A blinking US/DS light typically means your device is having trouble communicating with your Internet Service Provider’s (ISP’s) network. It is the status for your DOCSIS cable modem or modem/router gateway attempting to lock onto upstream (US) and downstream (DS) channels. If you use a separate Wi‑Fi router, check the modem’s US/DS lights first—most standalone routers do not have US/DS indicators.
While some US/DS blinking during start-up or brief maintenance is normal, if it persists for long periods, you likely have a connectivity problem that requires fixing.
Not to worry—in most cases, you can restore your internet by following a few basic troubleshooting steps. Below is a clear, linear flow you can use to resolve US/DS blinking issues on your own before waiting for a service technician.
Quick Fix for a blinking US/DS light—Unplug the cable modem or gateway from power for at least one minute, finger‑tighten the coax at the modem and wall jack, then plug power back in and wait up to 10 minutes for the US/DS (or Online) light to go solid.
Key Takeaways – US/DS Blinking Light
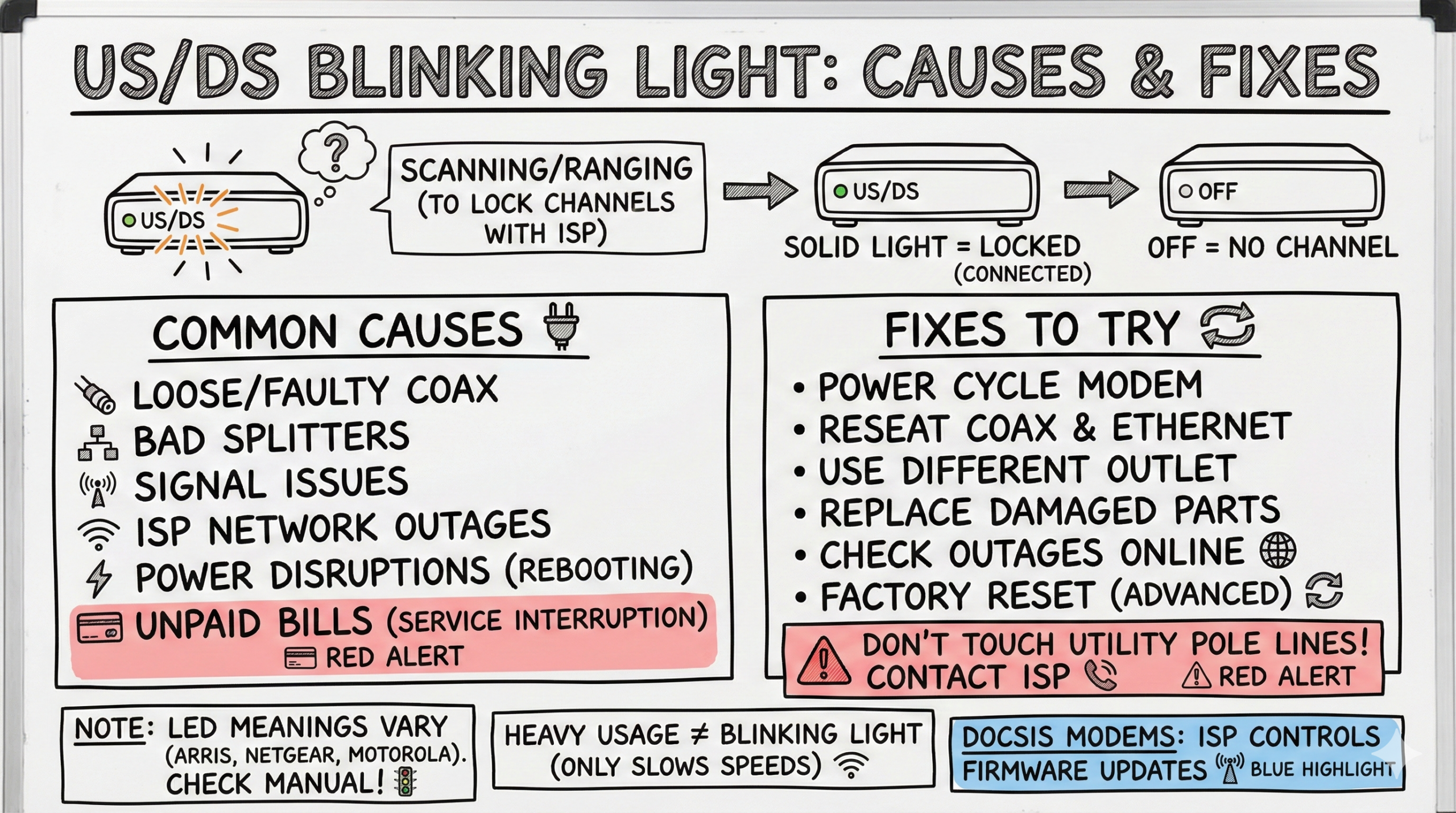
- 💡 Blinking US/DS light indicates your cable modem or gateway is scanning/ranging to lock channels with your ISP; a solid light means locked, and off means no channel.
- 🔌 Common causes include loose or faulty coax, bad splitters, signal issues, and ISP network outages.
- 🔄 Try power cycling the modem, reseating coax and Ethernet, using a different coax outlet, and replacing visibly damaged coax/splitters. Do not work on lines attached to a utility pole—contact your ISP.
- 🌐 Check for ISP outages online or with neighbors to confirm wider service issues.
- 🚦 LED meanings vary by model (Arris, NETGEAR, Motorola, etc.). Always confirm with your device’s manual instead of relying on color alone.
- ⚡ Power disruptions and surges can cause blinking while the modem reboots; a UPS can improve stability.
- 💳 Unpaid internet bills can lead to temporary service interruption by some ISPs.
- 📶 Heavy home usage can slow speeds, but by itself it does not cause US/DS lights to blink—blinking reflects channel lock status.
- 🔄 Factory reset is an advanced step; follow your device manual for the correct hold time and sequence.
- 📞 If problems persist, contact your ISP for diagnostics, signal checks, or equipment replacement.
- 📡 For DOCSIS modems, your ISP controls firmware updates; you can update standalone router firmware yourself.
What Does a Blinking US/DS Light Mean?
A blinking US/DS light means your cable modem or gateway is searching for and negotiating upstream/downstream channels with your ISP (scanning/ranging). A solid US/DS or Online light indicates channels are locked and the link is established, and no light indicates no channel at all.
US/DS stands for “upstream” and “downstream“—the two directions of your internet connection. Upstream sends data from your devices to the internet, while downstream brings data to you.
To better understand these indicators, consider the following scenarios:
| State of US/DS Light | Meaning |
| Flashing Slowly | The US/DS may blink briefly when first powering on as it searches for and connects to your ISP’s network. This is normal. |
| Blinking fast with shorter intervals | Indicates the cable modem or gateway is attempting to sync (ranging/channel lock) with your ISP. |
| Solid Light | A solid US/DS (or Online) light means the modem/gateway has locked channels and established an active connection with your ISP. |
| No Light | No US/DS (or Online) light means the connection with your ISP is inactive or unavailable. |
In short: solid = locked, blinking = negotiating/connecting, and off = no channel. LED colors and labels differ by brand/model (for example, some models use blue to indicate DOCSIS 3.1 operation). Always verify with your device manual.
If you notice long periods of blinking or no US/DS lights, your internet connectivity is impaired. Let’s look at why this happens and how to restore it.
Why Does My US/DS Light Keep Blinking? Common Causes
There are a handful of common culprits for US/DS blinking connectivity problems:
- Internet or ISP network outages
- Loose modem/gateway cables
- Faulty coaxial cables, connectors, or splitters
- Congested home usage (may slow speeds but does not itself cause US/DS blinking)
- Firmware updates (brief blinking during maintenance)
- Power failures or surges
- Unpaid internet bills
- Hardware failure
Let’s break these down in more detail:
1. Internet and Network Outages
Service interruptions are frequent triggers for US/DS blinking. ISPs occasionally go down for large regions due to mass equipment failures, infrastructure damage, or planned maintenance.
- Mass network equipment failures
- Infrastructure damage from natural disasters
- Planned maintenance windows
When this happens, even if your in‑home connections are fine, the break in your ISP link causes US/DS blinking while the modem searches for a connection.
You’ll typically see service updates for widespread outages on your ISP’s website, app, or social media pages.
For smaller neighborhoods, reach out to neighbors to see if they have connectivity before assuming an isolated equipment issue. Outages usually resolve without action beyond waiting.
Here are the outage maps for some popular internet service providers located across the United States:
Alternatively, you can search for ISP outages at https://downdetector.com/
2. Loose Cables
Like any electronic device, modems and gateways rely on secure physical connections to function.
If power cords or data cables like coaxial or Ethernet become slightly loose from vibrations or accidental bumps, it can create enough instability for US/DS lights to blink. Firmly reseat all connectors at the modem/gateway and wall jack.
3. Faulty Cables and Hardware
Aged coax, damaged connectors, or failing splitters can degrade signal and prevent channel lock.
Examine any coaxial runs, connectors, and splitters for:
- Visible cracks, tears, or holes
- Corrosion or rust
- Crimped or severely bent segments
Any defects indicate it’s time to swap in new replacement hardware. Do not attempt to remove or replace the drop line from a utility pole; contact your ISP for that work.
4. Congested Bandwidth and Overloads
Like a crowded highway, your home’s internet can feel slow during heavy use. However, congestion does not cause US/DS lights to blink. Blinking reflects whether the modem has locked channels with the ISP. If you experience slow speeds while US/DS is solid, reduce simultaneous high‑bandwidth activity or consider a plan upgrade.
5. Firmware Updates
Manufacturers and ISPs periodically update firmware. Brief US/DS blinking during these windows is normal. For DOCSIS cable modems, firmware is tested and pushed by your ISP. End users generally cannot manually update modem firmware. You can update firmware on a standalone router.
6. Power Disruptions
Surges, spikes, and outages can force reboots. Afterward, US/DS may blink while systems recalibrate. Consider a UPS if electrical stability is an issue in your area.
7. Unpaid Internet Bills
Some ISPs temporarily block service when accounts fall delinquent, which can appear as nonstop US/DS blinking. Check your account status if blinks coincide with billing cycles.
8. Faulty Hardware
If you’ve eliminated other factors, the modem or gateway may be failing to sync due to hardware issues. Replacement may be required.
Step-By-Step Guide to Fixing Blinking US/DS Lights
Before calling your ISP or replacing equipment, try these steps to resolve a blinking US/DS light yourself:
- Step 1: Check for Outages
- Step 2: Power Cycle the Modem and Router
- Step 3: Check for Outstanding Internet Bills
- Step 4: Replace Faulty Hardware
- Step 5: Factory Reset Your Modem
- Step 6: Reduce Bandwidth Congestion
- Step 7: Update Modem/Router Firmware
- Step 8: Contact Your ISP
Step 1: Check for Outages
Your ISP likely has an outage map or status page on their website or mobile app. Look up your area to see if there are any reported issues. Many times, simply waiting out an outage will restore your connection without other action needed.
Here are the outage maps for some popular internet service providers located across the United States:
You can search for ISP outages at https://downdetector.com/
Alternatively,
- Check social media for customer complaints
- Contact neighbors to confirm an isolated issue
- If there is a major outage, just patiently wait for restoration (it may take hours)
Step 2: Power Cycle the Modem and Router
Rebooting your equipment gives it a fresh start and forces a new channel lock. Unplug the modem and router, wait at least one minute, plug the modem back in first, and wait up to 10 minutes for US/DS (or Online) to turn solid before powering the router. If US/DS keeps blinking past ~10 minutes, proceed to check signal and cabling.
- Unplug the power cable from your modem and router.
- Wait at least one full minute before plugging them back in.
- Make sure your modem boots up fully (about 2-3 extra minutes) before reconnecting your router.
This power cycle flushes out glitches and reestablishes the connection.
Check the US/DS light status. Remember solid = locked, blinking = connecting, and off = no channel. If the US/DS light is still blinking, move on to the next step.
Ensure Coaxial Cables are Tight
Loose cabling is common. Verify all coaxial cable connections at both ends are finger‑tight. Check the connections to your modem/gateway, router, and any wall outlets or splitters.
- Firmly push all connectors into their ports
- Electrical
- Coaxial
- Ethernet
Try Different Coaxial Outlets
Not all outlets in your home necessarily work. Move the modem’s coax to a different jack to see if that resolves the blinking light.
Test internet once US/DS lights solidify.
Step 3: Check for Outstanding Internet Bills
Sometimes, a blinking US/DS light means your ISP has temporarily interrupted service due to late payments. Log into your account and clear any overdue balance.
Step 4: Replace Faulty Hardware
If the above steps do not help, the issue may lie with your coax, splitters, or the modem itself.
Swap Out Damaged Coaxial Cables
Inspect all coaxial cables for kinks, cracks, corrosion, or other damage. Replace any faulty in‑home cables. Do not attempt to replace the cable running from the utility pole; contact your ISP to service or replace the drop.
Replace a Malfunctioning Coaxial Splitter
If your coax feeds both internet and TV, verify the splitter is rated and functioning. Swap it with a known good splitter to restore signal strength.
Purchase a New Modem
If your modem is older or malfunctioning, resets will not solve the problem permanently. Contact your ISP about replacing leased equipment or purchase your own compatible model.
Step 5: Factory Reset Your Modem
If you’d prefer not to replace your modem yet, a factory reset can clear persistent software issues. Follow your device manual for the correct button and hold time (for example, some Arris models require holding Reset until the LEDs flash).
Perform a Factory Reset
Consult your modem manual for the proper reset procedure. In most cases, press and hold the reset button until the LEDs flash, then release. This returns settings to factory default.
Instructions for Popular Providers
For Arris modems, hold the reset button until lights flash in accordance with the model’s manual.
You can reset the Spectrum modem by following the steps in your device guide.
You can reset the Xfinity modem using the manufacturer‑recommended hold time for your model.
You can reset the AT&T router by using the hold time specified in the device manual.
Power Cycle Before and After
Power cycle your modem before and after a factory reset to clear residual issues. Allow several minutes for the reset to fully complete and for US/DS (or Online) to go solid.
Step 6: Reduce Bandwidth Congestion
If Steps 1–3 fail, ease bandwidth loads to improve overall performance (this will not change US/DS lock status but can improve stability once connected).
- Pause/disconnect non‑critical devices
- Temporarily use cellular data on devices that can
- Stop large uploads/downloads
- Stagger data‑heavy gaming, video, or VPN sessions
This helps determine if oversubscription plays a role in perceived slowdowns after the modem locks channels.
Step 7: Update Modem/Router Firmware
For DOCSIS cable modems, firmware is pushed by your ISP; you cannot usually update it manually. You can update your standalone router’s firmware via its admin page. Avoid interrupting power during any update. As DOCSIS 3.1 (and newer upstream technologies like OFDMA) roll out, some models display different blue/green LED behavior when higher‑tier channels are active.
Set a calendar reminder to review router firmware every 2–3 months.
Step 8: Contact Your ISP
If you still see a blinking US/DS light after trying the steps above, contact your ISP. Ask them to check signal levels, provision your modem, and investigate any plant issues. Provide details such as how long US/DS has been blinking and whether it ever turns solid.
Request Technical Support
Your ISP can run remote diagnostics, check channel bonding, and detect problems on their network causing your connectivity issues.
Ask for a Technician Visit
For cabling problems or defective leased equipment, your ISP can send a technician to inspect everything on‑site and make needed repairs.
Inquire About Modem Replacement
If your modem is provided by your ISP and is confirmed to be faulty, ask about getting it replaced. Leased modems with issues can often be swapped at no cost.
Preventing Future Blinking US/DS Lights
While any modem can incur glitches causing a blinking US/DS light, you can take proactive measures to avoid connectivity headaches:
- Avoid overloads: Stagger bandwidth usage across devices
- Update router firmware routinely: Check quarterly
- Use UPS battery backup: Protect against power blips
- Keep hardware current: Replace aging modems/routers
- Isolate supply lines: Use outlets independent of major appliances
- Maintain connections: Periodically reseat connectors
- Consider mesh systems: Improve Wi‑Fi coverage separate from the modem
- Handle modems and cables gently to prevent physical damage.
- Keep your router firmware updated; modem firmware is ISP‑managed.
- Pay internet bills on time to avoid service suspensions.
- Consider purchasing your own compatible modem for greater control.
Investing a little time up front significantly reduces headaches down the road!
Conclusion
Hopefully this guide has equipped you to handle a blinking US/DS light with confidence. Work through the steps in order, keep an eye on whether US/DS turns solid within ~10 minutes after a reboot, and lean on your ISP for signal checks or equipment swaps when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long should US/DS lights blink on new modem connection?
On a fresh boot or installation, US/DS blinking for 5–10 minutes is typical while the modem locks channels. Longer than that suggests a signal or provisioning issue.
Does US/DS blinking mean no internet connection?
Not necessarily. Blinking means the modem is trying to lock channels (scanning/ranging). Once US/DS or Online is solid, the link is established. If it never goes solid, you may have a signal or account problem.
Why does my US/DS light stay orange or blue?
LED colors vary by model. Some NETGEAR modems show amber when a single channel is locked and green for multiple; many Arris/Motorola models use blue to indicate DOCSIS 3.1 operation. Always check your device manual for exact meanings.
What causes the modem or gateway US/DS light to turn red?
Meanings differ by brand. On some devices, red can indicate a fault or overheating on a power/attention LED, not specifically US/DS. Verify the legend in your device manual before replacing hardware.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025