The Internet is an integral component of modern lives, and Ethernet cables play a critical role in connecting devices to the Web. But not all Ethernet cables are made equal; different versions excel in different scenarios. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive comparison between Cat 5 vs Cat 5e vs Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 vs Cat 8 Ethernet cables to aid you in making informed decisions about your connectivity needs.

Cat5 vs Cat5e vs Cat6 vs Cat6a vs Cat7 vs Cat8 Ethernet Cables
Key takeaways
| Ethernet Cable Category | Bandwidth | Data Rate | Crosstalk | Shielding | Maximum Distance | Key Characteristics | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
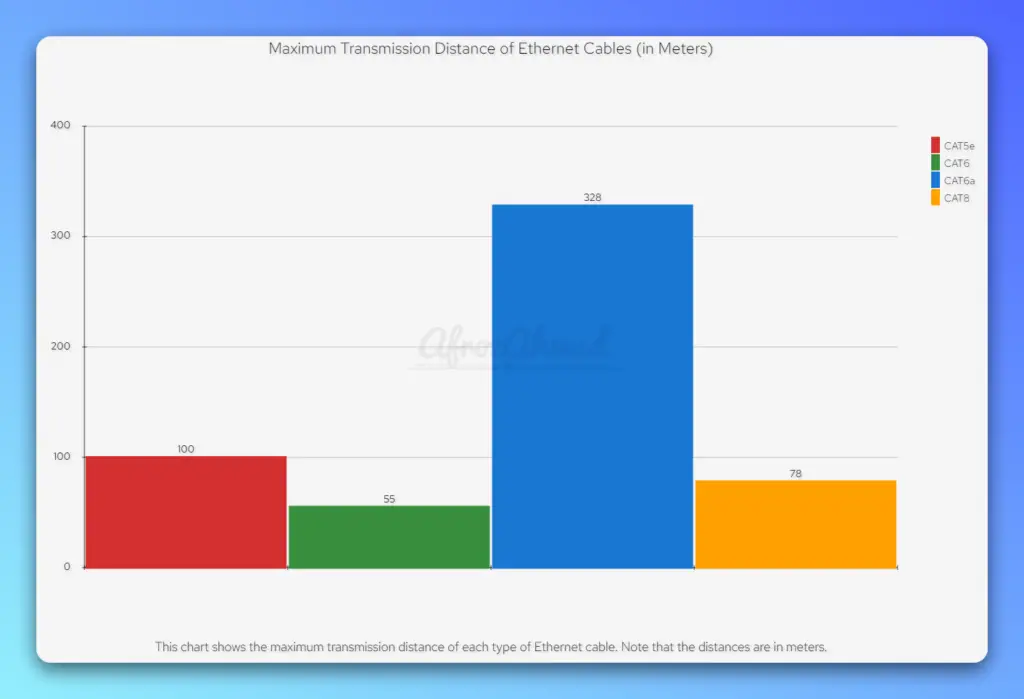
| CAT5 | Up to 100 MHz | 10/100 Mbps | Moderate | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) | 100 meters | The previous standard, moderate crosstalk handling | Not commonly used due to older technology |
| CAT5e | Up to 100 MHz | Up to 1 Gbps | Reduced | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) | 100 meters | Enhanced CAT5, better crosstalk handling | Telephony and video signal transmission |
| CAT6 | Up to 250 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps (limited to 55 meters) | Stricter Specifications | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) | 100 meters (for 1 Gbps), 55 meters (for 10 Gbps) | Less interference due to thicker gauge and tighter twist | Typical in modern office buildings |
| CAT6a (Category 6 Augmented) | Up to 500 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps | Augmented | Shielded (STP) | 100 meters | Improved CAT6, thicker and more expensive | High-speed networks where CAT6 doesn’t reach the required distance |
| CAT7 | Up to 600 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps | Relatively low | Shielded (STP) | 100 meters | Not an official IEEE standard; however, it is a recognized standard under ISO/IEC. Proprietary design and connector. | Not recommended due to lack of standardization |
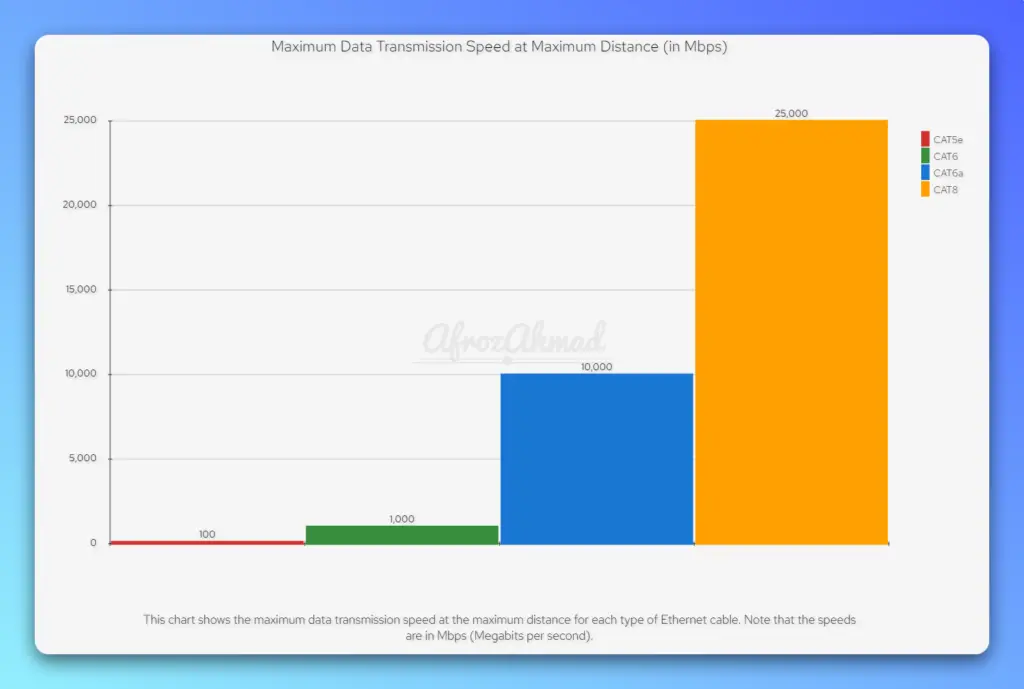
| CAT8 | Up to 2000 MHz | Up to 40 Gbps | Reduced | Shielded (STP) | 30 meters | Official successor to CAT6a, standardized across manufacturers | Best for data centers and high-speed equipment connections |
What are Bandwidth, Data Rate, Cross talk, and Shielding?
I know I have used technical terms in the beginning, but don’t worry here are the definitions of those terms in simple language:
- Bandwidth: This is like the width of a highway. A wider highway can carry more cars at once, and similarly, a higher bandwidth can carry more data at once. In technical terms, it’s the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time, usually measured in megahertz (MHz) for Ethernet cables.
- Data Rate: This is the speed at which data can travel across a network or the internet. Imagine it like the speed limit on a road – a higher speed limit lets cars travel faster, and a higher data rate lets data travel faster. It’s usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Crosstalk: Imagine you’re in a room full of people talking. If someone nearby speaks loudly, it can interfere with your own conversation. In networking, crosstalk is similar – it’s the interference that can happen when signals from one cable leak into another, disrupting the data transmission. Ethernet cables are designed to minimize crosstalk.
- Shielding: This is like a protective cover for the cables. Just like an umbrella protects you from rain, shielding in cables protects the data signals from external disturbances, such as electromagnetic interference. Shielded cables are especially useful in environments where there’s a lot of potential interference.
Now you are equipped with the knowledge of technical jargon often used in deciding ethernet cables, let’s begin with understanding each cable type in depth.
Checkout How to Extend An Ethernet Cable for Faster Internet and Stable Connections in case you want to extend your existing ethernet cable.

Understanding Cat5
Category 5 (Cat 5) cables were the standard for many years. These cables support Fast Ethernet speeds (up to 100 Mbps) over 100 meters and include 100 MHz bandwidth. However, they’ve largely been phased out in favor of Cat 5e.
The Introduction of Cat5e
Cat 5e (“e” stands for enhanced) offered improvements over Cat 5 by reducing crosstalk (interference between the wires inside the cable). These cables support the same bandwidth and length as Cat 5 but can handle up to 1000 Mbps, commonly referred to as gigabit Ethernet.

Advancements in Cat6
Cat 6 cables were the next significant upgrade from Cat 5e. With a bandwidth capacity of 250 MHz and the ability to support up to 10 gigabit Ethernet over 55 meters, Cat 6 cables significantly enhance data transfer speeds and overall network performance.
Advantages of Cat6 over Cat 5e
Cat6 cables have several advantages over Cat5e cables:
- Higher Bandwidth: Cat6 cables have a higher bandwidth capacity of up to 250 MHz compared to the 100 MHz bandwidth of Cat5e cables. This means that Cat6 cables can support faster data transmission and handle more network traffic.
- Faster Speeds: While Cat5e cables can support speeds up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps), Cat6 cables can achieve speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This makes Cat6 cables ideal for high-performance applications and networks that require faster connectivity.
- Better Performance: Cat6 cables have stricter specifications for crosstalk and system noise compared to Cat5e cables. This means that Cat6 cables are less prone to interference and signal degradation, resulting in better overall performance and reliability.
- Future-Proofing: Cat6 cables are designed to meet the performance requirements of future network technologies. By investing in Cat6 cables, you can ensure that your network infrastructure is ready to handle advancements in technology and increased data demands in the future.
Here’s a summary of the advantages of Cat6 over Cat5e:
- Higher bandwidth capacity
- Faster speeds
- Better performance and reliability
- Future-proofing for upcoming technologies
By upgrading to Cat6 cables, you can enhance your network’s performance and ensure a more efficient and reliable connectivity experience.
The High-Performing Cat7
Cat 7 cables come with notable enhancements over Cat 6, offering bandwidth up to 600 MHz and supporting 10-gigabit Ethernet over 100 meters. The key feature of Cat 7 is the stringent shielding of its twisted pairs, which reduces interference, making it ideal for environments with high electromagnetic interference.
It’s worth noting that Cat 7 lacks an official status as an IEEE or EIA cabling standard however, it is a recognized standard under ISO/IEC and uses proprietary connectors instead of the typical RJ45. If you’re looking for a faster copper alternative than Cat 6A, it’s best to consider Cat 8.
Advantages of Cat7 over Cat 6
Advantages of Cat7 over Cat6
| Category | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Speed | Supports speeds of up to 10Gbps, ten times faster than Cat6. |
| Bandwidth | Has a higher frequency range of up to 600MHz, providing greater bandwidth for simultaneous data transmission. |
| Shielding | Equipped with individual shielding for each twisted pair and an overall shield, minimizing crosstalk and signal attenuation. |
| Reliability | Offers more reliable and interference-free connections, making it suitable for environments with heavy network traffic. |
| Future-proofing | Provides long-term compatibility and ensures readiness for future network upgrades and technological advancements. |
Overall, Cat7 cables offer superior performance and reliability compared to Cat6, making them a preferred choice for high-performance networks demanding fast and stable connectivity.
Next-Generation: Cat8
Cat 8 cables are the latest variant of Ethernet cables. They are specially designed for high-speed data centers, delivering incredibly fast data transfer rates of up to 40-gigabit Ethernet over 30 meters, with 2000 MHz bandwidth.
Advantages of Cat8 over Cat 7
When comparing Cat 8 Ethernet cables to Cat 7, there are several advantages that Cat 8 offers:
- Higher Data Transfer Speed: Cat 8 cables can support transmission speeds of up to 40Gbps, which is significantly higher than the maximum 10Gbps speed of Cat 7 cables.
- Increased Bandwidth: Cat 8 cables have a bandwidth capacity of up to 2GHz, providing a wider frequency range for data transmission compared to the 600MHz bandwidth of Cat 7 cables.
- Improved Shielding: Cat 8 cables feature better shielding, such as individual foil shielding for each twisted pair and an overall braid shielding, which enhances protection against electromagnetic interference and reduces signal loss.
- Longer Transmission Distance: Cat 8 cables can maintain faster speeds and higher bandwidth over longer distances. They can support 25Gbps and 40Gbps speeds up to 30 meters and 10Gbps speeds up to 100 meters.
- Compatibility: Cat 8 cables are backward compatible with Cat 6a, ensuring they can be used with existing network infrastructure.
It’s important to note that Cat 8 cables are generally more expensive than Cat 7 cables, so the choice of which cable to use depends on the specific requirements and budget of the network installation.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences in features and specifications:
| Category | Bandwidth | Speed | Crosstalk | Shielding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat5 | Up to 100 MHz | 10/100 Mbps | Moderate | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) |
| Cat5e | Up to 100 MHz | Up to 1 Gbps | Reduced | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) |
| Cat6 | Up to 250 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps | Stricter specifications | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (FTP) |
| Cat6a | Up to 500 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps | Augmented | Shielded (STP) |
| Cat7 | Up to 600 MHz | Up to 10 Gbps | Relatively low | Shielded (STP) |
| Cat8 | Up to 2000 MHz | Up to 40 Gbps | Reduced | Shielded (STP) |
Check out the below post for more information on internet speeds:
- The Ultimate Guide to 200 Mbps Internet Speed: Is 200 Mbps Fast Enough
- Is 1000 Mbps Fast Internet? (The Gold Standard of Internet Speeds)
- The Ultimate Guide to 200 Mbps Internet Speed: Is 200 Mbps Fast Enough
Suitable use cases of Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 7, and Cat 8 Ethernet Cables
| Category | Ideal Environments and Applications |
|---|---|
| Cat 5 | Older, less demanding network setups, areas where high-speed internet isn’t required. Bare in mind that Cat5 cables are obsolete. |
| Cat 5e | Home networks, small businesses |
| Cat 6 | Small-to-medium-sized businesses, future-proofing home networks |
| Cat 6a | Suitable for industrial or commercial applications |
| Cat 7 | Large businesses, universities, and hospitals require high-speed and high-bandwidth connections |
| Cat 8 | Data centers, server rooms requiring ultra-high-speed connections |
Here are the suitable use cases for different categories of Ethernet cables:
- Cat5: Cat5 cables are suitable for basic internet connections and are commonly used in home networks or small businesses with low bandwidth requirements. They can support speeds up to 100 Mbps.
- Cat5e: Cat5e cables are an upgraded version of Cat5 and are suitable for environments that require higher speeds and reduced interference. They can support speeds up to 1 Gbps and are commonly used in larger business networks or for streaming media.
- Cat6: Cat6 cables are designed for high-performance networks and are ideal for demanding applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and data centers. They can support speeds up to 10 Gbps and provide better protection against crosstalk.
- Cat6a: Cat6a cables are an enhanced version of Cat6 and are suitable for industrial or commercial applications. They have stricter specifications for interference and can support higher speeds of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances.
- Cat7: Cat7 cables are designed for environments that require even higher speeds and greater interference protection. They are commonly used in data centers, server rooms, and other high-density network applications. Cat7 cables can support speeds up to 10 Gbps and frequencies up to 600 MHz.
- Cat8: Cat8 cables are the latest and highest-performing category of Ethernet cables. They are suitable for large-scale data centers and enterprise networks that require ultra-fast data transfer speeds. Cat8 cables can support speeds up to 25 Gbps and 40 Gbps.
Choosing the right category of Ethernet cable depends on your specific network requirements and the speed and bandwidth needed for your applications.
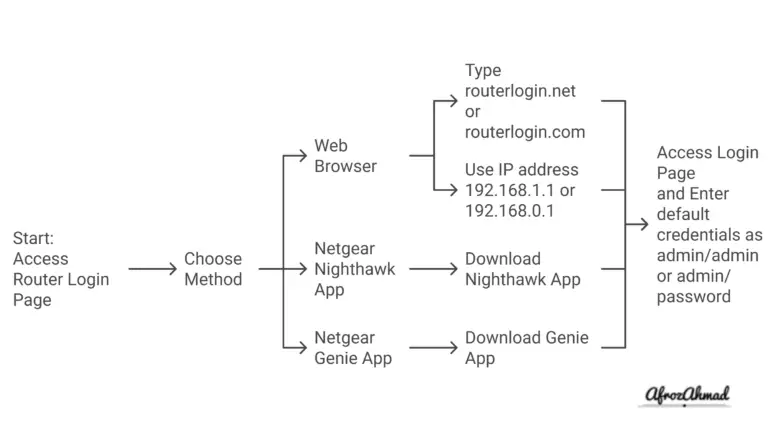
How to Choose the Right Ethernet Cable?
When choosing the right Ethernet cable, there are several considerations to keep in mind:
- Speed and Bandwidth: Different cable categories offer varying speeds and bandwidth capacities. Determine the maximum speed and distance requirements for your network to select the appropriate cable category. For high-speed and short-distance applications, Cat 8 stands out. For typical home networking, Cat 5e or Cat6’s balance of speed and cost makes it a popular choice.
- Transmission Distance: The maximum transmission distance for each cable category varies. Consider the length of your network cables and choose a category that can support the desired speed over that distance. Keep in mind that all Category cabling has a distance limitation of roughly 100 meters.
- Function: Consider what device the cable will be used for. For example, since a wireless access point typically has many devices sharing one or two cables, a Cat 6A would be a suitable choice.
- Shielding Type: Ethernet cables can be shielded or unshielded. Shielded cables provide better protection against crosstalk and interference, making them suitable for environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI). Cat 7’s increased shielding can be crucial if electromagnetic interference is an issue.
- Application Requirements: Consider the specific requirements of your network and the type of data being transmitted. Different cable categories offer varying levels of performance and resistance to interference.
- Cost: Budget is an important factor when selecting Ethernet cables. Higher-category cables like cat8 generally offer better performance but may come at a higher cost. Consider your budget and prioritize the specific needs of your network.
- Environment: Different environments call for different cable standards, such as plenum cabling for indoor use and OSP cabling for outdoor use.
By considering these factors, you can choose the cable that best suits your needs while also taking into account any potential temperature-related issues that might cause CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) errors.
As a general guideline, Cat 6 is ideal for office use and suitable for startups, while Cat 8 is excellent for data centers. If you’re looking to save money, Cat 5e serves as the most economical choice.
Armed with knowledge of these Ethernet cable categories and their specifications, you can confidently select the cable that will meet all your requirements.
Shielding Types of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables also come with different shielding types, which can affect their performance in different environments. Here are the common shielding types:
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Suitable for high-speed network and high-security transmission.
- SFTP (Shielded Foil Twisted Pair): The low attenuation of the internal signal makes it nice for the special environment of professional wiring.
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): Suited for network applications with transmission bandwidth less than 250MHz and no special performance requirements.
- FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair): Designed to provide the assembly with greater protection from crosstalk from adjacent pairs and other cables, RFI, and EMI.
- ASTP (Armoured Shielded Twisted Pair): Perfect opt for preventing rodent damage, also nice for explosion-proof wiring system.
Conclusion
Ethernet cables are a crucial part of any network, and understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision for your networking needs. Whether you choose CAT5e, CAT6, CAT7, or CAT8 will depend on your specific requirements for speed, distance, and price. Remember, the right Ethernet cable can significantly improve the performance of your network.
Here is a recap of what you are learned so far.
| Ethernet Cable Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Cat5 | The oldest category of Ethernet cables, with a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz and capable of supporting speeds of up to 100 Mbps. |
| Cat5e | An enhanced version of Cat5 cables with reduced crosstalk and improved signal quality. It has a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz and can support 1 Gbps speeds. |
| Cat6 | Offers higher performance and bandwidth, with a bandwidth of up to 250 MHz. It can support speeds of up to 10 Gbps. |
| Cat 6a | Offers higher performance and bandwidth, with a bandwidth of up to 500 MHz. It can support speeds of up to 10 Gbps and distances up to 100 meters. |
| Cat7 | Provides even better shielding and performance than Cat6 cables. It has a bandwidth of up to 600 MHz and can support speeds of up to 10 Gbps. |
| Cat8 | The latest standard in Ethernet cables, with a bandwidth of up to 2,000 MHz and capable of supporting speeds of up to 40 Gbps. |
- Epson EpiqVision Flex CO-W01 Projector Review - February 21, 2025
- How to Log in to Your Netgear Router - January 17, 2025
- Gaimoo GM200 Mini Projector Review - January 12, 2025