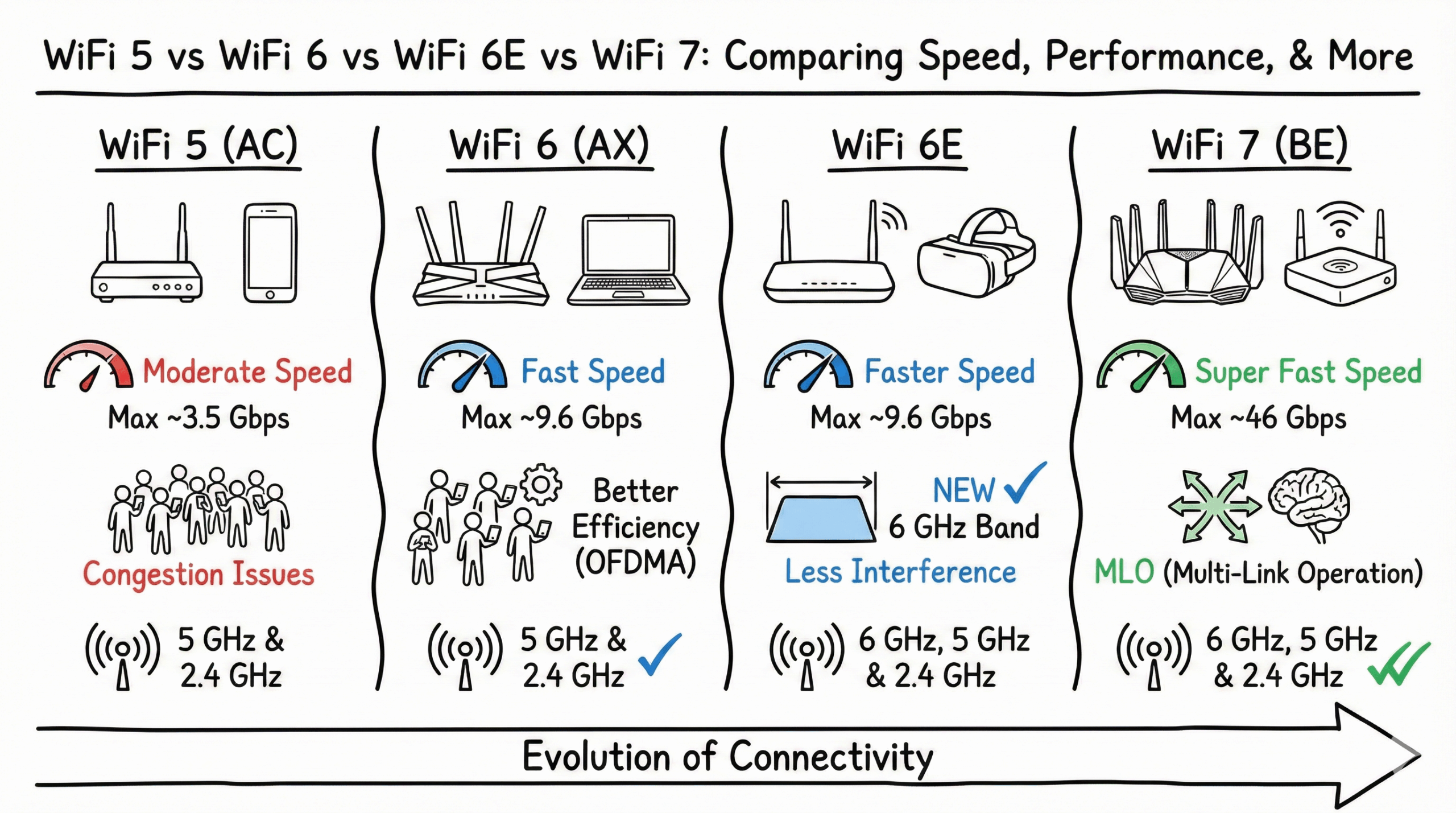
When comparing WiFi 5 vs WiFi 6 vs WiFi 6E vs WiFi 7, it’s crucial to understand the advancements in speed, range, and capacity that each generation offers. WiFi 6 introduced faster throughput and improved handling of multiple devices, while WiFi 6E expanded on these capabilities by unlocking the 6 GHz band. Now, WiFi 7 is taking performance to an entirely new level.
In the following sections, we’ll delve into how these technologies meet the demands of modern wireless networking and which scenarios each is best suited for, helping you make an informed decision for your next upgrade.
Key Takeaways: WiFi 5 vs. WiFi 6 vs. WiFi 6E vs. WiFi 7
- WiFi 5 (802.11ac) is a solid, budget-friendly option for basic internet use, offering decent speeds on the 5 GHz band but struggling in crowded network environments.
- WiFi 6 (802.11ax) is the current mainstream standard, providing a significant boost in efficiency and capacity for homes with many connected devices, thanks to technologies like OFDMA.
- WiFi 6E adds the exclusive 6 GHz band, a “superhighway” for compatible devices that dramatically reduces congestion and lowers latency, but its shorter range requires careful placement.
- WiFi 7 (802.11be) is the new frontier, offering unprecedented speeds and reliability with features like Multi-Link Operation (MLO). It’s built for next-generation applications like 8K streaming, AR/VR, and cloud gaming.
- Your choice depends on your budget, current devices, and internet needs. Upgrading your router won’t help if your devices and internet plan don’t support the new speeds.
WiFi Generations Comparison Table
| Specs | WiFi 5 | WiFi 6 | WiFi 6E | WiFi 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Released | 2014 | 2019 | 2020 | 2025 (Finalized) |
| Standard | 802.11ac | 802.11ax | 802.11ax | 802.11be |
| Frequency Bands | 5 GHz only | 2.4 GHz + 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz + 5 GHz + 6 GHz | 2.4 GHz + 5 GHz + 6 GHz |
| Max Speed (Theoretical) | 3.5 Gbps | 9.6 Gbps | 9.6 Gbps | Up to 46 Gbps |
| Max Speed (Real World) | Up to 1 Gbps | Typical 600 Mbps-1.2 Gbps per device | Typical 1.5-1.8 Gbps at 15 ft; up to 2.5 Gbps at close range | Typical 5-10 Gbps at close range |
| Range (Indoor) | Up to 150 feet | Up to 150 feet | Up to 150 feet (6 GHz band has reduced range) | Similar to 6E; MLO can improve connection stability at range |
| Key Features | MU-MIMO, 256-QAM | OFDMA, TWT, 1024-QAM | All WiFi 6 features + 6 GHz band | Multi-Link Operation (MLO), 320 MHz channels, 4096-QAM |
| Network Capacity | Good for dozens of devices | Up to 4x capacity over WiFi 5 | Increased capacity over WiFi 6 on 6 GHz | Significantly increased capacity and efficiency |
| Ideal Use Cases | 4K streaming, online gaming, small smart homes | Dense smart homes, 4K/8K streaming, AR/VR | High-density environments, competitive gaming, AR/VR | 8K+ streaming, cloud gaming, industrial IoT, immersive experiences |
Please note that real-world speeds and ranges can vary based on your internet plan, router, client devices, physical obstructions like walls, and interference from other electronics. The theoretical maximum speeds are lab-tested figures and are not typically achievable in a real home environment.
Deep Dive into WiFi Generations
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac): The Long-Standing Standard
Introduced in 2014, WiFi 5 (802.11ac) was a significant upgrade, moving primary traffic to the less-crowded 5 GHz frequency band. This provided two key advantages:
- Higher Bandwidth: The 5 GHz band offered more non-overlapping channels, allowing for higher throughput.
- Less Interference: It avoided the congestion from microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices that plague the 2.4 GHz band.
WiFi 5 has a theoretical maximum data rate of 3.5 Gbps, but real-world speeds typically top out around 400-800 Mbps for a single device. While still very capable for 4K streaming and online gaming, its performance can degrade in homes with dozens of connected devices all competing for bandwidth.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): Efficiency for the Modern Home
Released in 2019, WiFi 6 (802.11ax) has become the mainstream standard in new devices by 2024-2025. Its primary goal wasn’t just about boosting top speed for a single device but dramatically improving the network’s overall efficiency, especially in congested environments. Real-world speeds for a single device typically range from 600 Mbps to 1.2 Gbps.
Key enhancements that make this possible include:
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access): This is the star of the show. It allows a single transmission to deliver data to multiple devices simultaneously, like a delivery truck making multiple stops in one trip. This drastically reduces latency and improves capacity.
- TWT (Target Wake Time): Improves battery life for mobile and IoT devices by allowing the router to schedule when they wake up to send or receive data.
- 1024-QAM: Encodes more data into each signal, providing up to a 25% speed boost compared to WiFi 5’s 256-QAM.
These features make WiFi 6 perfect for the modern smart home, where laptops, phones, TVs, security cameras, and smart speakers are all fighting for a slice of the network.
WiFi 6E: The Exclusive Superhighway
WiFi 6E uses the same 802.11ax standard as WiFi 6 but adds one game-changing feature: access to the 6 GHz frequency band. Think of the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands as busy city streets. The 6 GHz band is a brand-new, multi-lane superhighway with no legacy traffic to slow it down.
The advantages are clear:
- Massive Bandwidth: The 6 GHz band adds up to seven additional 160 MHz channels for blazing-fast connections.
- Zero Interference: Only WiFi 6E or newer devices can use this band, meaning no competition from your neighbor’s old router or your microwave oven.
- Lower Latency: Due to the reduced congestion, WiFi 6E can lower latency by 5-10ms compared to a busy 5 GHz network, which is a noticeable improvement for competitive gaming and real-time video calls.
The 6 GHz Trade-Off: Speed vs. Range
However, there’s a crucial trade-off. Higher frequencies have more difficulty penetrating solid objects like walls and floors. As a result, the 6 GHz band has a shorter effective range than the 5 GHz band. For the best performance, WiFi 6E devices need to be closer to the router with fewer obstacles in between. In a large home with many walls, a WiFi 6 mesh system on the 5 GHz band might provide more consistent coverage than a single WiFi 6E router.
Below are some of my favorite WiFi 6E Routers.





If you’re curious about the practical implications of internet speeds, the below posts will provide a comprehensive analysis.
- Is 10 Mbps fast Enough?
- The Ultimate Guide to 200 Mbps Internet Speed: Is 200 Mbps Fast Enough
- Is 500 Mbps Fast? Exploring Internet Speeds and Performance in 2023
- Is 600 Mbps Fast Internet Speed?
- Is 1000 Mbps Fast Internet? (The Gold Standard of Internet Speeds)
WiFi 7 (802.11be): The Next Generation is Here
The future is now. Officially finalized on July 22, 2025, WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) represents another quantum leap in wireless technology. While building on the foundation of WiFi 6E by using the 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz bands, it introduces groundbreaking features aimed at delivering extreme speeds and rock-solid reliability.
Here are the key innovations of WiFi 7:
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): This is the headline feature. MLO allows a single device to connect to the router using multiple frequency bands (e.g., 5 GHz and 6 GHz) simultaneously. This increases throughput, reduces latency, and dramatically improves reliability by instantly switching bands if one encounters interference.
- 320 MHz Channels: WiFi 7 doubles the maximum channel width in the 6 GHz band to 320 MHz, effectively doubling the potential top speed compared to WiFi 6E.
- 4096-QAM: An even more sophisticated data modulation scheme that packs 20% more data into each transmission than WiFi 6’s 1024-QAM.
With theoretical speeds up to 46 Gbps and real-world performance expected to hit 5-10 Gbps, WiFi 7 is designed for a future of multi-gigabit internet plans, flawless 8K and 16K video streaming, and truly immersive AR/VR experiences.
Which WiFi Standard Is Right for You?
Choosing the right standard comes down to your specific needs, budget, and existing devices. Here’s a simple decision framework:
- Choose WiFi 5 if: You’re on a tight budget, have a smaller home, and your internet usage is mostly web browsing, social media, and streaming HD or 4K video on a few devices.
- Choose WiFi 6 if: You have a gigabit internet plan and a modern smart home with 25+ devices (phones, laptops, smart speakers, cameras, etc.). It’s the best balance of price and performance for most households today.
- Choose WiFi 6E if: You’re a competitive gamer, a tech enthusiast with the latest devices, or live in a very congested area (like an apartment building). You need the lowest possible latency and have compatible devices to take advantage of the 6 GHz band.
- Choose WiFi 7 if: You are an early adopter who demands the absolute best performance, have a multi-gigabit internet plan (2 Gbps or higher), and are investing in a network to last for the next 5+ years. It’s overkill for most right now but provides the ultimate future-proofing.
Device Compatibility and Upgrading Considerations
A new router is only half the equation. To get the full benefits of a new WiFi standard, your client devices (laptops, phones, etc.) must also support it. The good news is that all new WiFi standards are backward compatible, so your old devices will still connect, just not at the new speeds.
- WiFi 6 Support: Nearly universal in smartphones, laptops, and other connected devices sold since 2021. This includes devices like the iPhone 11 and later, the Samsung Galaxy S20 series and later, and most modern laptops.
- WiFi 6E Support: Now standard on most flagship devices released from 2023 onward. This includes the iPhone 15 Pro, Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra, Google Pixel 8 Pro, and many high-end Windows laptops.
- WiFi 7 Support: Still emerging. The first wave of WiFi 7-enabled phones and laptops was announced at CES 2025, with availability ramping up throughout the year. For now, it’s limited to the highest-end, latest-release devices.
Before you invest in a new router, check the specifications of your most-used devices to see which standard they support. Upgrading to a WiFi 7 router when your main laptop only supports WiFi 6 will provide some benefit, but you won’t unlock its full potential.
Check out WiFi Mesh vs Extender vs Booster vs Repeater article to find out which wifi device is best for your home.
What is WiFi, Anyway?
Before we conclude, let’s briefly touch on the basics. What is WiFi and how does it enable our wireless world?
WiFi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless high-speed internet and network connections. A router connects to your internet service provider and then broadcasts a wireless signal that compatible devices—like laptops, smartphones, and smart TVs—can connect to.
Each new generation of WiFi, defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), uses new techniques to make that radio signal faster, more efficient, and more reliable.
What Does the Future Hold Beyond WiFi 7?
With WiFi 7 now on the market, the industry is already looking toward the horizon. In the longer term, standardization efforts for 6G cellular technology are underway, with expected timelines in the 2030s. Future wireless standards will likely continue to blur the lines between cellular and WiFi, aiming for a single, seamless, and intelligent connectivity fabric that powers everything from our homes to entire smart cities.
Conclusion
Choosing the right WiFi standard is about finding the sweet spot between performance, price, and practicality. As of late 2025, WiFi 6 offers the best value for most people, while WiFi 6E is a worthy upgrade for gamers and those in congested areas. WiFi 7 is the ultimate in performance and future-proofing, but its benefits are currently reserved for those with the fastest internet plans and the very latest devices.
By understanding the differences between WiFi generations and matching the technology to your real-world requirements, you can build a wireless experience that is both powerful and cost-effective. As networking standards rapidly evolve, remember to periodically review your setup to stay on the cutting edge in our increasingly connected world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do I really need Wi-Fi 6?
For most households with multiple connected devices, WiFi 6 is a worthwhile upgrade. It’s not just about speed; its ability to handle many connections at once without slowing down makes a noticeable difference in modern smart homes. If you only have a few devices and a sub-gigabit internet plan, WiFi 5 is likely still sufficient.
Does WiFi 6 penetrate walls better than WiFi 5?
Wifi 6 vs wifi 5 wall penetration – Wi-Fi 6 offers slightly better range and performance at the edge of its coverage area than Wi-Fi 5 due to technical efficiencies like OFDMA. However, the difference in wall penetration is minor. Router placement and home construction materials have a much larger impact on signal strength through walls.
What is the difference between WiFi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E speed?
While both have the same theoretical top speed of 9.6 Gbps, WiFi 6E can deliver faster real-world speeds because its 6 GHz band is free from congestion. In ideal, close-range conditions, a WiFi 6E device might achieve 1.5-2.5 Gbps, whereas a WiFi 6 device on a crowded 5 GHz network might get 600-900 Mbps.
Should I upgrade to WiFi 7 now?
As of late 2025, upgrading to WiFi 7 is only recommended for enthusiasts, tech professionals, or users with multi-gigabit internet plans (2 Gbps+) who own compatible devices. For most users, the high cost of routers and limited device availability make WiFi 6 or WiFi 6E a more practical choice for now.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025