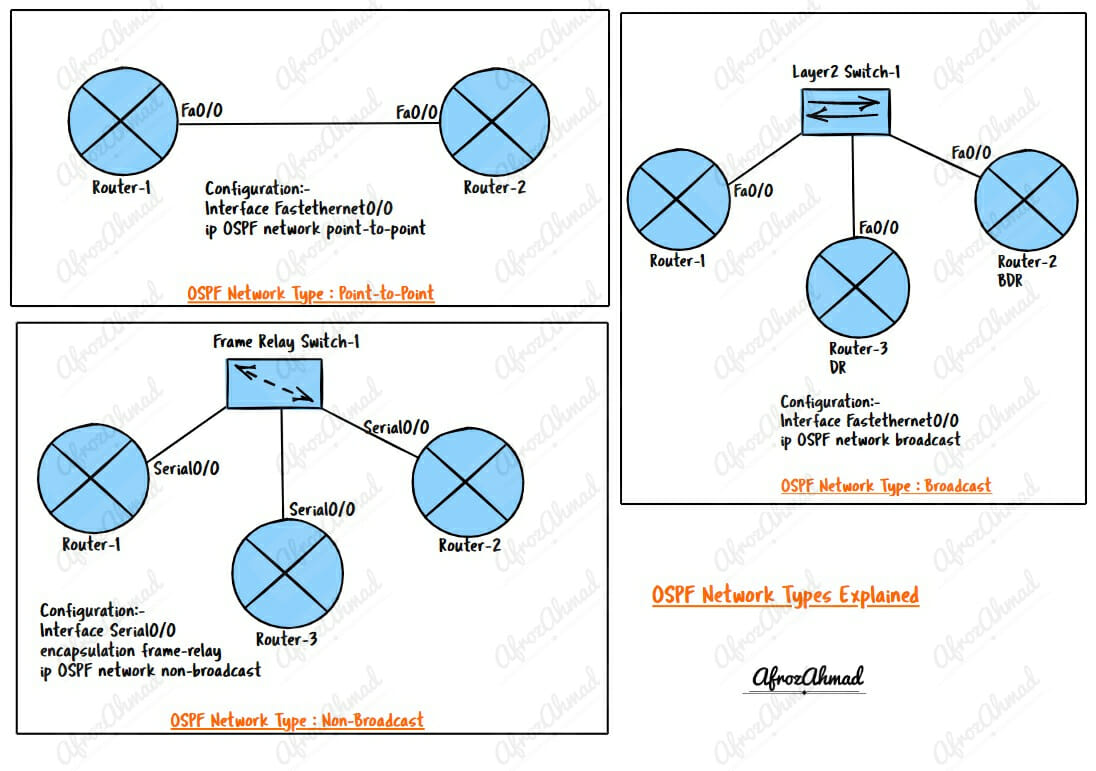
If you’re working with OSPF, you must be familiar with the different types of networks you can use. There are three core OSPF network types – Broadcast, point-to-point, and non-broadcast – and two Cisco-proprietary types – point-to-multipoint and point-to-multipoint non-broadcast. Each type has different configuration requirements, and you can use it in different scenarios.
In this post, we will explain all five types of OSPF networks. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to configure OSPF for any network type.
Before we start, I highly recommend reading these posts.
What is Routing in Networking, and How does Routing work
What is a Routing table, explained with Show IP Route Command Cisco
Understanding Dynamic Routing Protocols Types
OSPF states Explained [with Infograhic]
OSPF Area Types – [Infographics]
Why do we need OSPF Network Types?
- The OSPF network types are designed to give the best routing results in different topologies. For example, the point-to-point network type is intended for use in networks with only two routers. The broadcast network type is designed for use in networks with multiple routers.
- You can also use Network types to control which interfaces will form adjacencies with each other. By default, OSPF will only form adjacencies with interfaces on the same network type.
- Each type of interface on an OSPF router has its own data structure. So, if you change the network type, OSPF will make the necessary changes to the hello and dead timer.
- We need OSPF network types to help us create a more efficient and reliable network. By using different types of OSPF networks in different network topologies, we can better control the overall design and how data is routed through our network.
What are the Different Types of OSPF Networks?
When it comes to networking, OSPF is one of the most commonly used protocols. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that uses information about the state of the network links to determine the best route for data packets. One of the key concepts in OSPF is the network type. The network type determines how OSPF will route data packets across the network.
The three core OSPF network types are :
- Broadcast
- Point to Point
- Non-Broadcast
Two more network types are Cisco proprietary.
- Point to Multipoint
- Point to Multipoint Non-Broadcast
Bonus:-There is also a sixth network type known as “Virtual links.” We will discuss the OSPF virtual link in the next post.
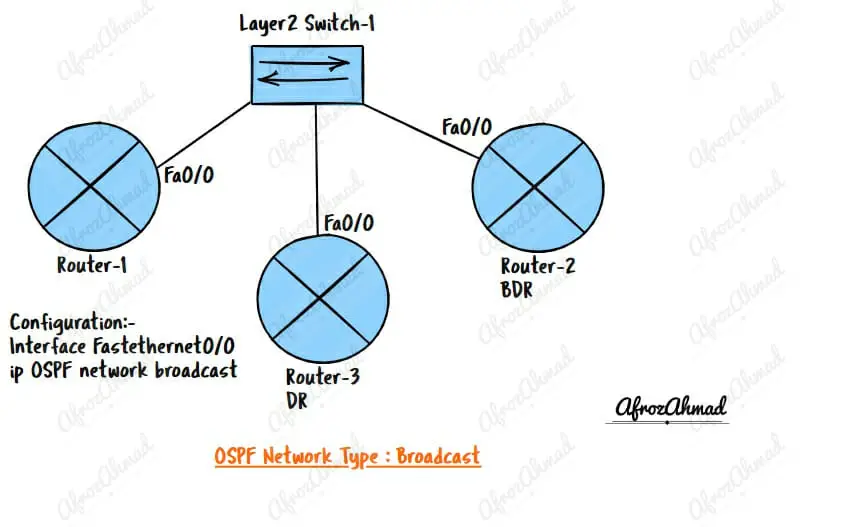
What is the OSPF Broadcast Network type?
The OSPF broadcast network type is used on networks with multiple OSPF routers connected to a single shared broadcast medium, such as an Ethernet LAN. For example, the broadcast network is the default network type on Ethernet interfaces.
Broadcast networks are the most common type of OSPF network. They are used when all routers in a network need to be able to communicate with each other.
OSPF Broadcast Network Key points:-
- Broadcast OSPF networks always elect a DR and a BDR.
- It uses the multicast MAC 224.0.0.5 (0 100.5E00.0005) for all Routers and 224.0.0.6 (0 100.5E00.0006) for DR and BDR.
- There is NO next-hop modification, which means the next-hop IP remains that of the originating router.
- Layer3 to layer2 resolution is required.
- Broadcast networks can’t have unicast neighbors configured.
- The hello and dead interval is 10 seconds and 40 seconds, respectively.
How to configure OSPF network type to Broadcast
Interface Fastethernet0/0
ip OSPF network Broadcast –> You should always use under Interface config, and make sure another side has the same network type defined.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the OSPF Broadcast Network type?
Advantages
- One of the main advantages of using a broadcast network type is that it’s very easy to configure. You need to specify the IP addresses with the wildcard mask under the OSPF router configuration of the devices you want to include in the network, and the OSPF broadcast network type will take care of the rest. It can be a big time saver compared to other types of network topologies where you have to define each neighbor manually.
- It scales well for medium-to-large networks.
- It converges quickly after a link or node failure.
Disadvantages
- The disadvantage of using an OSPF broadcast network type is that it is more vulnerable to network attacks and can generate a lot of network traffic.
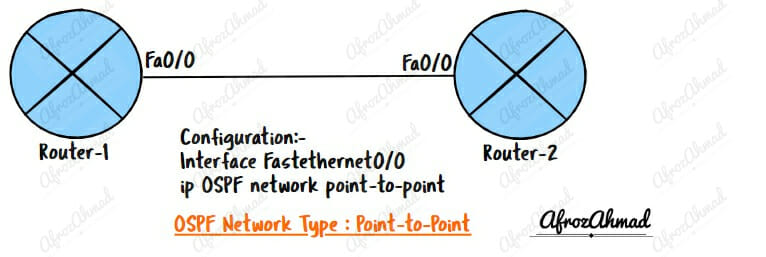
What is the OSPF Point-to-Point Network type?
OSPF point-to-point network type is used on networks with two OSPF routers connected by a single point-to-point link, such as a leased line or T1.
OSPF Point to Point Network Key points:-
- OSPF P2P network type is Default on T1, DS-3, and SONET links and on frame-relay point-to-point sub-interfaces.
- There is no DR/BDR election.
- Uses the multicast destination to AllSPFRouters (224.0.0.5), except for retransmitted LSAs, which are sent as unicast.
- The IP of the advertising router is the next-hop IP.
- On point-to-point links, OSPF doesn’t care if the subnet mask doesn’t match.
- The hello interval is 10 seconds, and the dead interval is 40 seconds.
How to configure OSPF network type to Point-to-Point
Interface Fastethernet0/0
ip OSPF network point-to-point –> You should always use under Interface config and make sure the other side has the same network type defined.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the OSPF Point-to-Point Network type?
The advantage of using a point-to-point network type is that it reduces router traffic because there is no need for multicast broadcasts.
Advantages:
- Reduced complexity: Point-to-point networks are much simpler to configure and manage than other types of OSPF networks. It is a big advantage if you work with a large network.
- Increased stability: Point-to-point networks are also more stable than other types of OSPF networks because there are fewer potential “failure points” in the network.
- Better performance: Point-to-point networks typically perform better than other OSPF networks because there is less “chatter” on the network, and traffic can flow more smoothly.
- It reduces router traffic because there is no need for multicast broadcasts.
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility: One of the big disadvantages of point-to-point networks is that they can be inflexible because you need to have a dedicated link between each router in the network.
- Lower redundancy: Another disadvantage of point-to-point networks is that they have lower redundancy than other types of OSPF networks. If one link goes down, the other end will be affected.
- More expensive: Point-to-point networks can also be more expensive than other types of OSPF networks because you need to purchase dedicated links for each router in the network.
- You can only have two nodes in a point-to-point network, so if you need to connect more than two nodes, you’ll need to use a different network type and more intermediate devices.
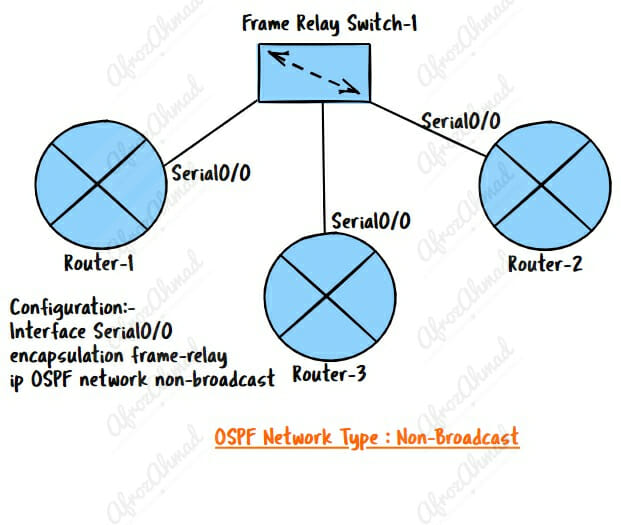
What is OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Type?
OSPF non-broadcast network type is used on networks with multiple OSPF routers connected by point-to-point links, such as Frame Relay or ATM virtual circuits. However, they are not widely used these days as frame-relay, and ATMs are considered to be obsolete technology.
OSPF Non-Broadcast Network Key points:-
- This network can connect more than two routers but can’t broadcast by default.
- It is the default network type for multipoint frame-relay interfaces.
- OSPF routers on N BMA networks choose a DR and a BDR, but all OSPF packets are unicast between each neighbor specified with the “neighbor” command.
- The next-hop IP doesn’t change. It stays the same as the IP address of the router that sent the packet.
- The default priority is 1, and it should be turned off (=0) on ALL SPOKES to stop a spoke from becoming a blackhole DR/BDR.
- The hello interval is 30 seconds, and the dead interval is 120 seconds.
How to configure OSPF network type to Non-Broadcast
Interface Serial0/0
ip OSPF network non-broadcast –> You should always use under Interface config and make sure the other side has the same network type defined.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the OSPF Non-Broadcast Network type?
Advantages:
- It can be easier to control traffic flow on the network. It can be helpful, for example, if you want to limit the amount of traffic that goes through a particular link.
- Non-Broadcast network types are more secure since hackers can intercept broadcasts.
Disadvantages:
- It can be more difficult to configure since it requires manual neighbor configuration.
- It can be more difficult to scale an NBMA network than other types of OSPF networks.
- Not all OSPF features are available when using this network type.
- NBMA networks can be more susceptible to certain types of faults.
What is OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type?
Point to Multipoint networks are used when there are multiple routers in the network, but they only need to be able to communicate with one router. Point to Multipoint network is typically used when multiple subnets are in the network.
It is a Cisco proprietary option that isn’t the default, but it might be the best choice for NBMA networks. It is useful when NBMA networks are set up in a special way and treated as a group of point-to-point links.
OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type Key Points
- It does not choose a DR and BDR, and OSPF packets are sent to all known neighbors simultaneously using a 224.0.0.5 multicast address.
- The next-hop IP is that of the neighbor who is advertising.
- You only need Layer3 to Layer2 resolution for neighbors that are directly connected.
- Recursive layer 3 IP routing is used for neighbors who are not connected directly.
- The endpoints of point-to-multipoint networks are also advertised as host routes (/32).
- The hello interval is 30 seconds, and the dead interval is 120 seconds.
How to configure OSPF network type to Point-to-Multipoint
Interface Serial0/0
ip OSPF network point-to-multipoint –> You should always use under Interface config, and make sure the other side has the same network type defined.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Network Type?
Advantages
- Less complex as it has no DR BDR election.
- Better than OSPF Non-broadcast network type in certain situations.
Disadvantages
- It is only used on cisco devices.
- Not widely used.
What is the OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network type?
Point to Multipoint Non-Broadcast networks are used when there are multiple routers in the network, but they don’t need to be able to communicate with all of the other routers. Point to Multipoint Non-Broadcast networks are typically used when multiple subnets are in the network.
Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network is also Cisco proprietary. It is the same as the point-to-multipoint discussed before, but it is set up with the extra keyword “non-broadcast.”
OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network Type Key Points
- There is no DR/BDR election, and each neighbor is given unicast instead of multicast.
- As a result, the “neighbor” command must be used to define the directly connected neighbor. You only need to configure one side, but it is best to do it on both.
- The next-hop IP is that of the neighbor who is advertising.
- At layer2, OSPF will use IP routing to connect devices that aren’t connected directly.
- This network was made so that you could assign the cost per neighbor instead of using the interface cost.
- The cost is based on the bandwidth of the “incoming” interface, not the “outgoing” interface of the neighbor.
- The hello interval is 30 seconds, and the dead interval is 120 seconds.
How to configure OSPF network type to Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast
Interface Serial0/0
ip OSPF network point-to-multipoint non-broadcast–> You should always use under Interface config, and make sure another side has the same network type defined.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of OSPF Point-to-Multipoint Non-Broadcast Network Type?
Advantages
- Less complex as it has no DR BDR election.
- Better than OSPF Non-broadcast network type in certain situations.
Disadvantages
- Only used on cisco devices.
- Not widely used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the five different types of OSPF networks each have their own special configuration requirements and are used in different scenarios. Therefore, depending on your needs, you must be familiar with all five types of networks to make the best choices for your network.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025