Arris Modem Lights are indicators that help you understand the status of your cable connection and, on gateway models, your Wi‑Fi radios. This guide explains what the colors and blinking patterns mean by function and model family, so you can pinpoint issues quickly and keep your connection stable.
Common Indicator Lights On Arris Modems
Most Arris SURFboard cable modems and gateways use similar front‑panel LEDs. Exact colors can vary by model (for example, SB8200 vs. S33 vs. SBG8300), but the functions are consistent:
- Power/Status – Indicates the device is on and status during boot/updates. On S33 this is a single multi‑color LED ring.
- Downstream (Receive/DS) – Cable signal from your ISP. Flashing = scanning; solid = locked channels (green often DOCSIS 3.0, blue indicates higher‑speed lock such as DOCSIS 3.1 or bonded DOCSIS 3.0, depending on model).
- Upstream (Send/US) – Cable signal to your ISP. Flashing = scanning; solid = locked channels (green typically DOCSIS 3.0; blue may indicate DOCSIS 3.1/OFDMA or bonded DOCSIS 3.0 if supported in your area).
- Online – Shows internet registration with the ISP. Solid = online; flashing = ranging/registration in progress. Some models use green for DOCSIS 3.0 and blue for DOCSIS 3.1.
- Wi‑Fi – (Gateways only, e.g., SBG10/SBG8300) Radio status and activity: solid = radio enabled; blinking = wireless traffic.
- Telephone/Voice – (Telephony models only) Landline service status.
Some models also include additional indicators:
- Link – Ethernet link/activity on the rear LAN port(s): green often = 1 Gbps, amber = 10/100; blinking = traffic.
- Broadband/WAN – Used on certain gateways; not present on modem‑only units.
- 2.4 GHz / 5 GHz – (Gateways) Band‑specific radio indicators: solid = band enabled; blinking = client activity.
- Ethernet – Wired port status (link speed/activity) on gateways.
Understanding these functions is the first step. See also: Technicolor Modem Lights
Meaning of Key Indicator Lights
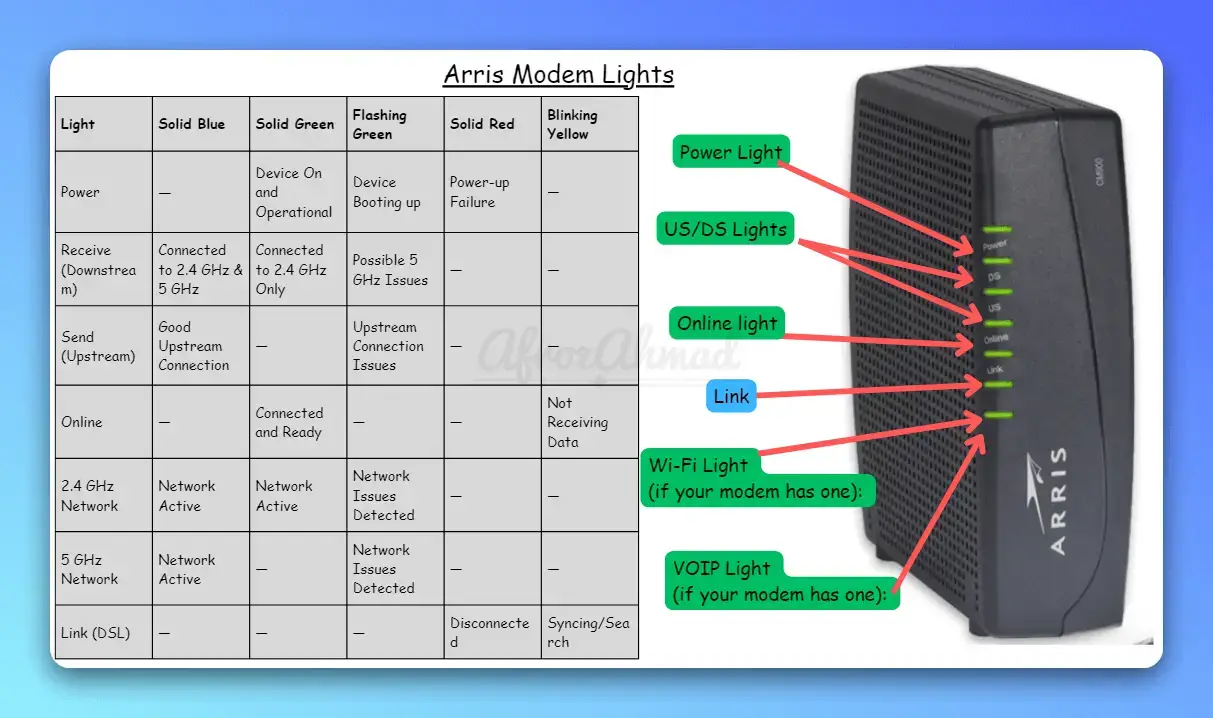
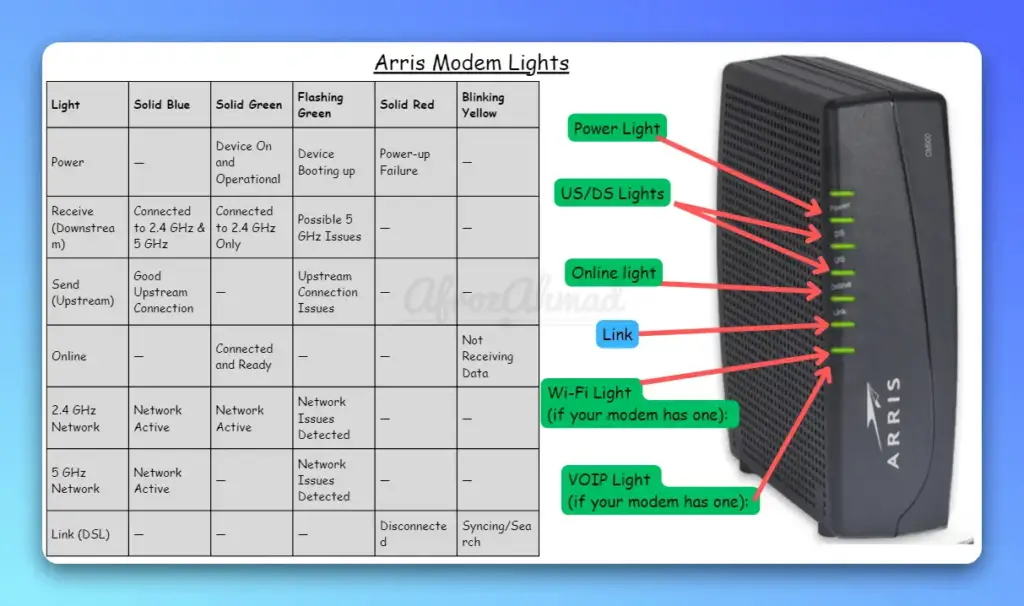
| Light | Solid Blue | Solid Green | Flashing Green | Solid Red | Blinking Yellow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power | DOCSIS 3.1 online on some models (e.g., S33 ring or SBG8300) | Powered on; often DOCSIS 3.0 online | Booting or scanning (color may vary by model) | Not commonly used for power on many SURFboard units | Firmware download or status activity (model‑dependent) |
| Receive (Downstream) | High‑speed lock (DOCSIS 3.1 on SB8200/S33 or bonded 3.0 on SB6183/SB6190) | Channels locked (typically DOCSIS 3.0) | Scanning for downstream channels | — | — |
| Send (Upstream) | High‑speed lock (DOCSIS 3.1/OFDMA where available, or bonded 3.0) | Channels locked (typically DOCSIS 3.0) | Scanning for upstream channels | — | — |
| Online | Online in DOCSIS 3.1 mode (model‑dependent) | Online in DOCSIS 3.0 mode | Ranging/registration in progress | — | — |
| 2.4 GHz Network | Radio enabled (gateways) | Radio enabled (gateways) | Wireless activity (not a fault) | — | — |
| 5 GHz Network | Radio enabled (gateways) | Radio enabled (gateways) | Wireless activity (not a fault) | — | — |
| Link (Ethernet) | — | 1 Gbps link present; blinking = traffic | 10/100/Activity (varies); blinking = traffic | — | — |
Now, let’s explore specific indicators and model‑aware nuances:
Power Light
This light denotes power and, on some models, overall status. Behavior varies by device:
- Multi‑LED models (SB6183/SB6190/SB8200) – Solid green = powered/online; flashing during boot; blue may be used on other LEDs rather than power.
- S33 single LED ring – Amber flashing = firmware download; green blinking = scanning; green solid = online DOCSIS 3.0; blue solid = online DOCSIS 3.1; alternating blue/green = status/error pattern.
- Gateways (SBG10/SBG8300) – Power LED is solid when on; firmware downloads may show distinct blink/alternate patterns.
If this light is off or stuck in a boot pattern, check the power adapter, outlet, and surge protector. A persistent abnormal pattern after a power cycle can indicate a hardware fault or failed firmware update—contact your ISP.
Downstream Light
Also labeled “Receive” or “DS”—this is your modem’s connection from the ISP.
- Flashing (color varies) – Scanning for downstream channels; not yet locked.
- Solid Green – Channels locked (typically DOCSIS 3.0).
- Solid Blue – High‑speed lock. On SB8200/S33 this indicates DOCSIS 3.1; on older models (SB6183/SB6190) it indicates bonded DOCSIS 3.0 channels.
Green instead of blue on DOCSIS 3.1‑capable devices can simply mean your ISP hasn’t enabled DOCSIS 3.1 downstream on your node yet.
Upstream Light
Also labeled “Send” or “US”—this is your modem’s connection to the ISP.
- Flashing (color varies) – Scanning for upstream channels; not yet locked.
- Solid Green – Upstream locked (DOCSIS 3.0).
- Solid Blue – DOCSIS 3.1/OFDMA upstream where available or bonded DOCSIS 3.0. Not all ISPs/markets have upstream DOCSIS 3.1 enabled.
If this light won’t go solid after a power cycle, check cabling and contact your ISP to verify upstream power levels and provisioning.
Online Light
This indicates internet registration status.
- Solid Green – Online (often DOCSIS 3.0 on models like SBG8300).
- Solid Blue – Online with DOCSIS 3.1.
- Flashing – Ranging/registration; if it doesn’t turn solid, there may be an ISP provisioning or signal issue.
If problems persist, you won’t have internet access until the modem completes registration—verify signal and account provisioning with your ISP.
WiFi Light
On gateways (e.g., SBG10/SBG8300), these LEDs show radio state and activity.
- Solid – Radio enabled.
- Blinking – Normal wireless traffic/activity (not necessarily an issue).
- Off – Radio disabled.
If devices can’t connect over Wi‑Fi but the online LED is solid, focus on Wi‑Fi settings and client device configuration.
Troubleshooting Arris Modem Based on Indicator Lights
Use the LED states to troubleshoot methodically. Note that cable‑modem firmware and channel bonding are controlled by your ISP; you cannot manually force firmware updates or “reset channels.”
Here is a step-by-step troubleshooting guide to resolve common Arris modem issues based on the indicator light status:
Power Light Not Lit
If your modem has no lights at all, the first step is checking the power supply. Try the following:
- Reconnect the power adaptor firmly into the wall socket and modem power port.
- Use a different wall socket or bypass the power strip.
- Test the socket with another appliance to verify it’s working.
- If the modem still doesn’t power on, the adaptor/modem hardware may be defective—contact your ISP or the manufacturer.
Downstream Light Struggling
A flashing downstream light means the modem is scanning; a solid green/blue indicates a lock. To improve signal quality:
- Ensure the coaxial cable is finger‑tight at both the wall and the modem.
- Connect the modem directly to the wall jack (avoid splitters if possible).
- Reboot the modem; then check the Status/Signal page for downstream power and SNR. If levels are out of spec, contact your ISP.
- If the light never stabilizes, request a technician to inspect outside lines and connectors.
Upstream Light Blinking Continuously
A constantly flashing upstream light indicates the modem can’t lock upstream channels:
- Check coax fittings and remove unnecessary splitters or attenuators.
- Power cycle the modem and review upstream power levels on the Status page.
- If levels are too high/low or provisioning failed, contact your ISP; firmware/channel profiles are ISP‑managed.
- Persistent failure after line fixes may indicate hardware replacement is needed.
Online Light Not Solid Green
If your online light keeps blinking, the modem is attempting registration. Try the following:
- Power cycle the modem and connected devices (router, computer, etc.).
- Confirm your devices receive valid IP addresses once the modem shows solid online.
- Log into the modem’s admin interface to view WAN status; if provisioning failed, contact your ISP to activate the modem.
- Ask your ISP to verify signal levels and account configuration.
No WiFi Connectivity
If you’re using a gateway (SBG series) and can’t connect wirelessly, first check that the 2.4 GHz/5 GHz lights are solid (radios on). If radios are off or there’s no traffic:
- Reboot the gateway to re‑enable radios and clear temporary faults.
- Verify Wi‑Fi settings like SSID and password (match the device label if unchanged).
- Update client device Wi‑Fi drivers and test multiple devices to isolate client issues.
- If configuration is corrupted, perform a factory reset and reconfigure Wi‑Fi.
For persistent Wi‑Fi issues with a solid online LED, your ISP can confirm signal to the gateway; hardware replacement may be appropriate if radios fail.
Helpful Troubleshooting Tips
Beyond LED checks, apply these basics:
- Inspect all cable connections: Loose coaxial, Ethernet, or power cables can cause intermittent connectivity. Verify fittings are snug.
- Eliminate signal splitters if possible: Multiple devices on the same splitter can degrade signal quality. Connect the modem directly to the outlet if feasible.
- Power cycle equipment: Power off and back on the modem, router, and connected devices for a fresh signal lock.
- Check for ISP network outages: Confirm with your provider if there are service alerts for your area before deep troubleshooting.
- Firmware handling: Cable‑modem firmware is controlled and pushed by your ISP; users cannot manually update.
- Reset the modem: A factory reset clears custom settings and may resolve configuration issues. You’ll need to reconfigure Wi‑Fi on gateways.
- Request replacement hardware: If all else fails, older or faulty units may need replacement.
Interpreting LEDs alongside signal levels in the admin interface is the fastest way to separate in‑home issues from ISP signal or provisioning problems.
Why Proper Connections & Maintenance Are Vital
Good cabling and placement prevent many stability issues. Follow these tips:
✔️ Use the manufacturer‑approved power adapter to avoid electrical damage.
✔️ Position the modem/gateway away from large electrical appliances and thick obstructions.
✔️ Allow ISP‑pushed firmware updates to complete uninterrupted.
✔️ Check indicator lights periodically to spot early warnings.
✔️ Contact ISP support for recurring errors, especially when LEDs won’t lock or the online light keeps blinking.
A correctly functioning modem ensures reliable internet for work and entertainment. Use the LEDs as your quick diagnostic dashboard, and loop in your ISP when signal or provisioning needs attention.
Conclusion: Monitor Lights for Fast Diagnosis
Reading your Arris LEDs accurately—especially blue vs. green on SB8200/S33/SBG8300—lets you distinguish DOCSIS 3.0 from 3.1 operation, confirm when the modem is simply scanning, and identify when to call your ISP. Use the troubleshooting steps above to resolve most issues quickly.
If your upstream never locks, the online light stays blinking, or the S33 ring shows alternating status for long periods, collect screenshots of the Status/Signal page and contact your ISP for signal and provisioning checks.
FAQ
What do the lights on my Arris modem indicate?
Answer: Power/Status shows boot and update state; Downstream/Upstream show cable channel lock; Online shows ISP registration; Wi‑Fi LEDs (gateways) show radio state/activity; Link shows Ethernet speed/activity.
What should I do if my Arris modem’s power light is off or red?
Answer: If off, verify the outlet, adapter, and power strip; many SURFboard models don’t use a red power LED. If abnormal patterns persist after a reboot, contact your ISP or Arris support.
What does a flashing green light on the Arris modem’s receive or send light signify?
Answer: It’s scanning for channels (not a Wi‑Fi band indicator). Solid green usually means DOCSIS 3.0 lock; solid blue can indicate DOCSIS 3.1 (SB8200/S33) or bonded DOCSIS 3.0, depending on the model.
My Arris modem’s online light is blinking. What does this mean?
Answer: Registration is in progress. If it never turns solid, there may be a provisioning or signal issue—reboot and then contact your ISP to activate/verify the modem.
Can the color of the lights on my Arris modem indicate a problem?
Answer: Yes. Blue vs. green often indicates DOCSIS 3.1 vs. 3.0 on SB8200/S33/SBG8300. Continuous flashing on Downstream/Upstream suggests no channel lock; investigate cabling and signal levels.
What steps can I take to troubleshoot a Wi‑Fi connectivity issue on my Arris modem?
Answer: On gateways, solid 2.4/5 GHz LEDs mean radios are enabled; blinking means traffic. Reboot, verify SSID/password, update client drivers, and factory reset if needed.
How do I check my Arris modem’s firmware is up-to-date?
Answer: Cable‑modem firmware is ISP‑managed and delivered automatically. You can view the current version in the admin interface; contact your ISP for update status.
Can I fix my Arris modem’s connectivity issues without calling tech support?
Answer: Often yes: reseat coax and power, remove splitters, reboot, and check the Status/Signal page. Call your ISP if levels are out of spec or provisioning fails.
What kind of problems can a solid red light on the Arris modem indicate?
Answer: Few SURFboard models use solid red for power; a red/amber error LED (where present) can indicate a fault. If you see a persistent error color, power cycle and contact your ISP.
Why are the receive and send lights on my modem different colors?
Answer: Color reflects the DOCSIS mode, not Wi‑Fi bands. On SB8200/S33, green generally = DOCSIS 3.0 and blue = DOCSIS 3.1; upstream blue may appear only where DOCSIS 3.1/OFDMA is enabled by your ISP.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025