Spectrum WiFi pause is a feature that allows network administrators, such as parents or employers, to temporarily disable internet access for specific devices on the network. In most cases this is enforced at the router by identifying a device’s hardware (MAC) address.
While these restrictions are often put in place for valid reasons—such as promoting healthier internet habits or maintaining network security—there are times when a user might seek to bypass these limitations. Before diving into potential methods to do so, it’s important to emphasize that bypassing network controls without permission is generally not advisable and may violate the terms of service (ToS) of your internet provider. It can also undermine the trust between users and network administrators.
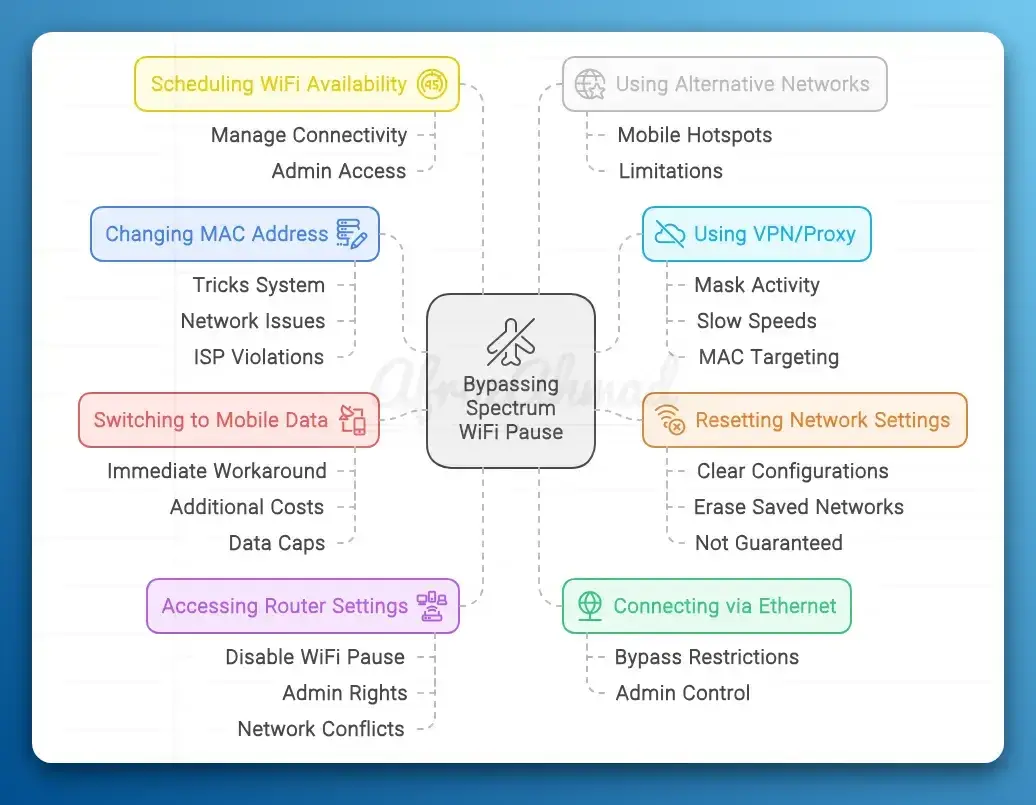
That said, here are some common methods for bypassing Spectrum WiFi pause and their associated risks. For clarity: a device that has been paused at the router level cannot regain connectivity with a VPN or proxy; those tools only affect content filtering, not device blocking.
Key Takeaways
- 🚫 If your device is paused at the router, a VPN or proxy will not restore connectivity. VPNs affect content/DNS filtering, not MAC-level blocks.
- 🔐 Apple iOS 18/macOS 15 support Private Wi‑Fi Address modes: Off, Fixed, or Rotating. Fixed is default on secured networks; Rotating is typical on weak/open networks and changes about every two weeks.
- 🤖 Android 10+ uses MAC randomization by default with a persistent per‑network address; forgetting and re‑joining usually keeps the same randomized MAC.
- 🪟 Windows 10/11 offer Random hardware addresses (global/per‑network), which can change how your device appears to the router.
- 🌐 Spectrum Advanced WiFi is primarily managed in the My Spectrum app. Many Spectrum‑issued routers limit local web admin access.
- 🔌 Ethernet may or may not be affected by a pause depending on your router/model and how the device is identified—don’t assume it will bypass controls.
1. Changing Your Device’s MAC Address
MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to each network interface on a device. Spectrum’s WiFi pause feature commonly works by blocking the MAC address of the targeted device. Some users suggest that changing or “spoofing” the MAC address can allow the device to reconnect to the network. Whether that works depends on your OS and privacy settings.
How it works:
- By altering your device’s MAC address, you can make the router treat it as a new device, potentially bypassing a pause that targets the old address.
OS-specific notes:
- iOS 18 / macOS 15: Each Wi‑Fi network can use Private Wi‑Fi Address set to Off, Fixed, or Rotating. Fixed is typically used on secured networks; Rotating is more common on weak/no‑security networks and changes roughly every two weeks. Resetting network settings or forgetting and rejoining can result in a new private address for that SSID.
- Android 10+: MAC randomization is on by default and persistent per saved network. Forgetting and re‑adding usually reuses the same randomized MAC. On some open networks (Android 12+), non‑persistent randomization may apply.
- Windows 10/11: Random hardware addresses can be enabled globally or per network (Settings > Network & Internet > Wi‑Fi). Toggling this can cause your device to appear as a new MAC to the router.
Steps:
- Check your device’s Wi‑Fi privacy/MAC settings (Private/Randomized/Random hardware addresses) for the specific network.
- If you have permission, adjust the setting (for example, switch from Fixed to a new Fixed/Rotating address, or toggle Random hardware addresses) and reconnect.
Risks:
- This method is not guaranteed and may conflict with network policies or ToS.
- Frequent address changes can trigger device blocks or create DHCP conflicts.
2. Using a VPN or Proxy Server
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) or proxy server can route your internet traffic through a different server, masking browsing activity from local observers and sometimes bypassing content or DNS filters. However, it cannot unpause a device that the router has blocked by MAC address.
How it works:
- By encrypting your traffic and hiding your IP address from the local network, a VPN can help with content restrictions—but it does not defeat a router‑level pause on your device.
Steps:
- Install a reputable VPN service on your device.
- Use it only for permitted purposes; it will not restore access if your device is paused at the router.
Risks:
- VPNs may reduce speed and, if misused, can violate policy. They do not bypass MAC‑based pauses.
When evaluating a VPN, focus on transparent privacy policies, independent audits, and performance—avoid assuming it can bypass device pauses.
3. Connecting via Ethernet
If your device has an Ethernet port, you might consider connecting directly to the router using an Ethernet cable. Whether this bypasses a pause depends on how your router enforces the control and how the device is identified.
How it works:
- Some implementations describe pausing Wi‑Fi specifically, but impact on wired connections varies by router/model and settings. Do not assume Ethernet will be unaffected.
Steps:
- Locate the Ethernet port on your device and the router.
- Connect your device to the router using an Ethernet cable.
Risks:
- Only viable for devices with Ethernet; administrators may still control or monitor wired access.
4. Resetting Network Settings
Another approach some users take is resetting the network settings on their device. This can sometimes change how the device identifies on Wi‑Fi, but it is not guaranteed to bypass a pause.
How it works:
- Resetting restores default network configurations. On Apple devices, rejoining a network after a reset or forget may generate a new Private Wi‑Fi Address. On Android, the randomized address is typically persistent per network and may remain the same after re‑joining.
Steps:
- Go to the settings menu on your device.
- Find the option to reset network settings (this may differ by device type), then reconnect to Wi‑Fi.
Risks:
- This can erase saved Wi‑Fi networks, passwords, and VPN settings and still may not bypass an intentional pause.
See also: How to Reset Spectrum Router
5. Switching to Mobile Data
When WiFi access is paused, using mobile data is a straightforward alternative to stay connected, provided it is permitted for your use case.
How it works:
- Mobile data uses cellular networks instead of Wi‑Fi, sidestepping restrictions on your local router.
Steps:
- Turn off Wi‑Fi on your device.
- Enable mobile data from your device’s settings.
Risks:
- Mobile data usage can lead to additional charges or throttling and does not resolve the underlying Wi‑Fi pause.
6. Accessing Router Settings
If you have administrative access, the correct way to manage pauses is through Spectrum’s tools. Spectrum Advanced WiFi is primarily controlled in the My Spectrum app, and many Spectrum‑issued routers limit or disable full local web‑GUI administration.
How it works:
- As the authorized admin, you can pause/unpause devices, set schedules, and manage profiles in the My Spectrum app.
Steps:
- Open the My Spectrum app and sign in with the account that manages your service.
- Find your device in the connected devices list, then pause/unpause or adjust schedules as needed.
- If a local web interface is available on your specific router, use it cautiously; many models will still require the app for pause controls.
Risks:
- Changing settings without authorization can cause conflicts or disrupt the network for everyone.
7. Scheduling WiFi Availability
Instead of bypassing the WiFi pause, another approach is to manage when the WiFi is available. This is best done by the admin in the My Spectrum app or, where available, the router’s interface.
How it works:
- Scheduling allows specific times for Wi‑Fi access, creating predictable windows without defeating controls.
Steps:
- Access the My Spectrum app or your router’s management interface (if supported).
- Set up a device schedule that fits your household’s agreement.
Risks:
- Requires admin access and cooperation if schedules already exist.
8. Using a Different Network
If the Spectrum WiFi pause is preventing you from accessing the internet, and you have access to another network, such as a mobile hotspot, you can switch to that instead, subject to any applicable policies.
How it works:
- Connecting to a different network avoids restrictions applied by the paused router.
Steps:
- Turn on the alternative network, such as a mobile hotspot.
- Connect your device to the new network.
Risks:
- Hotspots can be data‑intensive and costly, and may have limited coverage.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices
While there are several ways to potentially bypass a Spectrum WiFi pause, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications of doing so. Network controls like WiFi pauses are often implemented to protect users, manage bandwidth, or enforce rules that encourage balanced internet use. Attempting to bypass these controls can lead to conflicts, especially in households where these rules are set by parents to manage children’s screen time.
Best Practices:
- Communicate: If the WiFi pause is causing issues, discuss the situation with the person who controls the network and agree on schedules or profiles in the My Spectrum app.
- Respect Rules: Understand the intent behind pauses—limiting distractions, managing bandwidth, or improving security—and work within those guidelines.
- Seek Alternatives: If you need uninterrupted access, consider using mobile data or a public Wi‑Fi network when permitted.
- Follow Terms of Service: Bypassing restrictions may violate your service terms and risk penalties or disruptions.
Conclusion
While it’s possible to explore various methods to bypass a Spectrum WiFi pause, each comes with its own risks and ethical considerations. The most reliable and responsible approach is to communicate with the network administrator or, if you are the admin, manage devices and schedules within the My Spectrum app. Remember that these controls are often in place for good reasons, and working within the established guidelines helps maintain a positive, conflict‑free environment.
FAQs
1. Is it illegal to bypass a WiFi pause?
Bypassing a WiFi pause may violate your internet service provider’s terms of service and could have legal or contractual consequences. It is not recommended without permission.
2. Can a VPN bypass a WiFi pause?
No. A VPN or proxy cannot unpause a device that the router has blocked at the MAC layer; it only helps with content/DNS filtering.
3. What is the easiest way to bypass a WiFi pause?
There is no guaranteed method. With permission, adjusting Private/Randomized MAC settings might make the router see your device as new. Otherwise, mobile data or a different network are temporary workarounds.
4. Can resetting my device’s network settings remove a WiFi pause?
Sometimes it changes how your device identifies, especially on Apple devices using Private Wi‑Fi Address, but it’s not guaranteed and erases saved configurations.
5. What should I do if I need internet access but WiFi is paused?
Talk with the network admin to adjust schedules or profiles in the My Spectrum app. If that’s not possible, use mobile data or another permitted network.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025