Megabit vs Megabyte – 1 MegaByte = 8 Megabit. A Megabit is a unit of data transfer speed used for evaluating internet speeds, while a MegaByte measures file size or storage space.
MegaByte(MB), Megabit, Byte and Bit Converter
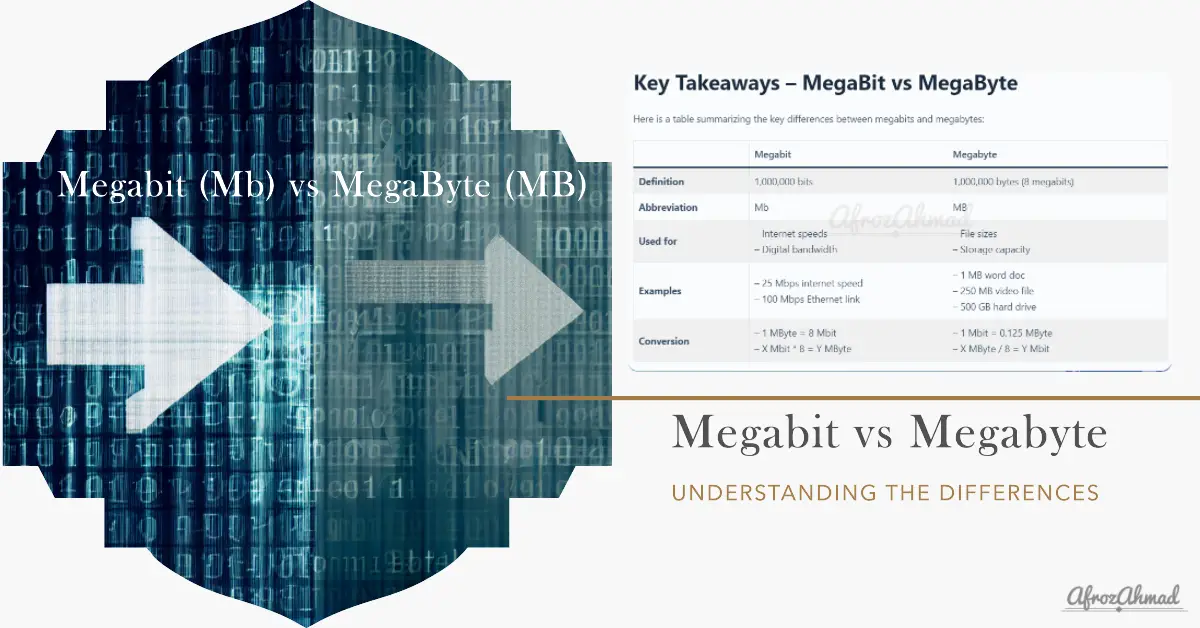
Key Takeaways – MegaBit vs MegaByte
The MegaByte vs. Megabit distinction affects how we interpret internet plans and file downloads. Here is a table summarizing the key differences between megabits and megabytes:
| Megabit | Megabyte | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1,000,000 bits | 1,000,000 bytes (8 megabits) |
| Abbreviation | Mb | MB |
| Used for | – Internet speeds – Digital bandwidth | – File sizes – Storage capacity |
| Examples | – 25 Mbps internet speed – 100 Mbps Ethernet link | – 1 MB word doc – 250 MB video file – 500 GB hard drive |
| Conversion | – 1 MByte = 8 Mbit – X Mbit * 8 = Y MByte | – 1 Mbit = 0.125 MByte – X MByte / 8 = Y Mbit |
What is a Megabit or Mbps?
A megabit (Mb) is a unit of digital data equal to one million bits. Bits are the basic unit of data in computing and networking, represented as either a 1 or 0 in binary code.
Eight bits make up a byte. So a megabit is different from a megabyte (discussed next). The main applications of megabits are for measuring:
- Internet transfer speeds – Internet and network speeds are measured in megabits per second (Mbps). A connection of 25 Mbps can transfer 25 megabits of data per second.
- Digital signal rates – In telecommunications, digital bandwidth capacity is measured in megabits, like a 10 Mbps Ethernet link.
So, in summary, a megabit is a million individual bits of data commonly used to measure internet speeds and digital bandwidth.
What is a Megabyte?
A megabyte (MB) is a unit of digital data equal to one million bytes. A byte consists of eight bits of data. Some key facts about megabytes:
- 1 MB = 8 megabits
- 1024 MB = 1 gigabyte (GB)
- 1024 GB = 1 terabyte (TB)
Megabytes are commonly used to measure:
- File sizes – Everything from the size of a Word doc to a YouTube video is measured in megabytes (or gigabytes for larger files).
- Digital storage capacity – The space on your computer’s hard drive, USB drive, or cloud storage is measured in megabytes and gigabytes.
In summary, a megabyte represents a million bytes of data, frequently used to measure file sizes and storage space.
Check out How Many Megabits in a Gigabit? Converting Between Gbps and Mbps post for more details related to Bits and conversion formulas.
Megabit vs Megabyte: The Differences
Although the names sound similar, a megabit and a megabyte are fundamentally different units. This causes a great deal of confusion, but the distinction is critical.
The key differences:
- A megabit is one million bits, while a megabyte is one million bytes.
- There are 8 bits in 1 byte.
- Therefore, there are 8 megabits (Mb) in 1 megabyte (MB).
To put it another way:
1 megabit = 1,000,000 bits
1 megabyte = 1,000,000 bytes = 8,000,000 bits
So a megabyte is 8 times larger than a megabit! Understanding this core difference is key.
Here are some examples of the discrepancies:
- A 100 Mbps internet connection equates to 12.5 MBps download speeds.
- A 500 MB file is 4,000 megabits.
- A 16 GB memory card holds 128,000 megabits.
As you can see, interchanging megabits and megabytes can lead to very different values!
Why the Difference Matters
With megabits used for transfer speeds and megabytes for file sizes and storage, it’s essential to distinguish between them in the correct context. Otherwise, massive confusion can occur!
Some examples of when it matters:
- Comparing internet plans – An ISP may advertise “100 Mbps” speeds. But to calculate download times, you must convert to MBps.
- Estimating download times – A 50 MB file downloaded at 10 Mbps will take 40 seconds (50 MB * 8 bits/byte / 10 Mbps).
- Hard drive capacity – A 1 TB hard drive holds 1,000 GB or 8,000,000 MB. Confusing TB and Mb leads to vastly incorrect storage estimates.
- Streaming video quality – Video streaming quality is based on megabits per second, not megabytes. So a 5 Mbps video will have much lower quality than a 5 MBps video.
As you can see, using the wrong units in the wrong context can lead to significant problems. When dealing with data transfer rates, always think of megabits. For file storage and downloads, use megabytes.
How to Convert Megabit to Megabyte
To convert between units, you simply need to know that there are 8 megabits in 1 megabyte. Then you can use this basic formula:
Megabytes = Megabits / 8
For example, to convert a 4-megabit file to megabytes:
4 megabits / 8 = 0.5 megabytes
Here is a conversion table for some common megabit values:
| Megabits | Megabytes |
|---|---|
| 8 Mb | 1 MB |
| 16 Mb | 2 MB |
| 64 Mb | 8 MB |
| 128 Mb | 16 MB |
| 256 Mb | 32 MB |
So if you know the file size or transfer speed in megabits, simply divide by 8 to get the megabytes.
How to Convert Megabyte to Megabit?
To convert in the other direction, from megabytes to megabits, you use:
Megabits = Megabytes * 8
For example, to convert a 100-megabyte file to megabits:
100 megabytes * 8 = 800 megabits
Here is a conversion table for some common megabyte values:
| Megabytes | Megabits |
|---|---|
| 1 MB | 8 Mb |
| 2 MB | 16 Mb |
| 8 MB | 64 Mb |
| 16 MB | 128 Mb |
| 32 MB | 256 Mb |
To summarize, just multiply the megabytes by 8 to get the equivalent megabits.
Megabit and Megabyte in Internet Speeds
One of the most common uses of megabits is for measuring internet connection speeds. ISPs advertise home internet plans in megabits per second (Mbps), like “50 Mbps” or “100 Mbps”.
This means the maximum transfer rate is 50 or 100 megabits per second. It determines how quickly you can download data like web pages, videos, and files.
However, to calculate download times, you need megabytes per second (MBps). To convert:
MBps = Mbps / 8
So for a 100 Mbps connection: 100 Mbps / 8 = 12.5 MBps
At 12.5 MB/s, you could download a 100 MB video in 8 seconds.
When comparing internet plans, look at the megabit speed. But for real-world usage, work in megabytes to estimate wait times.
Megabit and Megabyte in File Size
Unlike internet speeds, file sizes are always measured in megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB).
Some examples:
- A Word doc: 0.5 MB
- An MP3 song: 5 MB
- A full HD movie: 5000 MB (5 GB)
To convert file size from megabytes to megabits, multiply by 8:
5 MB music file * 8 = 40 megabits
And to estimate download time, divide the file size (MB) by your internet speed (Mbps / 8):
5 MB song / (100 Mbps / 8) = 5 MB / 12.5 MBps = 0.4 seconds
So megabytes are used for practical file storage and transfers, while megabits help compare internet connection speeds.
Conclusion
To summarize, a megabit is a unit of one million bits, while a megabyte is one million bytes (which is 8 megabits). Though they sound similar, these units are used in different contexts. Megabytes measure file sizes and storage capacity. Megabits measure internet speeds and digital bandwidth.
Converting between the units is as simple as multiplying or dividing by 8. But avoiding confusion in the first place comes down to remembering the fundamental difference:
- Megabytes = file sizes, storage space
- Megabits = transfer speeds, internet bandwidth
Understanding this key distinction will allow you to compare plans accurately, calculate download times correctly, and avoid costly mistakes when managing data.
Additional Resources
- Subnet and Wildcard Calculator
- Wifi Connected But No Internet: Causes, Fix, and Preventive Measures
- Why Is My Upload Speed So Slow? Reasons with Fixes
- Comparing Ethernet Cables – Cat5 vs Cat5e vs Cat6 vs Cat6a vs Cat7 vs Cat8
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025