Having a fast, reliable internet connection is crucial in the modern digital world. Whether you’re working from home, gaming online, or streaming movies, you need solid network performance. Ethernet cables provide faster speeds and lower latency than WiFi. But ethernet cables have a major limitation – length. Standard ethernet cables max out at 328 feet (100 meters). Exceeding this distance can lead to slower speeds, lost connections, and other issues.
Fortunately, with the right equipment, extending your ethernet cable past the 100-meter barrier is not difficult. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of how to extend an ethernet cable without losing speed.
An Introduction to Ethernet Cables and Their Limitations
Before jumping into the extension methods, let’s quickly go over what ethernet cables are and why they have distance constraints.
What is an Ethernet Cable?
Ethernet cables, also known as Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, or Cat 7 cables, are used to connect devices like computers, routers, switches, and gaming consoles to form a wired local area network (LAN).
Ethernet cables transmit data through copper wiring organized into four twisted pairs inside the cable jacket. The twists help reduce electromagnetic interference so the signal can travel farther without degradation.
Ethernet Cable Categories
Ethernet cables come in different categories, with each newer category bringing improvements in data transmission speed, noise resistance, and distance capabilities.
- Cat 5: Up to 100 Mbps at 100 meters
- Cat 5e: Up to 1 Gbps at 100 meters
- Cat 6: Up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters
- Cat 6a: Up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters
- Cat 7: Up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters
- Cat 8: Up to 40 Gbps at 30 meters
As you can see, 100 meters is the maximum distance for almost all types of ethernet cables at common network speeds. Exceeding this length causes reliability and performance issues.
Why Ethernet Cables Can’t Go Farther
The 100-meter limitation stems from how ethernet technology transmits data. The electrical signals traveling through the copper wires steadily attenuate and get distorted over long distances.
To ensure flawless data transfer, ethernet standards mandate that cables cannot exceed 100 meters. Even a small amount over this length risks lost packets, lag, and failed connections.
Now that you understand why ethernet cables hit a hard length limit let’s explore ways to break past that barrier.
How to Extend An Ethernet Cable without Loosing Speed
While a single segment of ethernet cable cannot go over 100 meters, you can connect multiple segments to reach much longer distances. You just need devices that can join and regenerate the ethernet signal between segments.
Here are the best options to boost your ethernet cable range for fast, reliable networking.
Option 1: Use Ethernet Network Switches
Ethernet switches are likely the simplest and most convenient way to lengthen your ethernet cable. Network switches are designed to expand the number of wired connection points on your network.
But conveniently, joining ethernet cables into a switch also regenerates the signal and essentially creates one extended logical cable between the switch and connected device.
How an Ethernet Switch Extends Cable Length
A network switch connects to your router on one side. Your existing ethernet cable plugs into one port on the switch. Then, you can connect another ethernet cable cable into a different switch port, which runs to your computer or other device farther away.
The switch receives the signal from your router, amplifies and retransmits it to the cable going to your device downstream. This allows you to place switches strategically to meet any extended cabling needs.
Extending with Multiple Switches
You can use multiple ethernet switches chained together to additively extend the total distance. Each switch-to-switch or switch-to-device segment can be up to 100 meters. So with two switches you can get approximately 200 meters total.
Network switches are plug-and-play and require no configuration. For simple setups, unmanaged gigabit switches like the NETGEAR 5-Port are ideal for extending ethernet cables farther throughout your home or office.
Benefits of Using Ethernet Switches
- Very easy to install and use
- Allows up to 200 meter extension with 2 switches
- Provides extra ethernet ports for connecting more devices
- Generates minimal signal degradation between switches
Potential Drawbacks
- Requires an available electrical outlet for power
- Only extends the total distance by 100 meters at a time
Option 2: Join Cables with Ethernet Inline Couplers
Ethernet inline couplers, also called RJ45 joiners, are simple devices for mechanically joining two ethernet cables together to create a longer single cable.
How Inline Couplers Work
Ethernet couplers are essentially two RJ45 female ports housed in a small plastic casing. One Extremely easy plug-and-play installation
- ethernet cable plugs into each side. The wires inside electrically connect each pin from one cable end to the other. Couplers introduce a slight signal boost so ethernet electrical signals can propagate an extra 100 meters from end to end. Like switches, inline couplers preserve your network speed and reliability. Benefits of Ethernet Inline Couplers
- Cost-effective way to extend short cable runs
Potential Drawbacks
- Limited to 100 meter extension segments
- Possible connectivity issues if poor quality
Option 3: Use Ethernet Over Coaxial Cable
If you need to cover very long distances, one option is converting the ethernet signal to transmit further over coaxial cable rather than copper twisted pairs.
Coaxial cable is commonly used for cable TV and antenna connections. An ethernet over coax converter allows sending your LAN data through your existing coaxial lines.
How Ethernet Over Coax Extenders Work
These solutions require a converter box on each end of the coaxial cable segment. On one end, the converter takes the ethernet signal and modulates it for transmission through the coaxial cable.
On the receiving end, another converter demodulates the signal back into ethernet for connection to your device or network. The coaxial cable linking them can span much farther than ethernet twisted pairs.
Benefits of Ethernet Over Coax
- Extend your network up to 1000 meters over coax
- Utilize existing coaxial cable lines in your walls
- Get farther reach than ethernet alone
Potential Drawbacks
- Requires compatible ethernet over coax hardware
- Configuration can be more complex than a switch
- Needs power outlets on both ends
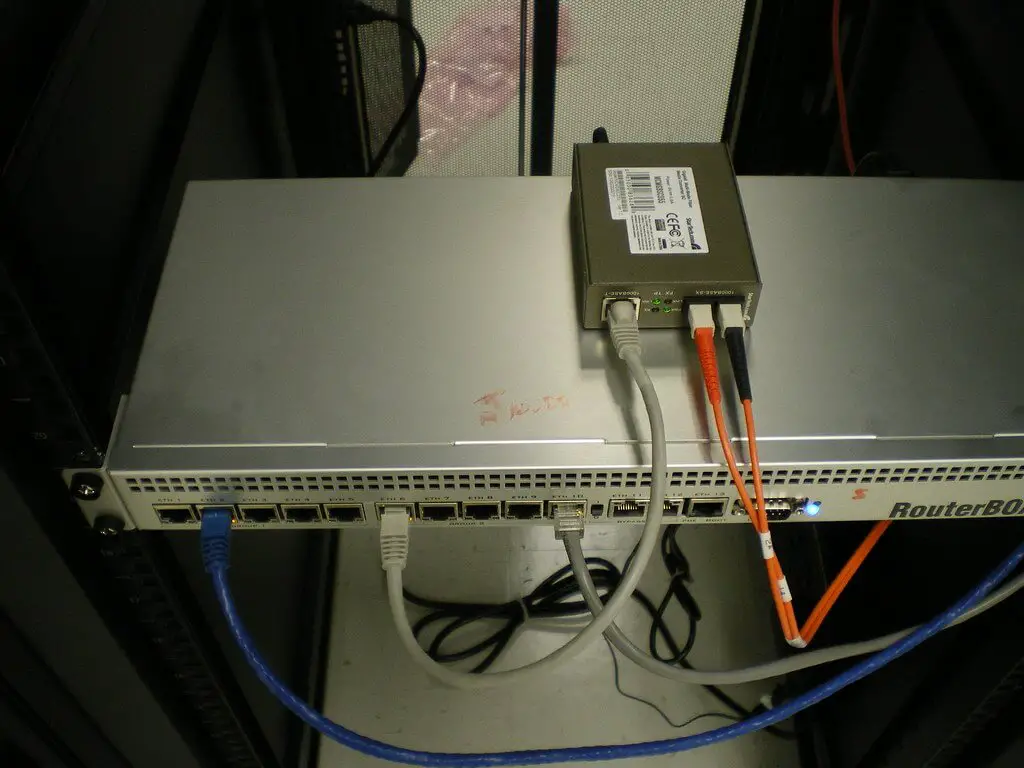

Option 4: Use Ethernet Over Fiber Media Converters
The most flexible way to extend ethernet cables over extremely long runs is converting the signal to fiber optic cabling. This leverages the immense range and interference resistance of fiber optics.
How Ethernet Over Fiber Media Converters Work
You need an ethernet media converter on each end, with one ethernet port and one fiber optic port. The source converter transforms ethernet electrical signals into light pulses and shoots them through the fiber optic cable.
The receiving converter reconstitutes the pulses back into ethernet data which can connect to your computer or other device. This facilitates ethernet transmission over many kilometers.
Benefits of Ethernet Over Fiber
- Extend ethernet up to 5 kilometers or more
- Fiber optics are completely immune to electromagnetic interference
- Outstanding reliability and speed over very long distances
Potential Drawbacks
- More expensive equipment cost for media converters
- Fiber optic cables are fragile and require careful handling
- Needs compatible fiber optic connectors on both ends
Tips to Extend Your Ethernet Cable Reliably
Whichever approach you take for extending your ethernet cables, following best practices ensures you get optimal network performance across the longer distances.
Use High Quality Ethernet Cables
Don’t cut corners on cable quality. Invest in solid Cat6 or Cat6a cables with sturdy shielding and well-insulated copper conductors. This maintains signal clarity across each extended segment.
Utilize Compatible, High-Performance Connectors
Choose connector types made specifically for your ethernet cable category. For instance, Cat6 cables should always use Cat6 rated RJ45 connectors. Avoid cheap inconsistent connectors that could hamper performance.
Test Extended Ethernet Cable Connections
Once your extended cable is set up, test it to validate speed, low latency, and error-free data transfer. You can use network tools like iPerf to measure metrics and check for anomalies. Verify it provides the performance you expect.
Carefully Label All Cables and Ports
Use cable labeling best practices to identify each extended segment for easier tracing, troubleshooting and system management. Make sure labels on wall jacks match endpoints.
Maintain Proper Bends and Avoid Damage
Always be gentle with ethernet cable handling. Keep bends and kinks gradual and avoid tight twists that could potentially break internal conductors. Protect cables from physical damage.
Separate Ethernet Runs to Avoid Interference
Don’t tightly bundle extended ethernet cabling with other wires. Keep ethernet cables separated from potential sources of electrical interference like AC lines.
Special Considerations When Extending Ethernet Cables Outdoors
Running ethernet cables outside your home or building has additional challenges. The outdoor environment can damage cables, connectors, and reduce signal strength. Follow these tips to make your outdoor ethernet extension successful.
Select Ethernet Cables Rated for Outdoor Use
Look for exterior-rated ethernet cables designed to endure sun, moisture, temperature extremes, and other outdoor hazards. Choose cables marketed as outdoor, direct burial, or UV resistant.
Protect Cable Ends from Environmental Exposure
Use weatherproof RJ45 connectors with sealed ends and uv resistant boot covers to prevent moisture or dirt from getting inside the plugs and corroding contacts.
Run Cables Through Conduit for Extra Protection
For direct burial situations, run your extended ethernet cables through conduit to prevent lawn equipment, animals, or other risks from harming your cabling. Use smooth conduit bends.
Conclusion
While standard ethernet cables max out at around 100 meters, you can easily overcome this limitation by joining cable segments with switches, inline couplers, or media converters. This allows you to extend your wired network to any distance needed.
Carefully choose the extension method that best fits your specific cabling scenario in terms of range, complexity, and budget. Adhering to best practices guarantees your extended ethernet connectivity remains just as fast and reliable as a single short cable.
For extremely long runs or challenging installations, don’t hesitate to enlist the help of a professional network cabling specialist. With the right approach, your extended ethernet cable will serve your home or business reliably for years to come.
- Epson EpiqVision Flex CO-W01 Projector Review - February 21, 2025
- How to Log in to Your Netgear Router - January 17, 2025
- Gaimoo GM200 Mini Projector Review - January 12, 2025