Is your AT&T internet running painfully slow? Frustrated with constant buffering, lagging, and endless load times? This guide will diagnose common causes and provide direct solutions for AT&T internet slow speeds, plus actionable troubleshooting tips to get your connection back up to speed.
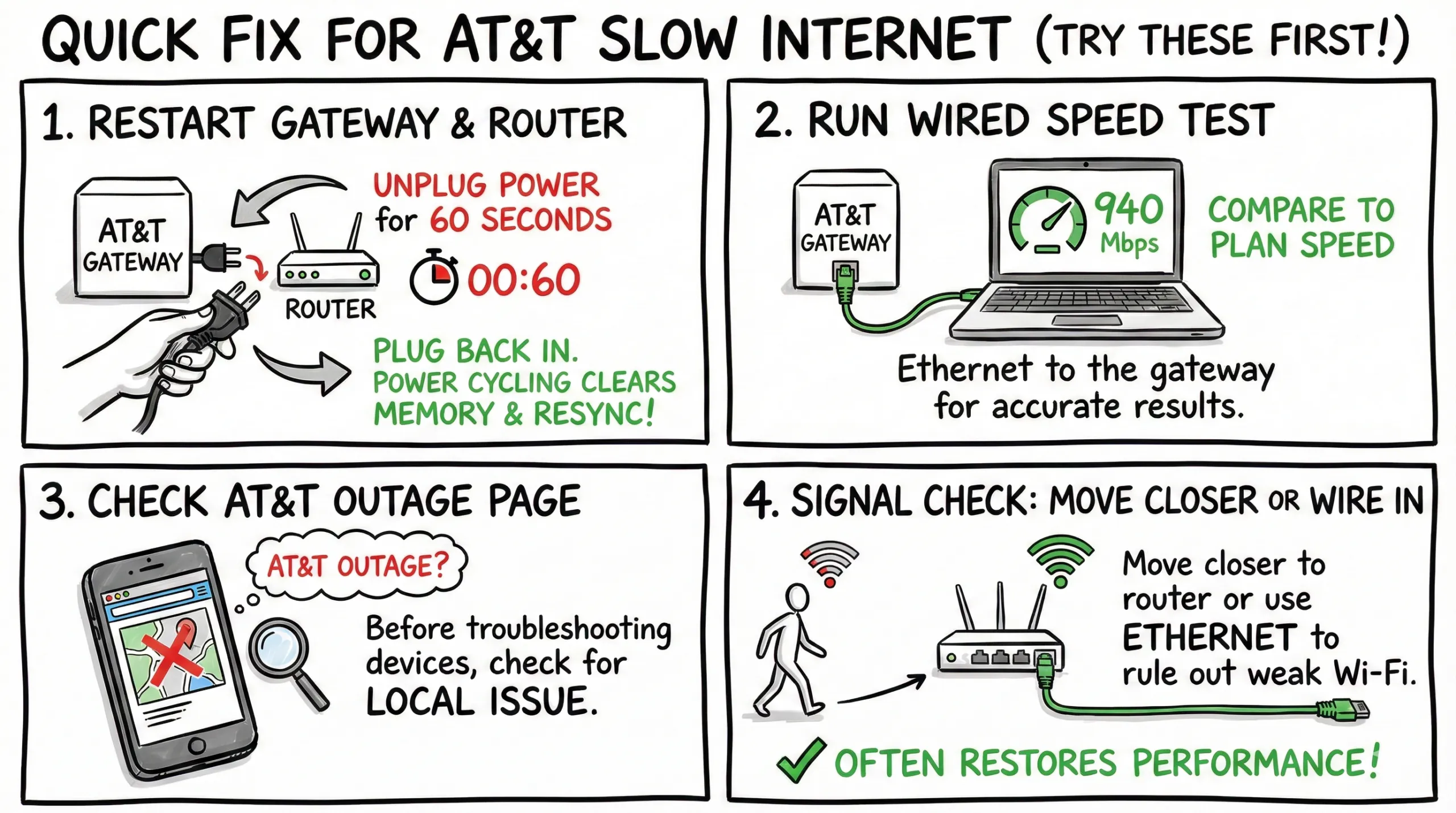
Quick Fix for AT&T Slow Internet
Try these first (takes 2–5 minutes):
- Restart your AT&T gateway and router: unplug power for 60 seconds, then plug back in.
- Run a wired speed test (ethernet to the gateway) and compare to your plan speed.
- Check the AT&T outage page in case there’s a local issue before you troubleshoot devices.
- Move closer to the router or temporarily connect via ethernet to rule out weak Wi‑Fi.
Power cycling clears memory leaks, resets connections, and resyncs everything cleanly—often restoring performance with minimal effort.
7 common causes of slow AT&T internet speeds and their fixes (Click on any Cause or Fix to read in detail)
Step-by-step troubleshooting guide to fix slow AT&T internet (Click on any step to read in detail)
- Verify slow speeds with speed tests over wired ethernet and WiFi and compare to your plan
- Inspect hardware connections and placement for issues like loose cables or poor router location
- Tinker with network settings like WiFi frequencies, channels, security protocols to optimize
- Update firmware on gateway, routers plus drivers and software on devices
- Try alternate public DNS providers like Cloudflare or Google DNS
- Power cycle modems and routers
- Reset networking equipment to factory defaults
- Contact AT&T support for technical consultation if issues persist, request technician dispatch for repairs
The key is methodically testing and eliminating possible factors dragging down your speeds. Start with easiest hardware checks and settings tweaks. Seek professional support if you can’t achieve your advertised internet speeds after exhausting self-help steps. Don’t settle for slow internet!
What Defines “Slow” Internet?
Before we dig into what’s causing your sluggish speeds, let’s set expectations on what qualifies as slow internet.
Internet speeds are measured by download rate and upload rate, referring to how much data you can pull down from the internet and push back up, respectively. These rates are measured in Megabits per second (Mbps).
To determine if your internet is underperforming, run a speed test and compare the results to the speeds advertised in your AT&T plan. If your speeds are significantly lower than what you pay for, your connection is running slow. Also compare results to your plan’s Broadband Facts label (which lists typical speeds and latency).
The current fixed broadband benchmark used by the FCC is 100 Mbps download and 20 Mbps upload. That’s a useful yardstick for modern households with multiple devices and 4K streaming. If you consistently test far below this on a comparable plan, you have a problem to solve.
See also: Why Is My Upload Speed So Slow? Reasons with Fixes
7 Common Causes and Fixes of Slow AT&T Internet Speeds
If you’ve determined your AT&T broadband speeds are slower than expected, what’s to blame? There are a number of factors that can put a drag on your connection.
1. Network Congestion
One of the most common culprits behind pokey internet is network congestion. This happens when too many devices connect to your AT&T router simultaneously, overloading the bandwidth “pipe.”
With the bandwidth choked, there isn’t enough capacity for all the devices to transmit data at maximum speeds. The more devices hitting your router at once, the slower each one will crawl.
This effect intensifies if your household is actively using bandwidth hungry apps like video streaming, gaming, VPNs or torrenting software across multiple devices concurrently.
Fix for Network Congestion
Combat congestion by cutting down the number of devices simultaneously connected to your router. Start by disconnecting devices that aren’t actively in use like laptops, tablets, e-readers, media streamers, smart home gadgets, etc.
You can also try temporarily disabling your WiFi and switching devices to wired ethernet connections where possible for lag-free connectivity.
If minimizing devices doesn’t help, it may be time to upgrade your AT&T internet plan to expand your bandwidth pipeline to handle peak usage times without choking.
2. Poor WiFi Signal
Even if your modem receives speedy broadband from AT&T over a physical line, that high-speed connection still has to make the jump to your devices over the air via WiFi.
Unfortunately, standard WiFi connections can degrade drastically with distance and obstacles like walls or furniture blocking direct line of sight between devices. Metal containers like appliances or aquariums are also nasty sources of WiFi interference.
The result is weak signal strength, unstable connectivity, and painfully slow speeds throughout areas of your home – the dreaded “dead zone.”
See also: Is Internet the same as WiFi?
Fix for Poor WiFi Signal
Pinpoint dead zones by walking throughout your home with a mobile device, noting WiFi bars and speeds in different areas. Then strategically address them by:
- Relocating your AT&T router to a central area clear of obstructions
- Upgrading WiFi router: Consider AT&T’s All‑Fi Pro package with a Wi‑Fi 7 gateway and included extenders for better throughput, latency, and coverage when available for your plan
- Adding WiFi extenders: Cheaper range expanders to amplify your router’s native signal
For devices demanding top speeds, run ethernet cable as an alternative to WiFi altogether.
See also: https://afrozahmad.com/blog/why-is-my-att-router-blinking-red/
3. Faulty AT&T Hardware
Like any electronic equipment, the networking hardware AT&T installs to deliver your internet is prone to technical problems over time.
Specifically, faults in your AT&T modem, router or other connection points manifest as intermittent connectivity drops, unstable ping rates, or network-wide sluggishness.
Fix for Hardware Problems
If inconsistent speeds plague your entire home network, faulty AT&T equipment may be the smoking gun. Connect directly to the AT&T modem via ethernet and re-run speed tests to isolate the devices slowing your speeds.
You can also eyeball your AT&T modem, router or wireless gateway for diagnostic indicator lights signalling hardware issues. If problems persist across different devices, contact AT&T support to request replacement networking hardware.
See also: How to connect an AT&T gateway: A Step-by-Step Guide
4. Firmware & Software Out of Date
Networking gear frequently receives software firmware updates enhancing connectivity, speeds, and security from hackers. Similarly, keeping OS, drivers, browsers and security up-to-date is crucial.
However, missing these important updates can degrade network performance and leave you more vulnerable to cybercriminals.
Outdated OS/apps may also lose compatibility with recent AT&T network infrastructure upgrades required to deliver speeds you pay for. Not cool!
Fix for Outdated Firmware & Software
AT&T gateways receive firmware automatically. Use the Smart Home Manager app or web to restart your gateway so the latest software can apply cleanly.
If you use your own router behind the gateway, enable auto-updates there too. On your devices, enable automatic OS and security updates, and install the latest network drivers and browser versions. Reboot all hardware when done.
5. Throttling by AT&T
For wireline home internet, AT&T states it does not throttle or block lawful traffic based on content, application, service, user, or device. Temporary measures may occur to mitigate specific security threats.
If you’re experiencing slowdowns only at certain times, it’s more likely local congestion, Wi‑Fi issues, device limits, or routing to a specific site. Note that VPNs typically reduce speed and may cause compatibility issues; they aren’t a cure for wireline congestion.
Fix for Bandwidth Throttling
Verify performance with wired tests, review your plan’s typical speeds, and contact AT&T if results are persistently below expectations. Avoid assuming throttling if only Wi‑Fi or specific apps are slow.
6. DNS Issues
Your internet browser relies on the Domain Name System (DNS), essentially an address book matching website URLs to their location (IP address) on the internet.
Before loading a web page, your device queries DNS to fetch the current address for that domain. Slow DNS response causes delays establishing connections and loading sites.
AT&T runs its own DNS servers handling requests from customers. While reliable, they aren’t immune to connectivity hiccups or overload slowdowns.
Alternatively, slowness localized to certain sites may indicate the website’s DNS records are outdated. Their true server address must be re-fetched before establishing a connection.
Fix for DNS Issues
You can sidestep DNS issues by switching to alternative public DNS providers like Cloudflare or Google Public DNS. These large resolvers offer fast domain lookups. Encrypted DNS (DoH/DoT) requires compatible devices or routers; standard AT&T gateways typically forward regular DNS unless replaced or bridged.
Try changing your AT&T router’s DNS settings to route requests through their servers instead for snappier web browsing and streaming. If speeds improve, old DNS was the culprit!
7. Line Issues & Local Outages
Despite their size, even AT&T’s networks aren’t bulletproof. Service outages happen intermittently when backbone connections fail or infrastructure suffers damage.
Incidents range from local disruptions just affecting your area to wide scale regional outages. Similarly, the phone or cable lines supplying your home may develop faults.
Equipment failure at the main distribution hub providing broadband to surrounding homes can also severely slow speeds or knock out neighbors’ connections.
Fix for Local Internet Outages
If your entire area suffers from slow AT&T speeds or dead connections simultaneously, an infrastructure-level outage is likely to blame.
You’ll need to sit tight until AT&T engineers remedy the issue. Confirm with AT&T’s outage map before wasting time troubleshooting your devices. For qualifying interruptions, AT&T may apply a service credit under its customer guarantee.
For recurring localized issues, request a technician visit to inspect supply lines leading to your home and hub equipment powering surrounding blocks. Damaged cables or hardware replacement at the street or neighborhood level will be necessary.
How to Troubleshoot & Fix Slow AT&T Internet
Armed with the most likely culprits behind your lagging AT&T internet, here is our step-by-step guide to troubleshooting and resolving speed issues once and for all:
Step 1: Verify Slow Speeds with Testing
Start by validating sluggish speeds with concrete data. Run wired speed tests at both Speedtest.net and AT&T’s Speed Test site over an ethernet connection plugged directly into your AT&T gateway/modem.
Compare results across multiple devices to determine whether the slowness stems from your router WiFi network or AT&T’s broadband backbone. Also compare to your plan’s Broadband Facts label, which lists typical speeds and latency for your service tier.
Repeat over WiFi to pinpoint hardware with the weakest speeds. Areas with lowest results need addressing first since your network performs at the speed of its weakest link.
Collecting hard speed data is key for identifying the weak spots dragging down overall performance.
Step 2: Inspect Hardware Connections & Placement
With slow speeds confirmed in specific areas or devices, it’s time to visually inspect the physical layer delivering your connectivity.
Follow all ethernet cables from your AT&T gateway/modem to devices, checking:
- Tight cable connections with audible clicks
- Cables firmly plugged into correct LAN ports
- No extreme bends or physical cable damage
- Verify cables rated for ethernet (Cat 5e, Cat6, etc.)
Damaged ethernet cabling unable to adequately carry network data will throttle speeds.
For WiFi networks, examine gateway/router placement. Units should be:
- Centrally located in your home
- Away from potential wireless interference (electronics, microwaves, etc.)
- Not obscured by walls, obstacles or tucked away in closets
Also ensure antennas are screwed tightly into the back of the device. Loose connections block transmission strength!
Step 3: Tinker With Network Settings
With physical hardware inspected, it’s time to tweak settings.
Log into your AT&T gateway web interface by pointing your browser to http://192.168.1.254. Navigate to the wireless settings dealing with your network names, passwords, channels, frequencies and security protocols.
Under advanced options, consider:
- Enabling the 5GHz (and 6GHz if available) WiFi bands for less interference
- Setting 2.4 GHz channels to non‑overlapping 1, 6, or 11, choosing the least congested channel
- Testing channel width based on environment (e.g., 20 MHz on 2.4 GHz; 40/80 MHz on 5 GHz where stable)
- Using WPA2/WPA3 security and strong passwords
Alter one setting at a time, testing speeds before and after to gauge impact. Don’t leave security disabled.
If using a third‑party router, consider QoS or device prioritization to guarantee speed to work devices.
Step 4: Update Firmware, Drivers & Software
As discussed earlier, outdated firmware and software often spurs speed issues.
AT&T gateway firmware is pushed by AT&T; use Smart Home Manager to restart if prompted. Avoid manual firmware file uploads to AT&T gateways.
On your devices, enable auto OS and security updates, and update network adapter drivers and browsers. Reboot all hardware when done for changes to take effect.
Step 5: Try an Alternative Public DNS
By changing DNS settings, you can sidestep bottlenecks caused by overloaded, distant or misfiring DNS resolvers.
We recommend switching to Cloudflare DNS or Google Public DNS. These public servers are extremely quick and support modern protocols like DNS over TLS encryption (DoT) and DNS over HTTPS (DoH). Encrypted DNS requires compatible devices or custom routers; most AT&T gateways forward standard DNS.
To point your AT&T network to alternate DNS, head back to your gateway interface. Find the page governing DNS server IP addresses under advanced settings:
- Cloudflare DNS server IPs:
1.1.1.1
1.0.0.1 - Google DNS IPs:
8.8.8.8
8.8.4.4
Save your changes then reboot hardware for the new DNS to fully activate. Run before and after speed tests to confirm if DNS tweaking helps!
Step 6: Reset Networking Equipment
If your AT&T gateway firmware and router settings check out, resetting devices to factory defaults may clear any problematic customization or corruption.
Resetting often fixes flaky performance, so it’s worth a shot! Just be sure to back up custom settings you wish to restore later.
Power cycle gadgets by unplugging them from electrical outlets completely before restarting. For WiFi routers, press and hold the reset button on the back using a paperclip. Hold for up to 30 seconds until lights flash, signaling the reset.
Devices will require reconfiguration once booted. Follow the manufacturer setup process and retest connectivity across your network.
Step 7: Request an AT&T Troubleshooting Consultation
If you’ve worked through these self-help steps without resolving slow speeds, it’s time to bring in the professionals.
Call AT&T customer support or connect to their live chat portal to consult technical troubleshooters.
An AT&T representative can view technical details regarding your account’s connection quality. They may diagnose issues like line problems causing noise disrupting your speeds. The rep can also check backbone network operations affecting your area.
If repairs are required, the representative logs a dispatch ticket to send AT&T field technicians to your home or neighborhood fixing physical connection issues. They also can replace faulty modems/routers if needed.
Stuck waiting for an AT&T technician visit? You can request interim equipment like a MiFi mobile hotspot to restore connectivity until they solve your case.
Don’t Settle for Slow Internet!
Life is too short for crawling internet speeds when you pay for fast connectivity from AT&T.
We hope pinpointing the most common lag culprits helps you resume blazing broadband through methodical troubleshooting and settings tweaks suggested above. Just take fixing your internet slowness step-by-step.
However, if the self-help tips above fail to deliver improved performance, don’t hesitate reaching out to AT&T technical support. The professionals can remotely access your equipment’s telemetry data to diagnose problems. They will dispatch repair technicians after identifying any infrastructure issues requiring hands-on fixes.
If chronic problems plague your address and reliable speeds remain elusive from AT&T, explore switching providers to escape flawed infrastructure restrictions once and for all!
Did these troubleshooting steps help identify and fix the issues slowing your AT&T internet speeds? What tricks have worked to accelerate your home broadband network? Share your tips below to pay it forward helping other readers resume faster speeds!
FAQs
Is there an AT&T outage in my area?
Answer: Check AT&T’s outage page and, if applicable, watch for automatic credits under AT&T’s customer guarantee.
Solution:
- Visit the AT&T Outage Center ([https://www.att.com/outages/]) and enter your address.
- If an outage is reported, check the estimated restoration time.
- Consider using your mobile data as a temporary backup if needed.
How can I restart my AT&T router/modem?
Answer: Unplug power for 60 seconds (and battery if present), then plug back in and wait for lights to stabilize.
Solution:
- Locate your router/modem and unplug the power cord.
- Wait for 30 seconds, then plug the cord back in.
- Wait for the lights to stabilize, indicating a successful restart.
How do I change the Wi‑Fi channel on my AT&T router?
Answer: Use non‑overlapping channels 1, 6, or 11 on 2.4 GHz (pick the least congested); on 5 GHz/6 GHz, use wider channels only if stable.
Solution:
- Access your router’s settings page via a web browser. (Consult your manual for the specific address.)
- Navigate to the “Wi‑Fi” or “Wireless” settings section.
- Look for the “Channel” option and select 1, 6, or 11 for 2.4 GHz based on least congestion (use a Wi‑Fi scanner). For 5 GHz/6 GHz, choose a stable, less‑busy channel and appropriate channel width.
- Save your changes and restart your router.
What devices are using the most bandwidth on my AT&T network?
Answer: Check Connected Devices and usage in your gateway or Smart Home Manager, then pause or schedule heavy apps.
Solution:
- Log in to your router’s settings page.
- Look for a section titled “Connected Devices” or “Bandwidth Usage.”
- Identify devices using high bandwidth and consider pausing downloads or streaming activities on them.
- Consider using a parental control app to manage bandwidth allocation for different devices.
How do I update the firmware on my AT&T router?
Answer: AT&T pushes gateway updates automatically; restart via Smart Home Manager if prompted.
Solution:
- Access your router’s settings page.
- Look for the “Firmware” or “Software Update” section.
- Check if a new update is available and download it.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install the update.
Note: Don’t interrupt the update process, as it can damage your router.
How many devices can be connected to my AT&T internet at once?
Answer: It depends on your plan and Wi‑Fi environment; multiple devices are fine, but heavy simultaneous use can slow things down.
Solution:
- Check your specific plan details on the AT&T website or contact customer support for an accurate estimate.
- Generally, you can comfortably connect several devices, but exceeding the recommended limit can impact speed.
What can I do to improve the signal strength of my AT&T Wi‑Fi?
Answer: Place the gateway centrally, reduce interference, use channels 1/6/11 on 2.4 GHz, and consider mesh or All‑Fi Pro extenders.
Solution:
- Location: Move your router to a central location, away from walls, electronics, and other signal obstructions.
- Antenna: If your router has external antennas, adjust their position for optimal coverage.
- Channel: Use non‑overlapping channels 1/6/11 on 2.4 GHz; pick the least congested.
- Mesh Wi‑Fi: For large homes or weak signal areas, consider a mesh Wi‑Fi system for seamless coverage throughout your space.
How can I tell if my AT&T internet speed is what I’m paying for?
Answer: Run a wired speed test and compare it to your plan’s advertised and typical speeds on the Broadband Facts label.
Solution:
- Run a speed test on a reliable website like Speedtest.net.
- Compare the results to your plan’s advertised download and upload speeds.
- If the difference is significant, contact AT&T technical support for troubleshooting or plan adjustments.
What should I do if my AT&T internet keeps dropping?
Answer: Inspect cables and placement, reduce interference, restart equipment, and run AT&T diagnostics; contact support if drops persist.
Solution:
- Check for loose cables connecting your router/modem and wall outlets.
- Minimize interference from other electronics near your router.
- Restart your equipment as mentioned earlier.
- Run a diagnostics tool provided by AT&T to identify potential network issues.
- If the issue persists, contact AT&T technical support for further investigation and repair.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025