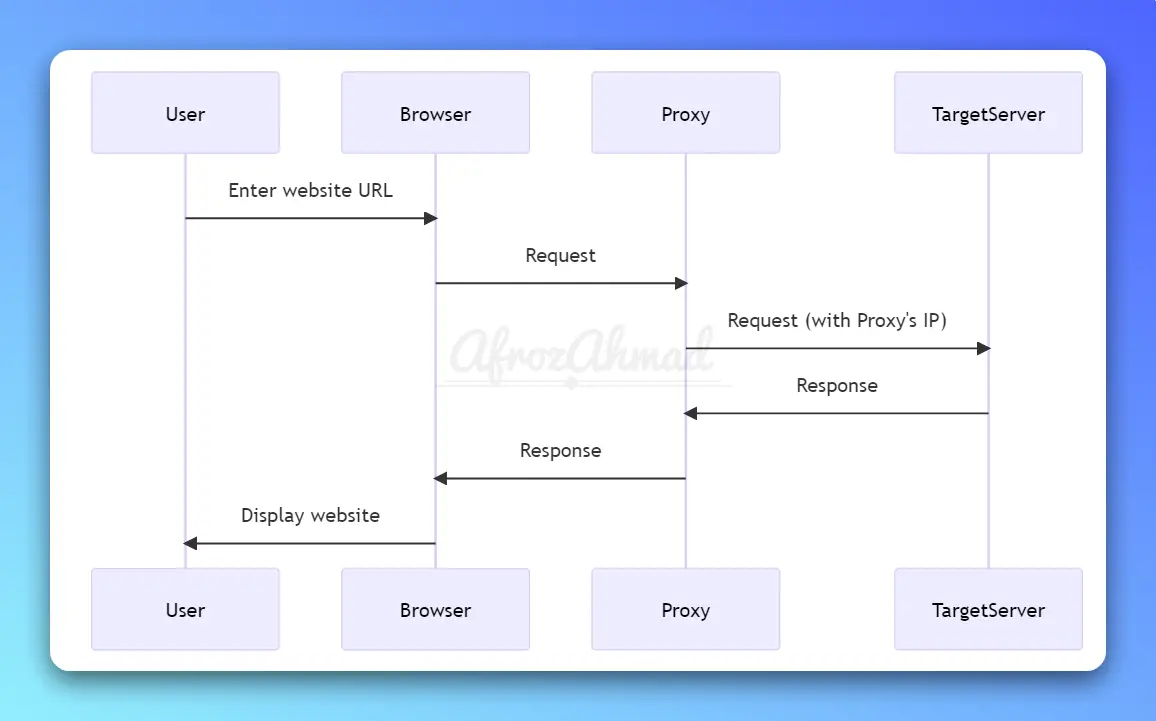
What are proxies in networking, and what are they used for? Proxies serve as intermediaries between users and the internet, enhancing privacy, security, and content accessibility.
This guide will explain proxy functionality, applications, limitations, and available options—including free, open-source, and paid services. Discover how to leverage proxies for your needs in the following sections.
What are Proxies, and How Do Proxies Work?
Proxies act as middlemen between your device and the internet, masking your identity and providing anonymity. They can enhance your privacy, security, and web experience in many ways.
Proxies are intermediaries in the online world. They help you visit websites without directly connecting to them. When you use a proxy, it takes your request, masks your IP address and sends it to the website on your behalf, and then brings the website’s response back to you. This way, the website only sees the proxy’s information, not yours, keeping your identity hidden, maintaining your anonymity, and protecting your privacy.
Proxies can also help you access websites that are blocked in your region by making it look like you’re connecting from a different place.
What are proxies used for?
Proxies are used for various purposes, including:
- Anonymity and privacy: Proxies hide your IP address, making it difficult for websites and third parties to track your online activities.
- Bypassing geo-restrictions: Proxies can help you access blocked or restricted content by routing your traffic through servers in other countries, making it appear as if you’re connecting from that location.
- Load balancing: Reverse proxies are used by web servers to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, improving network performance and preventing server overloads.
- Content filtering and access control: Organizations and institutions often use proxies to control internet access, block specific websites, or filter out unwanted content.
- Improved network performance: Proxies can cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and speeding up response times for users.
- Monitoring and logging: Proxies can be used to monitor internet usage within an organization or network, helping administrators identify potential security threats and policy violations or simply gathering usage statistics.
- Security: Proxies can provide an additional layer of security by blocking malicious websites, scanning for viruses and malware, or preventing unauthorized access to internal networks.
These are some of the primary reasons proxies are used, demonstrating their versatility and importance in the digital world.
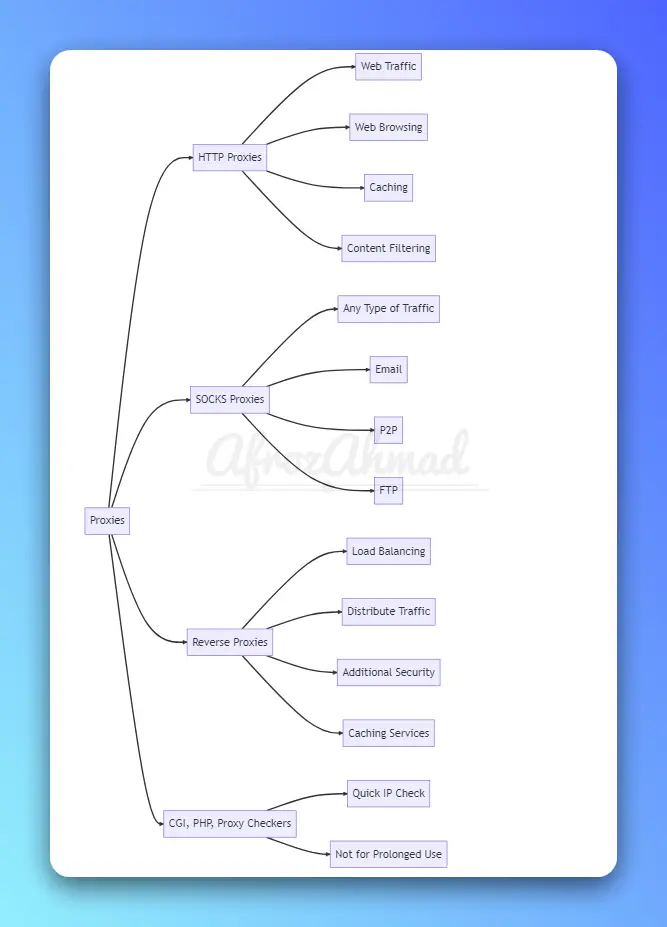
Types of Proxies
There are various types of proxies, each with its unique characteristics and use cases. Here are the most common ones:
- HTTP Proxies: These proxies handle web traffic and are typically used for web browsing, caching, and content filtering. They’re the most popular type of proxy and support only HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
- SOCKS Proxies: These are more versatile than HTTP proxies and can handle any type of traffic, including email, P2P, and FTP. They provide a higher level of anonymity but might be slower due to their complexity.
- Reverse Proxies: These proxies are used by web servers to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, thus improving load balancing and performance. They can also provide additional security and caching services.
- CGI, PHP, Proxy Checkers: Special proxies that allow you to check if your IP address is visible. You should only use it for a quick IP check, as it is not designed for prolonged use.
What are the potential drawbacks of Proxies?
- Latency: Introducing an additional step in the communication process can cause latency, particularly when connecting to distant proxy servers.
- Security Concerns: Poorly configured or malicious proxies can compromise your data or inject malware into your traffic.
- Potential Misuse: Proxies can be used for malicious activities, such as hiding the origin of cyberattacks or facilitating illegal content distribution.
Proxy Configuration and Use
Proxy Configuration
To use a proxy, you will first need to find a proxy service that meets your needs.
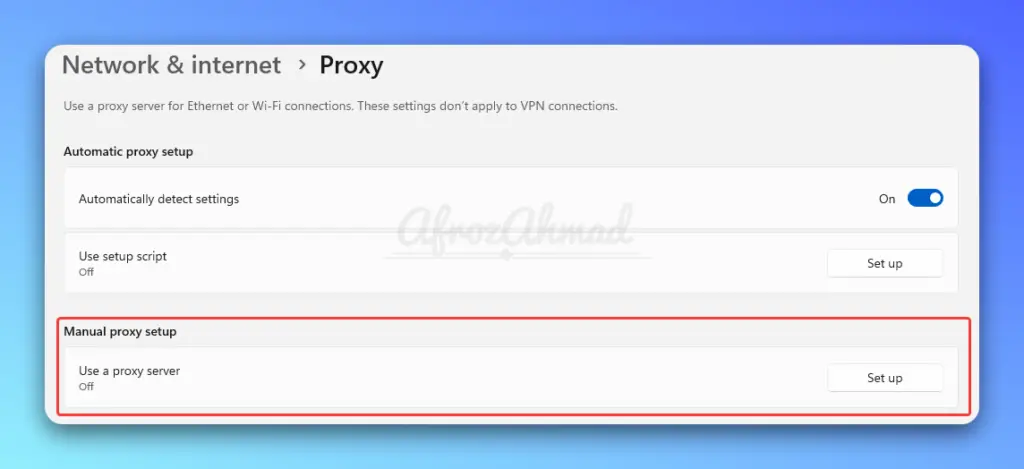
Once you choose a service, you will be given the proxy hostname/IP address and port number to configure in your Computer proxy settings. For example:
Proxy hostname: proxyserver.com
Port number: 8080
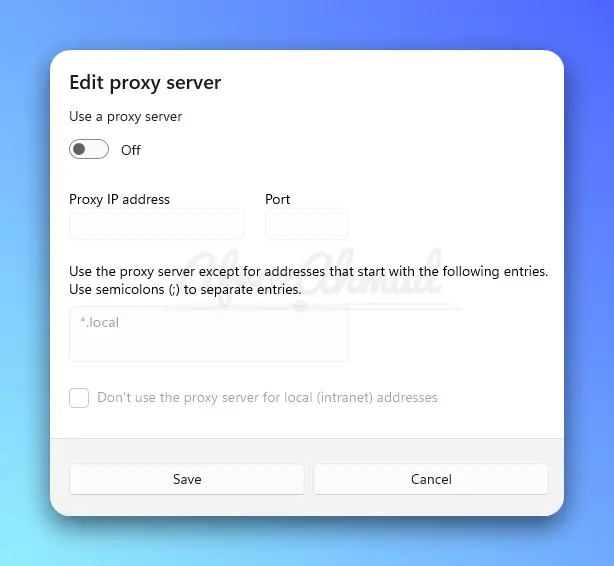
In your Windows computer, input the proxy IP address and Port information as shown in the above picture to route your traffic through the proxy server. Some proxies will also provide a username and password for authentication.
I would recommend starting with a paid proxy service trial to find a reliable option before committing long-term. Free proxies should only be used for very basic needs. For the most sensitive activities, a proxy alone may not provide sufficient anonymity, in which case a VPN or Tor are better alternatives.
With the power of proxies comes responsibility. Wield your newfound internet superpowers wisely!
Proxy Usage
Choosing the right proxy for your needs depends on your specific use case and requirements. When configuring a proxy, consider factors like speed, anonymity, and security. Some popular proxy configurations include:
- Web-based Proxies: These proxies allow you to browse the web through their websites without any additional setup.
- Browser Extensions: Proxy extensions can be added to your browser for easy configuration and use.
- Standalone Proxy Applications: These applications provide advanced proxy configuration options and can handle multiple proxy protocols.
Proxy Services and Software
There’s no shortage of proxy services and software available, catering to different needs and budgets. Some popular options include:
Free Proxy Services:
These services provide a simple way to connect to proxy servers without any cost. However, they might have limited features and slower speeds.
- HideMyAss – Free web proxy and proxy switching tool. Limited data and speed.
- KProxy – Free unlimited web proxy. Simple to use but lacks advanced features.
- Zend2 – Free PHP proxy for basic web use. Open-source but limited functionality.
Paid Proxy Services:
These services offer premium features, faster speeds, and better security but come with a subscription cost.
- Bright Data – Data aggregation platform with a rotating proxy network. Used for web scraping and market research.
- Smartproxy – Rotating proxy network with over 10 million residential proxies. Unlimited data and bandwidth.
- Storm Proxies – High-performance proxies optimized for social media marketing and SEO. Custom proxy plans are available.
- Microleaves – Over 2 million proxies with unlimited bandwidth. Affordable proxy plans for individuals and businesses.
Open-Source Proxy Software:
Solutions like Squid and Privoxy can be self-hosted and configured to meet your specific requirements.
Proxy Management Software:
- ProxyRack – Tool for proxy automation, rotation, and management. It can be used with various proxy services.
- NetNut – Headless browser with built-in proxy rotation. Used for creating automated web scraping bots.
- ProxyMesh – Proxy orchestration tool that provides a proxy API for managing other proxy services.
- Smart Proxy Manager – Desktop app for managing and rotating proxies from multiple providers. Free to use.
Alternatives to Proxies
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server. They offer similar privacy and geo-restriction bypassing benefits as proxies but provide better security and encryption.
- The Onion Router (Tor): Tor is a decentralized network that routes your traffic through multiple volunteer nodes, making it highly secure and anonymous. However, it can be slower than proxies and VPNs due to its complex routing process.
- Tails OS: A portable operating system you can boot from a USB stick. Comes pre-installed with privacy tools like Tor and VPNs for maximum anonymity.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of proxies is essential for anyone concerned about internet connectivity, privacy, and security. From HTTP and SOCKS proxies to reverse proxies, each type serves a unique purpose and offers various benefits. While proxies can help protect your privacy and bypass geo-restrictions, they also come with potential drawbacks, such as latency and security concerns.
To get the most out of proxies, it’s important to choose the right configuration and service, keeping in mind the trade-offs involved. Alternatives like VPNs and Tor can also be considered, depending on your specific requirements. Ultimately, the key is to strike the right balance between privacy, security, and performance, ensuring a seamless and safe online experience.
- NETGEAR Nighthawk (RAX54S) WiFi 6 Router Review - August 24, 2024
- TP-Link AX1800 Archer AX21 WiFi 6 Router Review - August 24, 2024
- How to Connect Nanit to Hotel WiFi? - August 12, 2024