Hey there, router users! If you’ve ever found yourself scratching your head while staring at your TP-Link router, wondering what all those flashing lights mean, you’re not alone. As one of the leading router brands, TP-Link equips their devices with a variety of LEDs to serve as status indicators. Understanding these lights is crucial for troubleshooting network issues—just remember that exact colors and behaviors can vary by model.
In this guide, we’ll break down the meanings behind each light on your TP-Link router, so you can quickly diagnose and solve problems. Let’s dive in and shed some light on the subject!
TP‑Link Router Lights Types and Colors – Summary
| Light Type | Color/Status | Meaning/Description |
|---|---|---|
| Power Light | Solid Green | Router is powered on and passed basic self‑check. |
| WAN Light | Solid Green | Physical link on the WAN port to your modem/ONT is up. |
| Flashing Green | WAN port activity (data traffic). | |
| Not Lit | No cable/link on the WAN port. Internet availability is shown by the Internet LED. | |
| USB Light | Solid Green | USB device recognized and ready. |
| Blinking/Identifying | Some models briefly blink while identifying or during activity. | |
| Not Lit | Device not recognized or unplugged (or model has no USB LED). | |
| Internet Light | Solid Green | WAN connected and internet available. |
| Orange/Amber | WAN is connected but no internet (common on many Archer models). Some models use Red instead. | |
| Not Lit | WAN unplugged or internet function disabled (see WAN LED for link). | |
| 2.4 & 5 GHz WLAN | Solid Green | Wireless band enabled. |
| Flashing Green | Active Wi‑Fi traffic on that band. | |
| Not Lit | Band disabled or radio off. | |
| Phone Light | Solid Green | VoIP/SIP account registered (VoIP models only). |
| Blinking Green | Flash rate varies by event (e.g., ringing or voicemail); see model guide. | |
| Not Lit | Not registered/no phone service. | |
| WPS Light | Flashing Green | WPS pairing in progress (typically up to ~2 minutes). |
| Solid Green | WPS connection established (often turns off shortly after). | |
| Not Lit | WPS inactive. | |
| LAN LEDs | Solid Green | Ethernet device connected at that port. |
| Blinking Green | LAN data transmission. | |
| Not Lit | No device/link on that LAN port. |
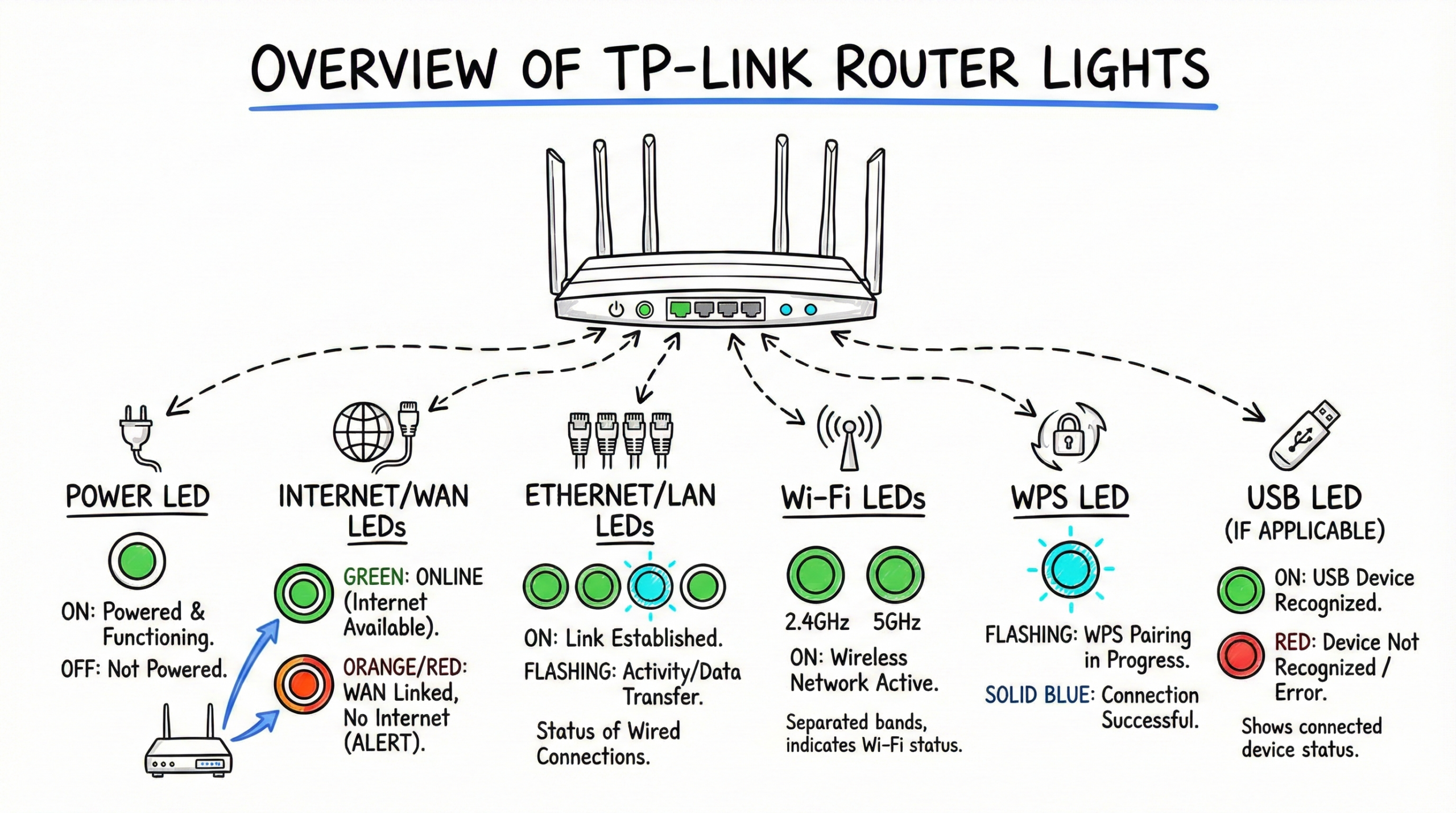
Overview of TP‑Link Router Lights
Most TP-Link routers have a similar set of LED indicators, each with its own function. Here’s what you’ll typically find, noting that exact colors can differ by model:
- Power LED: Indicates whether the router is powered on and functioning properly.
- Internet/WAN LEDs: The WAN LED shows the physical link to your modem/ONT. The Internet LED reflects internet availability (e.g., green when online, orange/red when WAN is linked but no internet).
- Ethernet/LAN LEDs: Show the status of wired connections to your router via LAN ports (on=link, flashing=activity).
- Wi‑Fi LEDs: Display the status of your wireless network, often separated into 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
- WPS LED: Indicates the status of Wi‑Fi Protected Setup pairing.
- USB LED (if applicable): Shows the status of connected USB devices (recognized vs not recognized).
LED Colors and Their Meanings
Now that you know what each light represents, here’s what the different colors and patterns usually signify across popular TP‑Link models:
- Solid green: Normal operation for that function (e.g., WAN linked, internet available, Wi‑Fi enabled).
- Flashing/blinking green: Network activity on that LED (e.g., data passing on WAN, LAN, or Wi‑Fi).
- Yellow/orange/amber: Often means the WAN is connected but there’s no internet (common on Archer AX/C series). Some models use red for the same condition. See your model’s guide for exact color mapping.
- Red: On models that support it, usually indicates an internet or system error (for example, WAN up but no internet). Color usage varies by model.
- No lights: That function is disabled, there’s no link, or the router lacks power. Check the power switch, outlet, and cables.
Model‑Specific TP‑Link Router Light Behaviors
While most TP-Link routers follow similar patterns, there are important model differences:
- TP‑Link Archer Series (A, C, AX models): Many Archer models use green for internet available and orange/amber when WAN is connected but no internet. Some older models use red for issues. 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands usually have separate LEDs.
- TP‑Link Deco Mesh System Lights: Deco units use a single multi‑color LED. Typical mappings include: M5/P7/M9—Yellow=startup, Blue (pulse)=ready, Blue (solid)=setup in progress, Green=OK, Red=issue; M4/E4/W2400—White (solid)=OK, White (pulse)=upgrading, Red (pulse)=satellite disconnected, Red (solid)=issue. Always check your Deco’s manual.
- Differences between Wi‑Fi 5, Wi‑Fi 6, and Wi‑Fi 7: Consumer TP‑Link routers do not include dedicated LEDs for features like OFDMA or MU‑MIMO. Wi‑Fi 7 BE‑series models may use different LED designs (e.g., light bars or a single status LED). Behavior is still reported through power/internet/WAN/LAN/Wi‑Fi/WPS/USB indicators.
- Older TP‑Link Router Light Meanings: If you have an older model, colors and labels may differ slightly. Always consult your specific router’s manual or support resources for accurate information.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Armed with your knowledge of TP-Link router lights, you can start troubleshooting efficiently. Use the light states to pinpoint where the problem sits—power, WAN link, internet reachability, Wi‑Fi, or LAN.
- Internet down: If the Internet LED is orange/amber or red, your WAN is likely connected but there’s no internet. Quick flow: 1) Reseat/replace the WAN cable and confirm the WAN LED is on. 2) Power‑cycle modem/ONT and router (turn off 30 seconds, then on—modem/ONT first). 3) Check your router’s Internet settings (DHCP/PPPoE credentials). 4) If your ISP requires it, try MAC clone from the old router/PC. 5) If still failing, contact your ISP to check provisioning or outages.
- No Wi‑Fi: When your Wi‑Fi LEDs are off, the wireless radios may be disabled. Log into the router’s settings (or the Tether app) and ensure both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz are enabled.
- Ethernet not working: If an Ethernet/LAN LED is off with a device plugged in, there may be a cable or device issue. Try a different cable/port or test the device on another port. On most TP‑Link models LAN LEDs are single‑color green (on=link, flashing=activity).
- Connection drops: Erratic flashing or periodic Internet LED color changes can indicate instability or reauthentication. Reduce interference (reposition router, separate from cordless phones/microwaves), and update firmware via the web interface or Tether app.
- Startup or overheating concerns: Multiple LEDs lighting at once often occurs during normal boot or reset sequences. If the router feels hot or keeps rebooting, improve ventilation and remove obstructions; avoid stacking devices.
Using Lights for Setup and Configuration
Your TP-Link router’s lights aren’t just for troubleshooting; they also guide you through setup and confirm configuration changes.
- During setup, LEDs follow a startup pattern before the Internet and Wi‑Fi LEDs settle into their normal states. Consult your model’s quick start for exact sequences.
- If you use WPS to connect devices, the WPS LED flashes while pairing (about 2 minutes) and turns solid when the connection is established.
- After changing settings, lights may blink or change color as the router applies the configuration and reconnects to your ISP or clients.
Lights Indicating Security Status
While LEDs can hint at activity, use your router’s interface for real security checks.
- A flashing WPS LED means pairing is in progress. If you didn’t start it, cancel WPS/Wi‑Fi pairing in the interface, disable WPS PIN, and review the connected devices list and logs.
- Unusual constant activity on LAN/Wi‑Fi LEDs when you’re idle can indicate background updates or heavy usage. To investigate, check the client list, DHCP leases, and traffic statistics; update passwords and firmware if needed.
Tips for Optimal TP‑Link Router Performance
Keep your TP-Link router running smoothly with these practical tips:
- Ideal Router Light Statuses to Look For:
- Power light: Solid on
- Internet/WAN light: Internet LED solid green when online; WAN LED on/flashing for link/activity
- Wireless lights: Solid (bands enabled) or blinking (data transmission)
- Ethernet/LAN lights: Solid (device connected) or blinking (data transmission)
- Router Placement for Best Light Visibility:
- Place your router in a central, open location for the best Wi‑Fi coverage.
- Ensure the router’s lights are easily visible for quick status checks.
- Avoid enclosed spaces that trap heat or block the LED panel.
- Using TP‑Link Router Lights for Network Troubleshooting:
- Glance at the Internet LED first (green vs orange/red), then confirm the WAN LED link state.
- Use the light statuses to narrow the issue to ISP link, router settings, Wi‑Fi radios, or a specific LAN port.
- Many models support LED Control/Night Mode in the Tether app so you can dim or schedule LEDs off without affecting connectivity.
- Built-in Router Tools for Error Light Diagnosis:
- Access your router’s web interface by entering its IP address in a browser or using the Tether app.
- Check diagnostics, logs, Internet status, and client lists for clues that match what the LEDs show.
- Some TP-Link routers include a network map/status page to identify connected devices and bottlenecks; Wi‑Fi 7 BE models may present LEDs differently but the status pages provide the same insight.
When to Check Your Router Manual
While this guide covers the general meaning of TP‑Link router lights, specific colors and patterns vary between models. For example, some Archer units show orange/amber for “WAN connected, no internet,” while others use red; Deco models use distinct color sets. If you’re unsure about a particular light, consult the official manual for your model.
Additionally, for advanced configuration or troubleshooting—such as changing internet connection type, cloning a MAC address, or scheduling LED Control/Night Mode—your manual and support resources provide step‑by‑step guidance.
Contacting TP-Link Support
If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting steps and your router lights continue to indicate a problem you can’t solve, reach out to TP‑Link’s customer support. They can help determine whether the issue points to configuration, ISP provisioning, or hardware.
In some cases, your router may be covered under TP-Link’s warranty, entitling you to a repair or replacement. Have your device’s model number and proof of purchase handy when contacting support.
Conclusion
By now, you should have a solid grasp on what your TP‑Link router’s lights are telling you. Understanding these status indicators is key to diagnosing and resolving network issues quickly and confidently.
Remember, this guide is a reliable starting point—but for exact color mappings and sequences, consult your router’s manual or contact TP‑Link support. With a little know‑how and some targeted checks, you’ll keep your home network running smoothly.
FAQ
What do I do if no lights are on at all?
If your router appears completely dark, first check that it’s plugged into a working outlet and the power switch (if present) is on. Try a different outlet and power adapter if available. If the issue persists, contact TP‑Link support as this may indicate a hardware failure.
Why is my internet light red?
Color meanings vary: on many Archer models, orange/amber means the WAN is connected but there’s no internet; other models use red for the same condition. Check the WAN cable and power‑cycle your modem/ONT and router. Verify your ISP settings (DHCP/PPPoE) and contact your ISP if the light stays orange/red.
How can I troubleshoot flashing lights?
Flashing green typically indicates normal traffic. If the Internet LED is orange/red or keeps changing, follow the steps under “Internet down.” If the WPS LED is flashing and you didn’t start pairing, cancel WPS in the interface, disable WPS PIN, and review connected clients.
What does the WPS button do?
The Wi‑Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button lets WPS‑compatible devices join your Wi‑Fi without typing a password. Press the button to start pairing—the WPS LED flashes during this time and turns solid when connected. For better security, disable WPS PIN when not needed and keep your Wi‑Fi password strong.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025