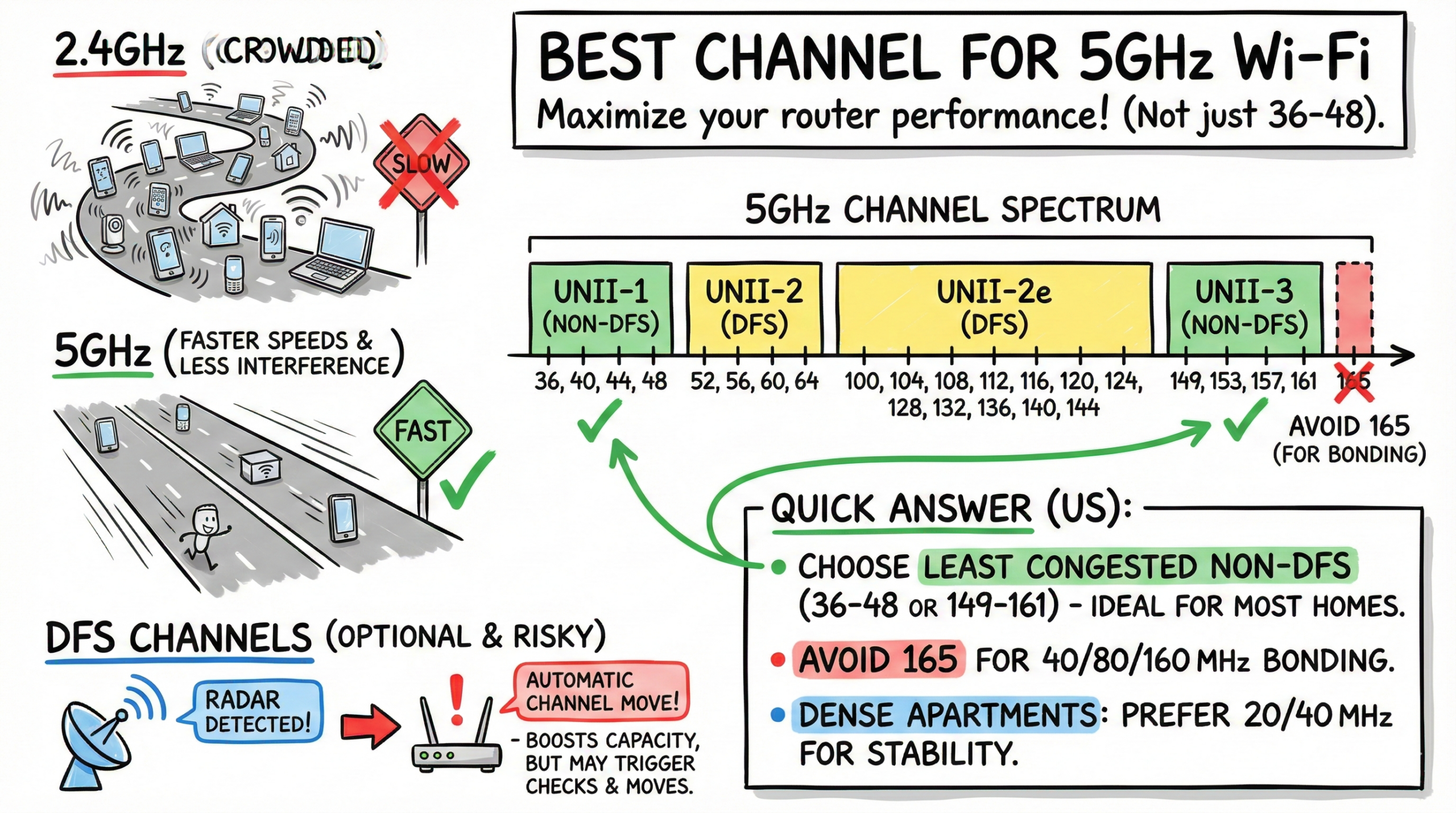
The 5GHz Wi‑Fi band offers faster speeds and less interference compared to crowded 2.4GHz networks. However, with more devices connecting wirelessly, even 5GHz networks can become congested.
Quick answer (US): choose the least congested non‑DFS set 36/40/44/48 or 149/153/157/161 for most homes; avoid 165 for 40/80/160 MHz bonding; in dense apartments prefer 20/40 MHz; DFS channels are optional and can boost capacity but may trigger checks and automatic channel moves when radar is detected.
Choosing the Best Channel for 5GHz WiFi (not just 36–48) for your router is crucial to maximize performance. The infographic below maps US 5GHz channels, DFS requirements, and bonding options at a glance.
This definitive guide will teach you how to identify and select the best 5GHz channel for faster, more reliable wireless connectivity. You’ll learn channel basics, use Wi‑Fi scanners to analyze your environment, and implement channel changes through your router settings.
Follow these practical steps to eliminate lag and disruptions when multiple devices compete for bandwidth on overloaded networks. Bid farewell to buffering videos, dropped VoIP calls, and glacial download speeds by configuring 5GHz channels strategically. Let’s get started!
Understanding 5GHz Wi‑Fi Channels
The 5GHz frequency band is much wider than 2.4GHz, with more available non‑overlapping channels. This allows signals to transmit without interfering with each other, enabling faster Wi‑Fi speeds.
There are a total of 25 non‑overlapping 20MHz‑wide channels in the 5GHz bands designated for Wi‑Fi in the US.
| Band | Frequency Range | Channel Range | Main Channels | Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNII-1 | 5.15 GHz to 5.25 GHz | 36-48 | 36, 40, 44, 48 | None; higher power and outdoor use permitted under current FCC rules |
| UNII-2 | 5.25 GHz to 5.35 GHz | 52-64 | 52, 56, 60, 64 | Requires DFS and TPC |
| UNII-2e | 5.47 GHz to 5.725 GHz | 100-144 | 100, 104, 108, 112, 116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140 | Requires DFS and TPC |
| UNII-3 | 5.725 GHz to 5.85 GHz | 149-165 | 149, 153, 157, 161, 165 | None |
The U‑NII‑1 and U‑NII‑3 bands are widely used for standard home and office Wi‑Fi. Within those bands, channels 36, 40, 44 and 48, plus 149, 153, 157 and 161 are commonly recommended for typical US home use, as they limit the chance of interference. Wider channels can be configured by bonding contiguous channels: 80 MHz is formed by two 40 MHz blocks (four adjacent 20 MHz channels); 160 MHz is two contiguous 80 MHz blocks; 80+80 MHz uses two noncontiguous 80 MHz blocks.
The U‑NII‑2 bands require dynamic frequency selection (DFS) and transmit power control (TPC) to avoid interference with radar systems. Most current consumer Wi‑Fi 5/6/6E/7 routers support DFS channels in settings. DFS involves a channel availability check (a brief listen before transmit) and can force an automatic channel change if radar is detected.
Note: The 5.850–5.895 GHz segment (often referred to as U‑NII‑4) is being opened for indoor unlicensed use in the US, but consumer client and router support remains limited; most home users can ignore it for now.
See also: 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz WiFi Bands
Why 5 GHz Channel Selection Matters
Choosing the optimal 5GHz channel for your wireless router is important for several reasons:
- Avoid interference – Using the same channel as neighboring Wi‑Fi networks can cause contention and lower throughput.
- Faster speeds – Clearer channels enable higher data rates, especially with wider channel widths.
- More bandwidth – Wider channels (when feasible) increase total throughput.
- Reliability – Less interference means fewer disconnects and latency spikes.
While leaving the router on automatic channel selection can work with newer routers, manually selecting the clearest 5GHz channel typically performs better in busy environments.
How to Find the Best 5 GHz WiFi Channel?
Finding the optimal 5GHz Wi‑Fi channel takes just a few quick steps:
1. Download a WiFi Analyzer App
The first step is to download an app that scans for Wi‑Fi channels in use and identifies the least congested options.
Popular Wi‑Fi analyzer apps include:
- Windows – Acrylic WiFi Home, WiFiInfoView, inSSIDer
- Mac – WiFi Explorer, NetSpot
- Android – WiFi Analyzer, WiFiAnalyzer Open-Source
2. Scan and Analyze 5 GHz WiFi Channels
Open your Wi‑Fi analyzer app and scan for nearby 5GHz networks. Look at the visualized channel usage graphs:
- See which channels have the strongest signal strength (between −30 dBm and −65 dBm is ideal).
- Check which channels have the fewest networks using them to avoid interference.
- Select the channel with the optimal combination of strong signal and low utilization.
For US homes, channels 36, 40, 44, 48 and 149, 153, 157, 161 typically perform best; channel 165 is often limited to 20 MHz and can’t bond to 40/80/160 MHz on most gear.
For example, NetSpot provides real-time visualization of channel usage and interference across 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. It reveals the channels experiencing maximum contention in your environment.
Based on identified “hot spots,” NetSpot recommends specific channels for optimal performance. It also displays the number of networks detected on each channel.
Now that you’ve pinpointed candidate 5GHz channels, it’s time to reconfigure your router settings.
Changing the 5GHz WiFi Channel on Your Router
Once your Wi‑Fi analyzer recommends better‑performing channels, you can manually switch to those options.
Here is the overall process to change 5GHz channels on common router brands:
- Log in to your router admin interface using a web browser
- Navigate to the Wireless, Wi‑Fi or Network settings tab
- Locate the section for configuring 5GHz wireless networks
- Switch from Auto channel selection mode to Manual mode
- Choose your newly scanned 5GHz channel from the dropdown menu
- Click Save to apply the updated channel selection
For Asus routers, disable Auto Channel Selection under the 5GHz tab and choose a specific channel instead. Netgear genie allows picking 5GHz channels when customizing the wireless network.
Refer to your router’s user manual for exact steps tailored to that model. Once reconfigured, connect devices to the 5GHz network and test performance.
See also: How to isolate 2.4 and 5 GHz channels on your WiFi Router
Verifying and Retesting 5GHz Wireless Channel Selections
After implementing new 5GHz channel settings, validate that the changes took effect and monitor the impact:
- Reconnect wireless clients to the 5GHz SSID
- Run speed tests to compare before/after throughput
- Rescan 5GHz channels using Wi‑Fi analyzers over time
- Switch channels again if congestion arises
- Consider router placement to optimize wireless coverage
Ideally, the revised channel will showcase faster speeds with no discernible packet loss. The Wi‑Fi scanner should also show that channel experiencing less contention.
However, as neighboring networks evolve, channel interference can return. Rerun the channel selection process occasionally, or whenever slowing 5GHz connectivity is experienced.
Other 5GHz Optimization Tips
Beyond channels, additional router configuration changes can boost performance:
Update Channel Width for Higher Throughput
Wider Wi‑Fi channel widths enable faster data rates, including:
- 20/40/80/160 MHz options (80 MHz is common for 5GHz)
Reduce channel width if slowing speeds, high interference, or spotty device connections occur.
Enable Consistent Roaming with Band Steering
Band steering encourages dual‑band devices to use clearer 5GHz signals instead of 2.4GHz. For faster access‑point‑to‑access‑point hand‑off, look for support for 802.11k/11v/11r (fast BSS transition and neighbor reports) on both your APs and clients.
Limit Legacy Device Connections
The 802.11ax Wi‑Fi 6 standard transmits more efficiently than older protocols. Reduce collisions by limiting legacy 5GHz clients (e.g., 802.11a/n) on busy radios; note that 802.11b/g operate only on 2.4GHz.
Prioritizing modern devices accessing the network optimizes overall usage.
See also: Is Internet the same as WiFi?
Factors Impacting 5 GHz WiFi Channel Performance
There are a few key factors that determine which 5GHz channel will provide the fastest and most reliable Wi‑Fi performance:
WiFi Congestion
In densely populated areas, many competing 5GHz networks may lead to channel overcrowding and interference. Analyzing channel utilization in your environment is key.
Client Device Location
Higher 5GHz frequencies don’t penetrate solid objects as well as 2.4GHz. Place client devices closer to the wireless access point for optimal performance.
Channel Width
Using wider channels (40 MHz, 80 MHz) increases speed but also risk of interference. Narrow 20 MHz channels are more resistant to congestion.
DFS Certification
Dynamic frequency selection (DFS) allows using more 5GHz channels but can introduce short service interruptions: routers perform a channel availability check before enabling a DFS channel and will automatically move channels if radar is detected.
Consider all these elements when selecting your channel. An analyzer app that visualizes signal strength per channel simplifies finding the ideal option.
Choosing Channels for Optimal Performance
Selecting uncongested 5GHz Wi‑Fi channels tailored to your environment is vital for robust wireless connectivity. Avoid using routers’ default auto channel settings without proper scanning validation.
This guide covered practical techniques to:
- Evaluate channel selections using Wi‑Fi analyzers
- Identify and configure the best 5GHz channels
- Validate and retest channel changes over time
Take control of increasingly crowded airwaves by applying these wireless optimization best practices. Follow the steps outlined here to eliminate lag and get the most out of your home or office 5GHz network!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about choosing the best 5GHz Wi‑Fi channel:
How many non‑overlapping channels does 5GHz have?
In the US there are 25 total 5GHz channels at 20 MHz width. Sixteen of these require DFS (channels 52–64 and 100–144). Non‑DFS channels are 36–48 and 149–165.
What are the best default 5GHz channels?
For home use in the US, pick from 36, 40, 44, 48 or 149, 153, 157, 161 based on least congestion. Channel 165 is typically limited to 20 MHz and is not suitable for 40/80/160 MHz bonding.
Does it matter if I don’t manually select a 5GHz channel?
Leaving auto channel selection enabled can work well with newer routers, but manually checking for interference often performs better in apartments and other dense areas.
Can I use a wider 80 MHz or 160 MHz channel for faster speeds?
Yes, when clients are close and the spectrum is clean. 80 MHz is formed by two contiguous 40 MHz blocks (four 20 MHz channels). 160 MHz is two contiguous 80 MHz blocks; 80+80 MHz uses two noncontiguous 80 MHz blocks.
How do I change the 5GHz channel on my wireless router?
Log into your router admin console, go to wireless settings, disable auto channel selection, and pick your preferred channel.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025