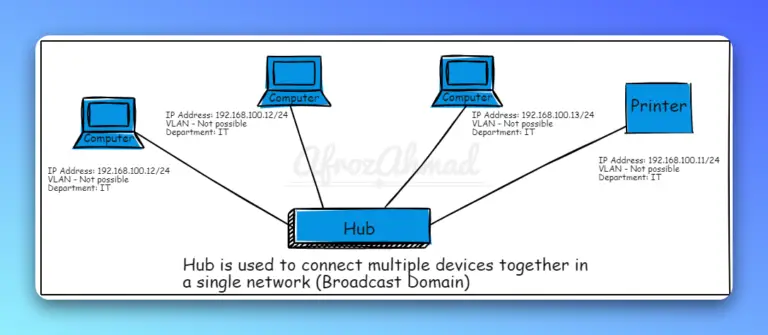
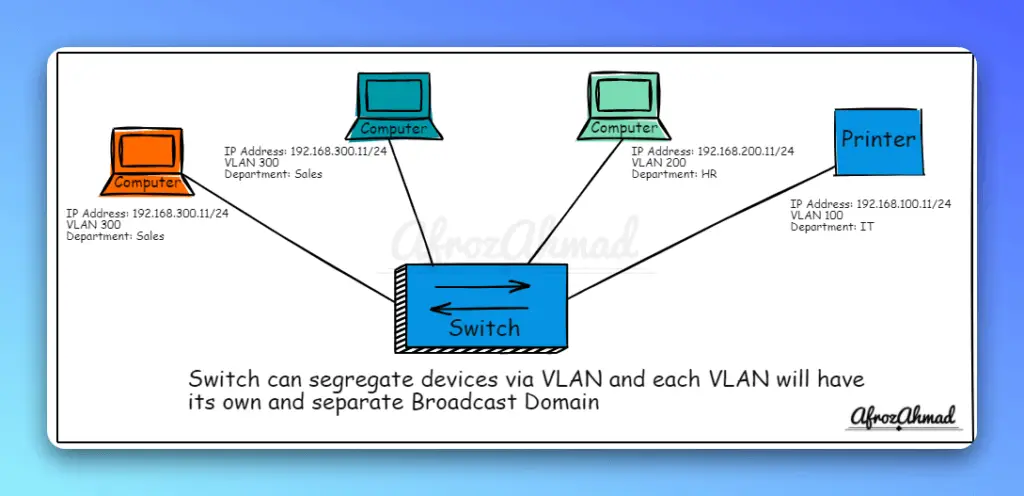
Ethernet switches can segregate network devices into groups by using VLANs.
Check out the Ethernet Switch vs Hub vs Router article for a more in-depth comparison.
See also: What is a Router and What Does it Do?
What are the different types of ethernet switches?
There are several different types of ethernet switches. The main categories are:
Modular Switches
- Chassis-based switches with slots to add modules and ports as needed
- Flexible and scalable, can expand as network grows
- More expensive than fixed switches
- Examples: Cisco Catalyst 6000, Huawei CloudEngine series
Fixed Configuration Switches
Unmanaged Switches
- Basic “plug and play” switches
- No configuration options
- Lowest cost option
Smart Switches
- Offer basic management like VLANs, port monitoring etc
- Some configuration possible via GUI
- Cost effective for small and medium networks
Managed Switches
- Fully configurable via CLI or web interface
- Advanced features like SNMP, VLANs, LAGs etc
- Most expensive, for large and complex networks
- Examples: Cisco Catalyst, HPE Aruba, Juniper EX series
Stackable Switches
- Multiple switches connected as single logical unit
- Scalability and resilience benefits
- Cisco Catalyst, HPE Aruba, Huawei CloudEngine series
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Switches
- Provide power over ethernet cables to devices like IP phones, cameras
- Standards like 802.3af, 802.3at, 802.3bt
- Cisco Catalyst, Juniper EX, HPE Aruba support PoE
Optical Fiber Switches
- Support fiber optic cable connections
- Used for backbones, data centers, high speed networks
- Examples: Cisco Nexus, Juniper QFX, HPE SN6000
So in summary, factors like budget, scalability needs, network size and applications determine the ideal ethernet switch type for an organization.
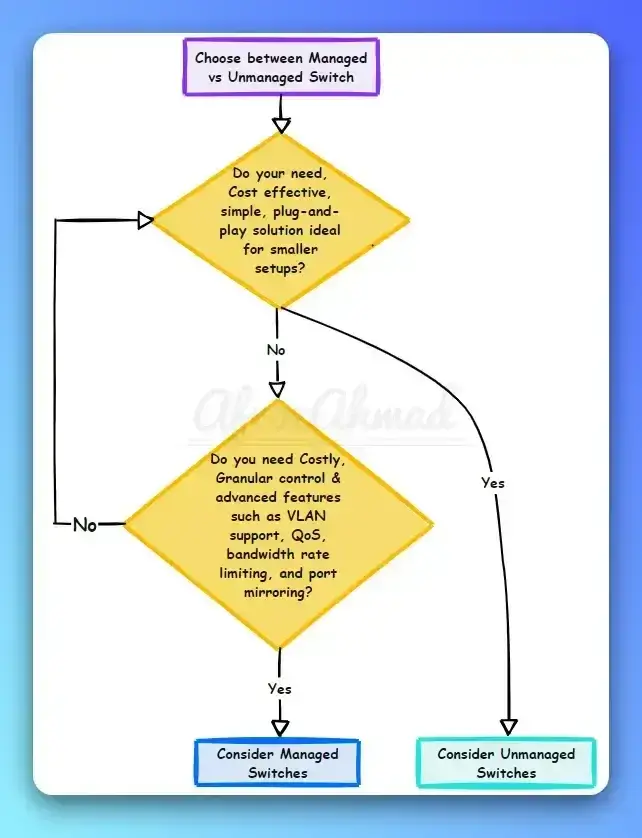
See also: managed vs unmanaged switch
Advantages and Disadvantages of an Ethernet Switch
| Advantages of an Ethernet Switch | Disadvantages of an Ethernet Switch |
|---|---|
| Switches have port ranges between 8-48 ports suitable for small and large Local Area Networks. You can use switches inside the home as well if you have heavy usage applications like multiplayer games or heavy music file sharing. | Switches with more ports are costlier. |
| Switches are more Intelligent than hubs and have many features, including device identification, layer2 security, flood identification, prevention, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), etc. | You need networking knowledge to configure a switch properly. A wrong or improper switch configuration can do disaster in the network. |
| The switch reduces the number of broadcast domains. | Switches are not as good as routers in limiting a broadcast; however, nowadays, there are layer3 switches that can handle broadcasts like routers. |
| The switch supports VLANs for logical port segmentation. | Some switches only support normal VLAN ranges from 1-1005 and do not support extended VLAN range(1006 to 4094). Therefore, you should always check a switch VLAN limits as per your requirement. |
| Switches can use the CAM database or MAC address tables to map the port to MAC. | Some switches have a specific limit for MAC address tables; you should always check the maximum CAM database size before deploying switches. |
| Switches are robust and can handle broadcast and multicast packets. | Although switches can handle broadcast and multicast packets well, handling Multicast packets in switches requires careful planning and design. |
| Administrators can manage VLAN security and turn ports on and off using intelligent ethernet switch features. | Again these advanced features need proper networking knowledge and careful planning. |
Conclusion
Ethernet switches are essential for building local area networks. They allow multiple devices to connect, communicate, and share data at fast speeds in a seamless plug-and-play manner. Investing in a quality ethernet switch is a great way to improve network performance and expand connectivity.
- Epson EpiqVision Flex CO-W01 Projector Review - February 21, 2025
- How to Log in to Your Netgear Router - January 17, 2025
- Gaimoo GM200 Mini Projector Review - January 12, 2025