When setting up your WiFi router, avoid common mistakes to guarantee a smooth experience. First, don’t place the router in a basement; instead, position it centrally in an open area for better coverage. Change the default passwords and SSID to enhance security and make your network less identifiable to hackers. Regularly update your firmware and use WPA2 or WPA3 security protocols. Keep WPS disabled and manage band usage to prevent overcrowding.
These simple adjustments can markedly improve performance and security. Continue to explore the ideal strategies for an even better internet connection!
Key Takeaways
- 📶 Position your router centrally in an open area, not in basements or closets, to avoid weak signals and connectivity issues.
- 🔐 Change default passwords and SSID to make your network less identifiable and more secure against unauthorized access.
- 🔧 Regularly update your router’s firmware and use secure protocols like WPA2 or WPA3 to prevent vulnerabilities.
- 📡 Disable WPS and manage your WiFi band usage to reduce security risks and network overcrowding.
- 🏷️ Customize your network’s SSID to a unique name that doesn’t reveal personal information for enhanced security.
- 👥 Set up a guest network to secure your main network from external threats and manage network traffic efficiently.
- 🔄 Check and select less congested WiFi channels using WiFi analyzer tools to improve connection stability.
- 🚫 Be aware of electronic devices and physical obstacles that can interfere with your WiFi signal and adjust router placement accordingly.
- 📶 Consider using range extenders or mesh systems for larger homes to eliminate dead zones and enhance coverage.
- 🔒 WPA3 is the latest and most secure Wi-Fi security protocol, providing significant upgrades over its predecessors.
- 🛡️ Each Wi-Fi security protocol, from WEP to WPA3, offers different levels of protection and compatibility.
- 🔄 Regular updates and understanding of Wi-Fi security settings are essential for maintaining a secure network environment.
Poor router placement
When you place your router in a tucked-away spot like a basement or closet, you’re setting yourself up for connection issues. Routers need space to send and receive signals effectively. By hiding your router, you’re blocking its ability to broadcast a strong WiFi signal throughout your home.
To fix this, position your router in a central, open location. Elevate it off the ground—placing it on a shelf or table can greatly enhance its range. Aim to keep it away from walls, metal objects, and other electronics that can interfere with the signal. Remember, obstacles can weaken the connection and create dead zones in your home.
Also, avoid putting your router behind furniture, as this can further limit its broadcasting capabilities. A clear line of sight improves performance, so try to keep the area around your router free of clutter.
Not changing default passwords
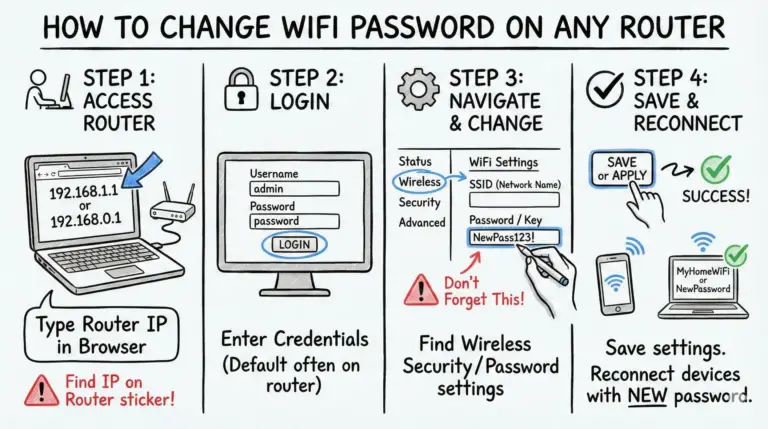
Many users overlook the importance of changing default passwords on their WiFi routers, leaving their networks vulnerable to unauthorized access. Default passwords are often widely known or easily found online, making it simple for hackers to gain control of your network. By not changing these passwords, you’re fundamentally giving anyone a free pass.
To secure your network, you should always change both the router admin password and the WiFi password.
- Start by logging into your router’s settings through a web browser. You’ll typically find this by entering the router’s IP address.
- Once you’re logged in, navigate to the password settings.
- Create strong, unique passwords that combine upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Aim for at least 12 characters to enhance security.
Don’t forget to document your new passwords in a secure location. Regularly updating passwords can also help keep your network safe. By taking these simple steps, you can greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your personal data from potential threats.
Using outdated security settings
Outdated security settings on your WiFi router can leave your network exposed to potential threats. If you’re still using outdated protocols like WEP or leaving default security settings in place, it’s time to make some changes. These outdated practices can make it easy for hackers to gain access to your personal information and devices.
Here are some quick fixes to enhance your router’s security:
- Change the default admin and WiFi passwords: Always use strong, unique passwords that combine upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Use WPA3 or WPA2 security: These are the most secure protocols available. Avoid WEP, as it’s easily compromised.
- Disable remote management: Unless you specifically need this feature, turning it off can reduce vulnerabilities.
Not updating firmware
Failing to update your router’s firmware can leave your network vulnerable, even if you’ve secured it with the latest settings. Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to patch security holes, improve performance, and add new features. If you neglect to apply these updates, you’re fundamentally leaving your network exposed to potential threats.
To fix this, make checking for firmware updates a regular part of your routine. Many modern routers have the option to automatically download and install updates, so take advantage of this feature. If your router doesn’t support automatic updates, set a reminder to check for updates every month or so.
When you log into your router’s interface, you’ll usually find an option labeled ‘Firmware Update’ or similar. Follow the prompts to download and install any available updates.
Using default network names (SSIDs)
Using generic default network names like ‘Linksys’ or ‘Netgear’ can make it easy for hackers to identify your router and target your network. When you keep these default SSIDs, you’re giving potential intruders a clear indication of what type of router you have, which can make it simpler for them to exploit known vulnerabilities.
To enhance your network’s security, consider changing your SSID to something unique that doesn’t reveal personal information. Here are some tips to help you create a stronger network identity:
- Be Creative: Choose a fun or quirky name that reflects your personality but doesn’t give away personal details.
- Avoid Personal Info: Don’t use names, addresses, or any information that could identify you or your household.
- Change Regularly: Update your SSID periodically to keep your network fresh and less predictable.
Ignoring guest networks
Neglecting to set up a separate guest network can expose your main network to unnecessary risks. When visitors connect to your primary WiFi, they gain access to devices, files, and sensitive information on your network. This can lead to unwanted breaches and potential malware infiltration. By ignoring the guest network feature, you’re fundamentally leaving the door wide open for security threats.
To fix this, enable the guest network option on your router. Most modern routers come equipped with this feature, and it’s straightforward to set up. Make sure to create a different password from your main network to keep things secure. This way, your guests can enjoy internet access without compromising your personal data or connected devices.
Additionally, a guest network typically restricts access to your shared files and devices, adding another layer of protection. It’s also a courteous way to manage your network traffic, as guest devices won’t interfere with your primary connection’s performance.
In short, taking the time to set up a guest network can considerably enhance your overall network security and make your home a safer place for both you and your visitors.
Incorrect channel selection
Selecting an overcrowded WiFi channel can lead to slow internet speeds and frustrating connectivity issues. When multiple networks operate on the same channel, they can interfere with each other, causing lag and dropped connections. To avoid this, you need to verify your router is set to use a less congested channel.
Here are some tips to help you select the right WiFi channel:
- Use WiFi analyzer tools: These tools scan for nearby networks and identify which channels are crowded.
- Manually set your channel: After identifying a less congested channel, go into your router settings and select it manually.
- Regularly check for changes: WiFi environments can change over time, so it’s a good idea to reanalyze your network periodically.
See also: Best Channel for 5GHz
Leaving WPS enabled
Many users often leave WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) enabled, which can create security vulnerabilities in their network. WPS is designed to simplify the process of connecting devices to your WiFi, but it comes with risks. If someone gains physical access to your router, they could exploit WPS to connect unauthorized devices, putting your data at risk.
To enhance your network’s security, consider disabling WPS altogether. If you need to connect a new device, you can temporarily enable WPS, but remember to turn it off right after. This way, you minimize the window of opportunity for potential intruders.
Disabling WPS typically involves accessing your router’s settings through its web interface. Find the WPS option, usually located under the wireless settings, and toggle it off.
Not optimizing for coverage
Failing to optimize your WiFi coverage can lead to dead zones and weak signals throughout your home, even if you’ve secured your network against unauthorized access.
To guarantee you’re getting the best signal everywhere, you should start by adjusting the antenna positioning on your router. Experiment with different angles; sometimes, a slight tilt can make a big difference.
If your home is large, consider using range extenders or a mesh WiFi system to boost coverage. Mesh systems create a seamless network, eliminating those pesky dead zones.
Here are some tips to help you optimize your WiFi coverage:
- Position your router centrally: Place it in a location that minimizes barriers between it and your devices.
- Elevate your router: Higher placement can enhance signal distribution.
- Avoid obstructions: Keep the router away from thick walls, metal objects, and electronic devices that could interfere.
Forgetting about interference
Ignoring potential interference from other electronics can greatly weaken your WiFi signal, leading to frustrating connectivity issues. Many people overlook this factor when setting up their routers. It’s important to know that certain devices can disrupt your WiFi connection. For instance, cordless phones, microwaves, baby monitors, and even fish tanks can emit signals that interfere with your router’s performance.
To avoid these problems, place your router away from these devices. Ideally, position it in a central location within your home, far from appliances that might cause interference. If you can’t relocate your router, consider using a dual-band router that operates on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. The 5 GHz band is typically less crowded and more resistant to interference. You can even try Tri-band or Quad-band routers; they are on the expensive side, but you will see the difference.
Here are some of the Tri-band Routers you can use:



In addition, be mindful of physical obstacles like walls and furniture that can also weaken your signal. If you notice connectivity issues, try relocating your router or the interfering devices and test your connection again.
Overcrowding a Single Band
While managing interference is important, another common mistake is overcrowding a single band on your router, which can lead to slower speeds and connectivity issues.
Many people tend to stick to the 2.4GHz band, thinking it’s the best option. However, this band can become congested, especially in homes with multiple devices.
To improve your WiFi experience, consider distributing your devices across both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands:
- Use the 5GHz band for devices that need faster speeds, like gaming consoles or streaming devices.
- Connect smartphones and tablets to the 5GHz band when you’re close to the router for better performance.
- Reserve the 2.4GHz band for devices that are farther away, like smart home gadgets or older devices that don’t support 5GHz.
Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up your Wi-Fi router doesn’t have to be a hassle.
By avoiding common mistakes like poor placement, sticking with default passwords, and neglecting updates, you can create a stronger, more secure network.
Remember to optimize for coverage and minimize interference to get the best performance.
With these tips, you’ll enjoy a reliable connection that meets your needs.
So, take a moment to check your setup and make those essential adjustments today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Improve My Wifi Speed Without Changing My Router?
To improve your WiFi speed without changing your router, try relocating it to a central spot, reducing interference from other devices, updating firmware, and limiting connected devices. These steps can greatly enhance your connection quality.
What Devices Should I Prioritize for a Stable Connection?
You should prioritize devices that require constant connectivity, like gaming consoles or smart home devices. Also, consider prioritizing your work devices to guarantee stable connections during video calls or important tasks.
Are There Specific Materials That Interfere With Wifi Signals?
Yes, certain materials can interfere with WiFi signals. Thick walls, metal objects, and appliances like microwaves can block or weaken the signal. Keep your router away from these obstacles to improve your connection.
How Do I Know if My Router Needs Replacement?
You’ll know your router needs replacement if your internet speed drops considerably, you experience frequent disconnections, or your devices struggle to connect. An outdated model can also hinder performance, so consider upgrading if necessary.
Can I Use Multiple Routers to Enhance My Wifi Coverage?
Yes, you can use multiple routers to enhance your WiFi coverage. By connecting them through wired or wireless methods, you’ll create a mesh network, improving signal strength and extending coverage throughout your home.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025