When you’re comparing Starlink and 5G, it still comes down to where you are—but the numbers have changed. Short answer: in cities with strong mid‑band or mmWave 5G, 5G is usually faster; in rural or remote areas, Starlink is often more reliable.
Today, Starlink users typically see about 45–280 Mbps down with 25–60 ms latency (many users exceed 100 Mbps). U.S. 5G mobile can peak above 2 Gbps in select areas, but typical median downloads are roughly 200–300 Mbps depending on carrier, with latency commonly around 25–55 ms.
5G Home plans typically publish 133–415 Mbps down and 12–55 Mbps up. If you’re in a well‑covered urban area, 5G often beats Starlink on speed; if you’re remote, Starlink remains the best bet for dependable access.
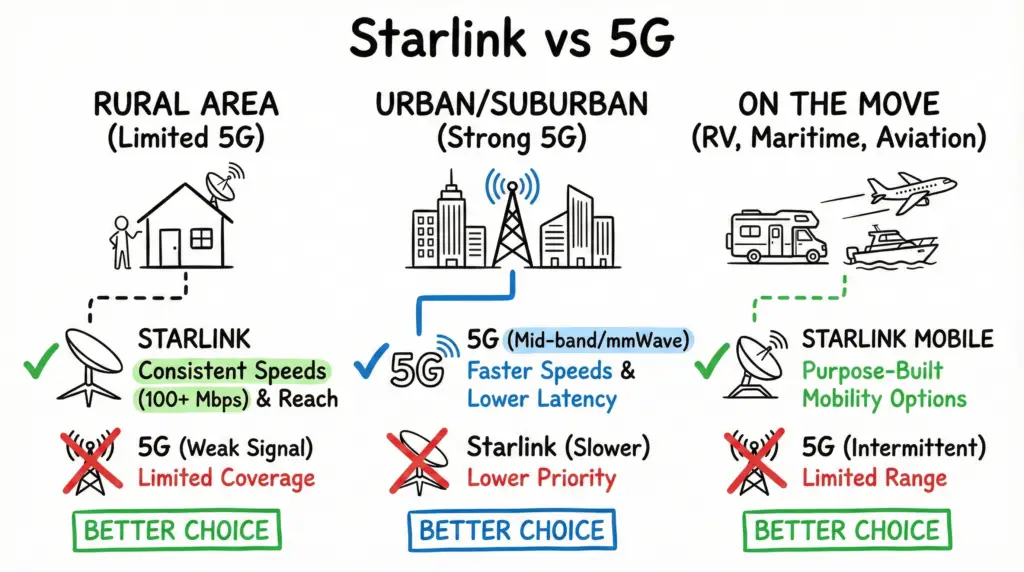
Here’s a simplified breakdown to help you decide:
- If you live in a rural area with limited wired or 5G coverage, Starlink is likely the better choice for consistent speeds (often 100+ Mbps) and reach.
- If you live in an urban/suburban area with strong 5G (mid‑band or mmWave), 5G usually delivers faster typical speeds and lower latency.
- If you need internet on the move (RV, maritime, aviation), Starlink Mobile/Mobile Priority offers purpose‑built mobility options.
Key Takeaways
- 5G mobile can peak above 2 Gbps in select mmWave spots, but typical U.S. median 5G downloads are roughly 200–300 Mbps depending on carrier.
- Starlink frequently exceeds 100 Mbps; typical user range is about 45–280 Mbps with 25–60 ms latency. In the U.S., median peak‑hour download is nearly 200 Mbps with median peak‑hour latency around 25.7 ms.
- Real‑world 5G latency is usually about 23–55 ms (1 ms is a theoretical target, not a consumer reality).
- Location is decisive: Starlink excels where wired/5G is scarce; 5G outperforms in dense areas with strong coverage.
- Both options have plan/priority nuances: Starlink offers Standard, Priority, Mobile, Mobile Priority; 5G Home plans publish typical speed ranges.
Pros and Cons of Starlink and 5G
Based on our research, here’s a closer look at the pros and cons of Starlink and 5G, beyond just speed:
Starlink
| Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Available in remote areas with limited internet options | Requires a clear view of the sky for optimal performance |
| Speed | Typically 45–280 Mbps with many users over 100 Mbps | Can be slower than strong mid‑band/mmWave 5G in cities |
| Latency | Low for satellite (often 25–60 ms) | Generally higher than well‑built 5G |
| Data Policy | Unlimited Standard data on many plans; Priority tiers available | Standard data may be deprioritized during congestion; Priority data is metered |
| Cost | No contracts and a 30‑day trial available in many regions | Hardware can be expensive; monthly fees vary by region |
5G
| Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High typical speeds in strong coverage areas; 5G Home commonly 133–415 Mbps | Performance varies with band and congestion |
| Latency | Usually ~23–55 ms | Coverage gaps remain in some rural areas |
| Cost | Often more affordable than satellite; equipment usually included | Plan terms and throttling/deprioritization vary by provider |
| Device Compatibility | Works with a wide range of phones, hotspots, and home gateways | Signals (especially high bands) can be impacted by obstructions |
| Power Efficiency | More efficient per bit than 4G in many cases | Real‑world battery impact depends on coverage, band, and device design |
| Network Capacity | Supports many devices with advanced features like network slicing | Mid‑band capacity can still slow at peak times |
It’s important to remember that both Starlink and 5G are evolving. As they mature, expect further improvements in speed and consistency.
Starlink vs. 5G: A Speed Comparison
When directly comparing Starlink and 5G speeds, the answer to “Is Starlink faster than 5G?” depends on coverage and congestion. Here’s a simplified view:
| Feature | Starlink | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Speeds | Hundreds of Mbps on dish‑based plans | Peaks above 2 Gbps in select mmWave areas |
| Typical Speeds | ~45–280 Mbps; many users >100 Mbps | Mobile medians ~200–300 Mbps; 5G Home typical 133–415 Mbps |
| Consistency | More consistent in rural/remote areas with limited alternatives | Varies by band (low/mid/mmWave) and network load |
| Latency | Often 25–60 ms on land | Commonly ~23–55 ms in real‑world use |
| Notes | Direct‑to‑Cell is a separate smartphone service (texting first), not a residential 300 Mbps offering | Home gateways publish typical speed/latency ranges by plan |
Starlink Speed Overview
Starlink offers a range of internet speeds that vary by service plan and local congestion. Whether you’re a casual user or running a business, there’s a plan that can fit.
Download Speeds
- Residential/Standard: typically ~80–220 Mbps (many users >100 Mbps)
- Business/Priority: about 120–290 Mbps
- Roam/Mobile: about 80–250 Mbps (performance varies and may be deprioritized in congestion)
Upload Speeds
- Residential/Standard: about 10–30 Mbps
- Business/Priority: about 14–35 Mbps
- Roam/Mobile: about 8–30 Mbps
Latency
Latency, which measures the delay in your connection, generally ranges from 25 to 60 ms for land‑based residential and business users. Mobile/Mobility plans can see higher latency during congestion and satellite cell saturation, often remaining under ~99 ms.
In peak hours, speeds may dip due to local demand. If you’re gaming or streaming in the evening, expect more variability than during off‑peak times.
With Starlink, choosing the right plan (Standard vs Priority vs Mobile/Mobile Priority) and ensuring a clear sky view makes a noticeable difference.
5G Speed Capabilities
5G’s Speed
5G can reach multi‑gigabit peaks in mmWave zones, but typical U.S. median mobile downloads land around 200–300 Mbps depending on carrier and location. 5G Home Internet plans commonly publish typical 133–415 Mbps down and 12–55 Mbps up, with latency often in the mid‑teens to 20s on labels but varying by signal quality. Real‑world 5G latency for consumers is generally not 1 ms; that figure is a theoretical target for specialized use cases.
Comparing Latency Rates
Latency is a critical factor when comparing internet options like Starlink and 5G, as it directly affects your online experience. It measures the time it takes for data to travel from your device to the internet and back.
Let’s break down how these two technologies stack up.
- Starlink commonly measures 25–60 ms on land, with continued improvements reported.
- 5G typically runs about 23–55 ms in the U.S., depending on carrier and band.
- The oft‑quoted 1 ms 5G latency is a theoretical target (URLLC) and not a consumer reality.
- Starlink latency can vary with weather, obstructions, and satellite handoffs, while 5G varies with signal strength, band, and network load.
- Starlink’s low‑Earth‑orbit design helps minimize latency versus legacy GEO satellite services.
Coverage Areas Comparison
In comparing the coverage areas of Starlink and 5G, it’s clear that each technology excels in different environments.
Urban Areas
In cities, 5G really shines. Dense mid‑band and mmWave deployments deliver fast speeds and low latency. Fixed 5G Home gateways are well‑suited to apartments and condos where wiring is limited or costly.
By contrast, Starlink may struggle with obstructed sky views among tall buildings, and speeds often trail strong urban 5G.
Rural Areas
In rural and remote settings, Starlink takes the lead by delivering reliable broadband where wired and robust 5G coverage are limited. Its footprint bridges the urban‑rural gap.
5G coverage can be sparse in these regions due to fewer towers. While 5G excels in cities, Starlink is often the better fit far from town.
Network Capacity Analysis
Evaluating network capacity reveals key differences. 5G’s dense cell architecture and features like network slicing help sustain performance under heavy load. Starlink’s low Earth orbit (LEO) reduces latency versus legacy satellites, but capacity per cell can tighten with subscriber growth, especially during peak hours.
On the other hand, Starlink can face congestion in busy cells and during satellite handoffs, which may reduce speeds.
Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
- 5G’s Versatility: Maintains high speeds under heavy load.
- Starlink’s Limitations: Performance can drop with congestion and during satellite switching.
- 5G’s Scalability: Expands via additional spectrum, sites, and backhaul.
- Starlink’s Dependency: Requires a clear line of sight to satellites.
- Future Prospects: Both are improving; 5G has a more established urban infrastructure.
In practical terms, if you need reliable speeds for gaming or streaming in a city, 5G is often your best bet.
Starlink shines in remote areas, but performance varies with congestion and obstructions. Choose based on your location and use case.
Cost of Starlink vs. 5G
When considering which service to choose, the cost of Starlink and 5G plays a significant role. Let’s break down the costs so you can see what fits your budget best.
| Service | Initial Hardware Cost | Monthly Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Starlink (US) | $499 | $120 |
| Starlink (UK) | $299 | $75 |
| 5G (UK, 12 mo) | $99 | $59.99 |
| 5G (UK, 36 mo) | $99 | $39.99 |
| T-Mobile 5G Home | N/A | Starting at $50/mo (as low as $35 with eligible voice line) |
Starlink’s upfront hardware is higher, and monthly fees add up. For example, with $499 hardware and $120 per month, the first‑year total is $1,939 before taxes/fees. Offers can vary regionally (including occasional hardware promotions). On the other hand, many 5G Home options are cheaper month‑to‑month and include the gateway. Additionally, T-Mobile provides unlimited data with published typical speeds, making it a cost‑effective urban/suburban option where available.
While Starlink offers broad coverage, it comes at a premium. If cost is your top priority and coverage is strong, 5G Home may be the better value.
Ideal Use Cases for Starlink
For those seeking reliable internet access in challenging environments, Starlink is an excellent solution.
It’s especially beneficial in rural and remote areas where traditional internet options simply don’t exist. You’ll find Starlink’s satellite technology well‑suited to varied scenarios.
Here are some ideal use cases for Starlink:
- Rural Areas: Stable internet access where wired connections are scarce.
- Off‑Grid Locations: Remote offices or retail sites lacking infrastructure.
- Digital Nomads: RV and temporary worksites (consider Mobile/Mobile Priority).
- Emergency Situations: Connectivity during rescue operations or disaster recovery.
- Backup Connectivity: Use Starlink as a backup for broadband, with lower latency than legacy satellites.
Starlink’s strong speeds and flexible plans make it competitive with older fixed wireless options.
It also offers wide coverage beyond 5G’s urban‑centric footprint. Whether you’re off‑grid or responding to emergencies, Starlink can keep you connected.
Ideal Use Cases for 5G
While Starlink excels in remote and rural environments, 5G technology shines in urban and densely populated areas. This high‑speed internet is great for fixed wireless broadband that connects homes without new wiring. With strong mid‑band or mmWave, you can enjoy seamless streaming and gaming.
Real-Time Responsiveness
5G is crucial for activities requiring real‑time responsiveness, like VR/AR or cloud gaming, thanks to lower typical latency compared to satellite.
IoT and Smart Cities
5G connects dense fleets of devices, from home sensors to city infrastructure, enabling smarter utilities, agriculture, and traffic systems.
Healthcare and Emergency Services
In healthcare, 5G supports real‑time data for remote consultations. For emergency services, reliable connectivity can improve response times.
In short, 5G is a game‑changer for connected urban living.
Future of Starlink and 5G
The future of Starlink and 5G holds exciting possibilities. Rather than competing head‑to‑head, they’ll often complement each other. Expect:
- Speed and Performance: 5G’s typical mobile speeds (~200–300 Mbps) often outpace Starlink in cities; Starlink delivers 100s of Mbps in many areas with improving peak‑hour results.
- Coverage and Accessibility: Starlink shines off‑grid; 5G expands quickly in metro and suburban zones.
- Technical Challenges: Starlink can see congestion in busy cells; 5G can slow during peak demand.
- Integration and Coexistence: Using both can provide redundancy.
- Cost Considerations: 5G Home is often more affordable where available.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Weather Affect Starlink Performance?
Weather can affect Starlink’s performance. Heavy rain, snow, or storms may cause temporary slowdowns or brief drops. Secure your equipment and clear snow build‑up to minimize disruptions.
Can 5G Work Without a Direct Line of Sight?
Yes, 5G can work without a direct line of sight, but performance drops as obstructions and building materials attenuate signals—especially at higher bands.
What Devices Are Compatible With Starlink Internet?
You can use various devices with Starlink, including the Gen3 dish, Mini, RV, Maritime, and Aviation systems. Ensure a clear sky view and a quality Wi‑Fi 6/6E router for best results.
Is Starlink Available in My Area?
To check availability, visit Starlink’s website and enter your address. If it’s not offered yet, you can reserve a spot with a deposit and receive updates.
How Does 5G Impact Battery Life on Mobile Devices?
5G radios can be more efficient per bit than 4G, but battery life depends on coverage, band, and device design. In weak‑signal areas, power use can increase.
Conclusion
To sum up, whether Starlink is faster than 5G depends on your situation. Starlink offers strong speeds and broad coverage in remote areas, while 5G shines in cities with consistently faster typical speeds and lower latency. If you’re in a city or suburb with great 5G, it’s likely the better pick; if you’re rural or mobile, Starlink could be a game‑changer. Choose based on your location, plan options, and budget—and enjoy the internet!
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025