As network technology evolves and becomes increasingly complex, understanding the different components and concepts is vital. In this article, we will discuss three essential networking concepts: MTU, Jumbo Frames, and MSS.
We will explain what each term means, how it impacts network performance, and why it is important for network engineers to be familiar with these concepts. By the end of this article, you should have a clear understanding of MTU, Jumbo Frames, and MSS and how they influence your network’s efficiency and performance.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is a critical parameter in networking that specifies the maximum size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a network. MTU is measured in bytes and varies depending on the transmission media.
For example, Ethernet’s standard MTU is typically 1500 bytes, which includes the payload but excludes the Ethernet header (14 bytes) and the CRC (4 bytes).
VLAN Tags and MTU
VLAN tags are essential for dividing a network into smaller segments and enabling virtualization. To ensure proper handling of VLAN tags, it is necessary to increase the maximum Ethernet frame size from 1518 bytes to 1522 bytes, accommodating the additional 4-byte VLAN tag. It is important to note that network devices that do not support larger frame sizes above 1500 may still process these frames without any issues, although they will be identified as “baby giant” anomalies.
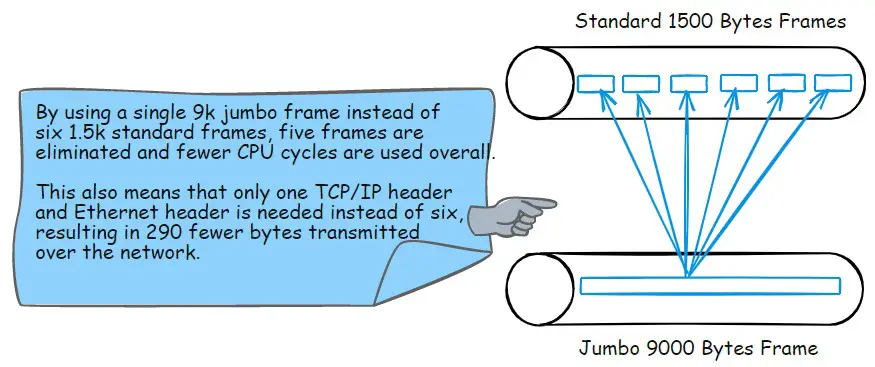
What are Jumbo Frames?
Jumbo Frames are data packets that exceed the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size of 1500 bytes in Ethernet networks. They can range from 9000 to 9600 bytes, which means they can carry more data in a single packet than standard Ethernet frames.
Benefits of Jumbo Frames
Jumbo Frames offer several advantages over traditional Ethernet MTUs:
- Reduced frame count: Fewer Ethernet headers are required, resulting in fewer frames being sent across the network.
- Lower CPU usage: Fewer headers need to be built and read, reducing CPU cycles on both the sender and receiver sides.
- Improved network bandwidth: Fewer headers mean less network overhead, freeing up more bandwidth for actual data transmission.
By reducing the number of frames and headers required, Jumbo Frames can significantly increase network performance.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Jumbo Frames
Drawbacks of Jumbo Frames include:
- Incompatibility: Not all devices support Jumbo Frames. If one device in the network does not support Jumbo Frames, communication issues may arise.
- Limited hardware options: Only some network interface cards (NICs) and switches support Jumbo Frames. You may require specialized hardware, which can be cost-prohibitive.
- Enabling Jumbo Frames on a slow network can cause network congestion and may lead to packet loss.
- Misconfiguration can lead to network instability, so it is important to configure Jumbo Frames carefully.
Jumbo Frames Facts and Use-Cases
- Jumbo Frames are not commonly used in everyday network environments.
- Jumbo Frames can be beneficial for data-intensive applications like video surveillance, virtual machine migration, and big data analytics.
- Jumbo Frames can significantly reduce network overhead and improve data transfer in high-speed LANs.
- Jumbo Frames are not a solution for all network performance issues.
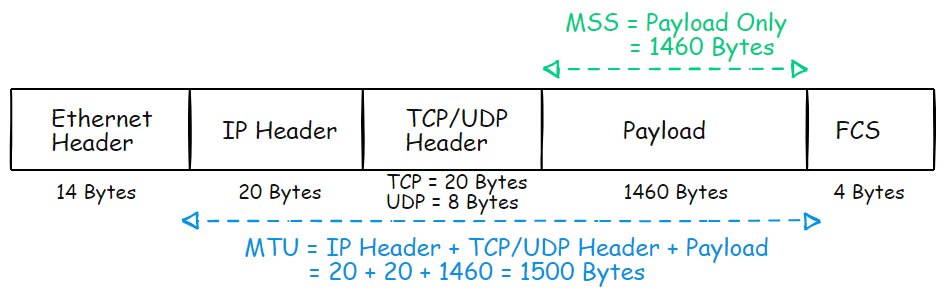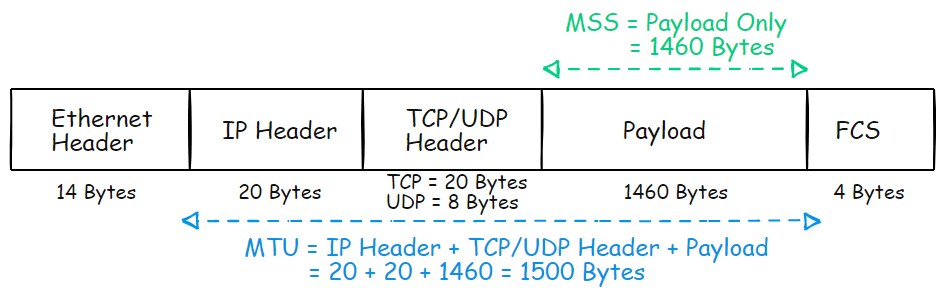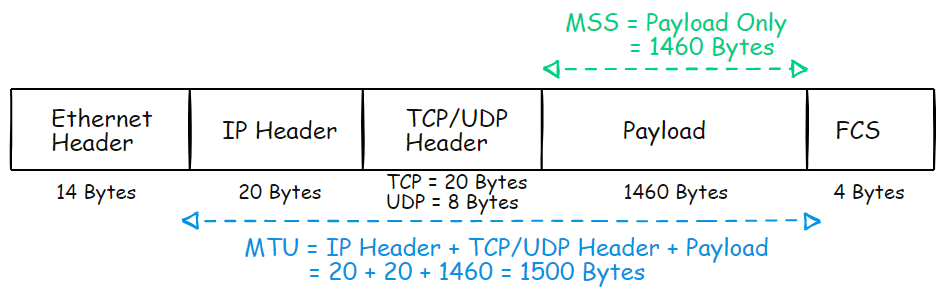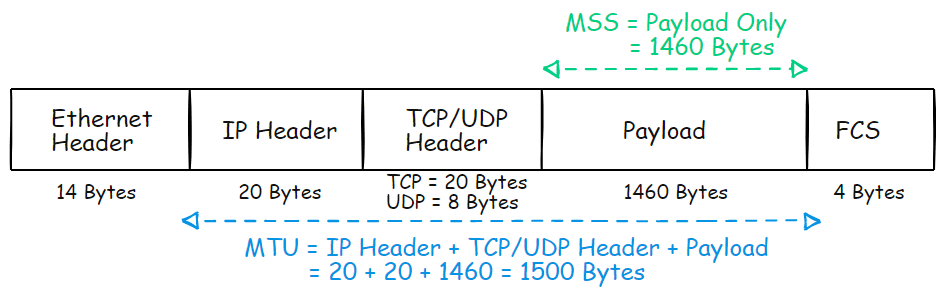
What is TCP MSS: Maximum Segment Size
The Maximum Segment Size (MSS) is a setting found in the TCP header’s options field. It determines the largest amount of data or Payload in bytes that a computer or communication device can receive in a single TCP segment.
Here are some of the key details of MSS:
- The MSS does not include the TCP or IP header.
- Communicated between endpoints in the SYN packet during the TCP 3-way handshake, influenced by factors like the operating system, MTU, and (NIC)Network Interface Card.
- Senders break data into chunks of MSS size or smaller, considering the lowest value in the path.
- Receivers reassemble data and send acknowledgments (ACKs) for each correctly received segment.
- If a segment exceeds the MSS value, the receiver sends back a message with the supported MSS to reduce segment size.
- Optimal MSS value depends on network factors such as MTU, packet fragmentation, and protocol-level considerations.
Common Symptoms and Troubleshooting MTU and MSS Issues:
Common Symptoms of MTU and MSS Issues:
Symptoms of MTU issues:
- Network connectivity issues, such as slow or intermittent connections
- Inability to connect to certain websites or services
- Packets being dropped or delayed along the network path
- Fragmentation of packets along the network path
Symptoms of MSS issues:
- Slow transfer speeds for file downloads or uploads
- Long transfer times for large files or data sets
- Repeated failed transfer attempts or partial transfer failures
- Network congestion during high-traffic periods
It is important to note that many of these symptoms can be indicative of other network issues as well and that effective network troubleshooting should always involve identifying and eliminating potential root causes logically and systematically. Nonetheless, if you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, it may be worth investigating MTU and MSS values on your network as a potential source of the problem.
How to Troubleshoot MTU Issues?
- Use the ping command with the ‘don’t fragment’ (-f) option to check if packets are being fragmented along the path. If the ping yields a “packet too big” error message, then packets are being dropped along the way, and you may need to lower your MTU.
- Reduce the MTU size in increments until the ping command is successful, then increase the MTU one step at a time until the ping fails again. This will help you determine the maximum MTU size for your network.
- Configure your routers with the appropriate MTU size for your network. This may involve setting the same MTU on all devices or setting smaller MTUs for certain paths, depending on the network topology.
How to Troubleshoot MSS Issues?
- Use a packet capture tool, such as Wireshark, to capture network traffic and observe the MSS values being exchanged during the TCP handshake. Look for discrepancies in these values, which may be causing issues with network performance.
- Use a tool such as the TTCP (Test TCP) utility to test network performance with different MSS values and identify the most efficient value for your network.
- Update or adjust the TCP/IP parameters on the networking devices, such as servers and routers, to reflect the correct MSS value. This may require adjustments to the device’s registry settings or configuration files.
Conclusion
Understanding MTU, Jumbo Frames, and MSS is crucial for network administrators and engineers who want to optimize their network’s performance. These concepts play a vital role in determining how data is transmitted across networks, and being familiar with them can help you make informed decisions about your network’s configuration and efficiency.
By leveraging Jumbo Frames and properly configuring MTU and MSS values, you can significantly enhance your network’s performance and reduce overhead, resulting in a more efficient and reliable system.




