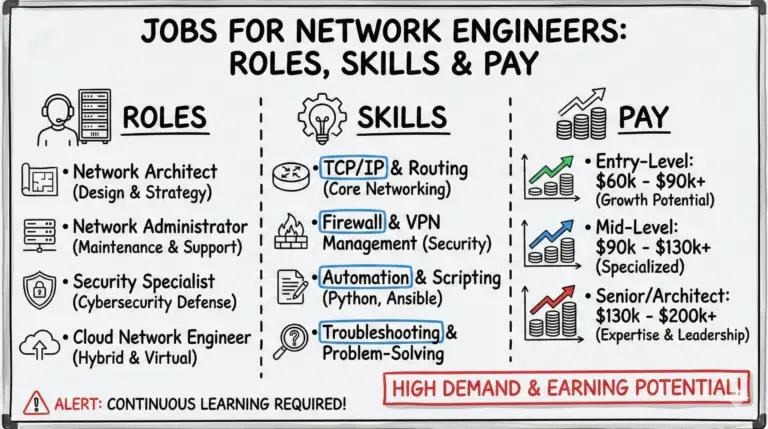
Network engineers play a crucial role in the tech industry, ensuring smooth network operations and earning attractive salaries. However, becoming one isn’t easy. It involves facing multiple rounds of interviews and being well-versed in basic and advanced network engineering questions.
To help you prepare effectively, I’ve written Interview Questions for Network Engineers to equip you with the knowledge needed to excel in your upcoming job interviews. Let’s get into it.
Interview Questions for Network Engineer with Answers(PDF Guide)
Things to do before you apply for a Network Engineer Job Interview:-
- Update your Resume – Update and make it specific to the position you have been interviewed for. Take the time to review for grammatical errors and mistakes and ensure that your skills and experience are appropriately showcased. Then, rinse and repeat for every new job interview.
- Update your Linkedin Profile – Linkedin is the best global platform to find jobs, so make sure your showcase all your hard-earned skills there.
- Take a close look at your Social Networks profiles– Employers are starting to take the Internet and social media into account when hiring and will search for your name on social platforms. So make sure it is clean, relevant, and you have nothing on your Facebook/Instagram profile or page that you wouldn’t want anyone to see.
- Perform a Google search on yourself and the company you interviewed for– You might be surprised at what pops up. Make sure everything is appropriate, make corrections if possible, or be prepared for such things in advance.
- Brush your Basic Networking Skills – Before going to your interview, familiarize yourself with the networking terms and technologies and do a thorough review of them. Make a handy note to revise just before the interview as well, and it will set your mood and boost your confidence for the interview in advance. If you have no idea what I am talking about here, don’t worry; I will provide the list of questions for you in the next section.
- Get Certified – Make sure you have at least entry-level certification like CCNA in your arsenal. It gives employers a comfort level and a quick and easy way to understand your knowledge levels.
- Prepare for Behavioural Interview questions and answers in advance.
- Prepare for Video Interview in Advance.
Network Interview questions depend on which type of role you have been interviewed for, so make sure you thoroughly study the job description before the interview. However, as a general rule of thumb, I found these questions helpful to jog your networking memory before the big event.
Senior Level Interview Questions of Network Engineer
Please make sure you have a fair idea of these questions before appearing for Senior Network Engineer.
- How do you approach Network Design? Please walk us through your complete process and mindset when designing large Networks.
- What is your Network troubleshooting process?
- What is the largest network you have ever designed or deployed? What problems have you faced, and how you had overcome them?
- What is your approach towards Network Security? and How you incorporate security in Network Designs?
- How would you add more connections to a large existing network?
- What are some fundamental techniques for increasing network performance?
- How do you make sure that you stay on top of innovations in the Network industry?
- Please draw a network topology you worked on before and explain the design.
- You have to explain complex technical concepts to coworkers and customers who lack technical expertise. How will you make sure they understand properly?
L1 and L2 Level Network Engineer Interview Questions with Answers
What is LAN?
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a network confined to limited space, such as a building or floor. If you have multiple computers in your home or office, you have a Local Area Network (LAN). A LAN is usually under the control of the company or entity that requires its use. A LAN can be tiny or huge, with one or thousands of users and devices in an office or school.
A LAN connects devices in a single, constrained area, regardless of size. A WAN or MAN, on the other hand, covers a greater geographic area. In addition, some WANs and MANs link several LANs.
What is WAN?
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network mostly provided by a third-party Internet Service Provider that connects many local area networks (LANs) geographically separated. ONE EXAMPLE IS an MPLS Network (offered by a telecommunications provider) connecting company headquarters in New York, Boston, and Los Angeles. The Internet is the most significant WAN.
What is Hub?
Hubs are fairly basic and not particularly intelligent devices. Any signal received on any port is transmitted/repeated out every other port inside the Hub.
What is a Collision Domain?
A collision domain is an area of an Ethernet network where collisions can occur. If one station can prevent another from sending because it uses the network, they are in the same collision domain. It mostly happens when multiple devices are connected through a hub or repeater.
What is a Broadcast Domain?
In an Ethernet network, a broadcast domain refers to the area where broadcasts are transmitted. Broadcasts are sent through switches (Layer-2 devices); however, in most cases, they stay within a Layer-3 network (unless forwarded). A router or a layer3 device often borders broadcasts.

What is a Switch or, more specifically, Ethernet Switch?
Any device that forwards frames based on their Layer-2 MAC addresses using Ethernet. While a hub repeats all frames to all ports, an Ethernet switch forwards frames only to the ports for which they are destined. An Ethernet switch creates a collision domain on each port, while a hub generally expands a collision domain through all ports.

What is a Layer 3 switch?
Layer3 switch is a switch with routing capabilities. Generally, VLANs can be configured as virtual interfaces on a Layer-3 switch.
What is the difference between fixed-configuration and modular switches?
Fixed-configuration switches are smaller—usually one rack unit (RU) in size. These switches typically contain Ethernet ports and are designed for situations where larger switches are unnecessary, like a building floor with 10-20 members. Typically fixed switch support ports up to 24 or 48 max.
Modular switches are bigger switches with lots of slots for a different types of cards. They can support ethernet ports up to 500 or more.
What is Auto-negotiation?
With the help of the Autonegotiation feature, Switch, router, and server ports can negotiate with one other to identify the best duplex mode and speed for a connection. Finally, the interface is dynamically configured by the network driver in accordance with the derived link’s parameters.
What is Autonegotiation Best Practice?
You have to make sure that both sides of the connection have the same values (duplex and Speed). For example, if one side of the link is set to auto-negotiation, make sure the other is also set to auto-negotiation. Likewise, if one side is set to 100/full, make sure the other side is also set to 100/full.
Describe VLANs?
Virtual LANs, or VLANs, are virtual separations within a switch that provide distinct logical LANs, and each behaves as if they were configured on a separate physical switch.
What is Router on a Stick Configuration?
Routing between VLANs or different network segments is commonly known as the router-on-a-stick configuration. Instead of connecting each VLAN to its own router interface, you can connect the switch and the router together using a single physical trunk link. Then you can use that single trunk link to pass all the VLANs.
What is a trunk?
Using Cisco’s terminology, a trunk is an interface or link that can carry frames for multiple VLANs at once. For example, a trunk can connect two switches so that devices in VLANs on one switch can communicate with devices in the same VLANs on another switch.
How to configure a trunk?
Configuring a trunk involves determining which port will be a trunk, which protocol the trunk will run, and whether and how the port will negotiate. Optionally, you may also wish to limit which VLANs are allowed on the trunk link. Trunk ports are also called VLANs Tagged ports by other switch vendors.
- switch-01(config)#int g1/1/4
- switch-01(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
- switch-01(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
- switch-01(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed VLAN?
What is VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)?
In complex networks, managing VLANs can be time-consuming and error-prone. The VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) is a means whereby VLAN names and numbers can be managed at central devices, with the resulting configuration distributed automatically to other devices.
What is the backbone network?
A backbone network is a high bandwidth network (mostly 10gigs or 100 gigs) used by large companies to connect various sub-networks and distribute different routes between them.
What are the layers of the OSI reference model and its functions?
There are 7 layers of the OSI model and below are their functions (most straightforward language):
- 1) Physical Layer: It is responsible for sending data over a physical medium (cables/fibers/wireless, etc.) and converting data bits into the electrical signal, and vice versa.
- 2) Data Link Layer: Responsible for transferring data between two network devices within a LAN.
- 3) Network Layer: Responsible for routing data between networks or two different subnets.
- 4) Transport Layer: Responsible for controlling data flow and ensuring that data is delivered across the network.
- 5) Session Layer: It establishes, maintains, and terminates the communication link between two computers.
- 6) Presentation Layer: Responsible for compressing and decompressing the data
- 7) Application Layer: This layer is responsible for everything it does for humans to interact with applications like reading/sending email, playing games, using a calculator, etc.
How many layers are there in the TCP/IP model?
There are four layers in the TCP/IP model, namely:
- The Network Layer
- Internet Layer
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
What is the difference between OSI and TCP/IP models?
The OSI model has seven layers (explained above). The TCP/IP model has four layers: Network Access, Internet, Transport, and Application Layer.
OSI model is developed by ISO (International Standard Organization), whereas TCP Model is developed by ARPANET (Advanced Research Project Agency Network).
What is a node?
A node is any device that can send or receive data on a network.

What is a router, and how is it works?
Routers are intelligent network devices that operate on Layer 3 of the OSI model. It is used to connect various networks and to route/send packets through the best path to the correct destination. It does that by storing information in its routing tables, which tell it where to send packets. A routing table is a list of information about networks and subnetworks that are connected to the network.
When a packet arrives at a router, the router uses the routing table to find out where to send the packet. First, the router looks up the destination network’s IP address in the routing table. If the IP address is found in the routing table, the router sends the packet to the corresponding destination through the outgoing port. If the IP address is not found, it simply checks for a default route as a last resort to send the packet. And if it does not find even the default route, then it drops the packet.
What is a point-to-point link?
A point-to-point connection is a cable/fiber connecting two devices on a network without using a network device (hub or switch or a router). Please note, when you connect two similar devices, for example, two computers always use a cross cable and a straight-through cable when connecting two different devices, such as a computer to a switch/router.
What is anonymous FTP?
This is an FTP server that does not ask for a username or password for authentication. Instead, most of the time, you get an anonymous ftp server for specific public servers directories.
And these directories are public directories or directories where information is released to the public.
What is an IPv4 address?
An IPv4 address is a 32-bit (4 bytes) unique identifier of your computer. It helps your computer identify itself on the network and route network traffic from one computer to another. For example, you can check your Ip address by simply typing “ipconfig” in the command prompt on Windows-based laptops.
What is a subnet mask?
A subnet mask is a 32-bit identifier that indicates which parts of an IP address are the network and the host.
- The “network” is the portion of an IP address that identifies a particular network.
- The “host” is the portion of an IP address that identifies a particular host on a network

What is the maximum UTP cable length?
The term “UTP” stands for unshielded twisted pair, and the maximum allowed length is 90 to 100 meters. You can use a repeater or switch to extend the length.
What is Data Encapsulation?
When information needs to be broken down into smaller, more manageable bits before being sent across the network, it is called data encapsulation. The source and destination addresses, as well as parity checks, are included in this process. This helps ensure that the information remains intact during transmission over the network.
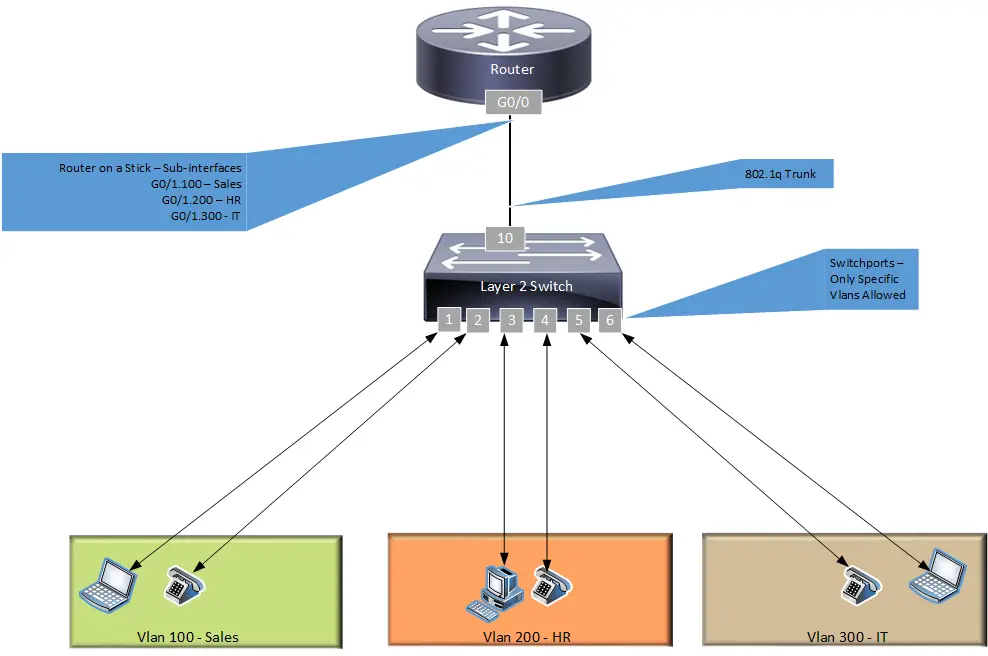
Describe Network Topology
A network topology is a diagram that describes the structure of a network. It tells us the physical and logical layout of the network and how it connects to other networks and devices. It also tells us the data path through the network and what networking devices (routers, switches, firewalls, etc.) are used.

What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, and it is a way of using a public network to connect to a private network. A VPN allows you to create a secure tunnel between two locations over the WAN or Internet.
You can use a VPN to encrypt all the data you send across the Internet. This prevents your ISP from reading it, and it also prevents anyone trying to snoop on your traffic from reading it.
Briefly describe NAT
The term NAT refers to Network Address Translation. It is a layer-3 (network) protocol that translates hosts’ internal Private IP addresses into a single external Public IP address and vice versa. NAT is commonly used for home and office networks, but you can also use it in small businesses or large organizations to connect to the Internet or hide the hosts’ real private IP addresses.
What is RIP?
RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol. It is an obsolete routing protocol and can be used by routers to manage routing tables. It does that by broadcasting its routing table to all other routers within the network. It is a distance-vector protocol and defines the network distance in units of hops.
How to secure a computer network?
To secure a network, there needs to be proper security software, devices, and protocols (set of rules) in place. The list is endless, but I have listed the most common ones below. You would highly secure the network if all of these were combined.
- Make sure the robust and updated Antivirus is installed on all Computers.
- Make sure the servers have the latest patches installed.
- Make sure network-level security devices like Routers, Firewall, VPN devices, IDS/IPS are in place and properly configured.
- Make sure network devices, computers, and servers are placed in a secured area and hardened for any unauthorized login.
- Use AAA to restrict, control, and log access to all devices. AAA stands for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting. Authentication is the process of proving who you are. Authorization is the process of deciding what you can do. Finally, accounting logs what you did while logging in.
What is NIC?
A NIC is a Network Interface Card, a piece of hardware that allows computers to communicate over a network. This card uses a unique physical MAC address to identify itself on the network and send data to and from one computer. You can use “ipconfig/all” to see all details of a NIC on your computer.
What are proxy servers, and what role do they play in network security?
A proxy server is a program that acts as an intermediary between a client and a server. The primary function of a proxy server is to allow clients to request data from one or more servers on the Internet without disclosing the client’s internal private IP address. This is often done for security reasons, to mask the location of a network from unauthorized individuals, or simply to hide its existence from other computers on the Internet.
How critical is it to implement a Fault Tolerance System?
A Fault Tolerance System (FTS) is a system that can continue operating even when a component fails. It can be considered as a backup system that has no downtime. FTS ensures that the availability of data is maintained during a fault condition.
What does 10Base-T mean?
The 10 refers to the speed at which data is transferred. In this case, it’s 10Mbps, and Base refers to the baseband.
What is private IP address used for?
Private IP addresses are allocated for use within an organization. These addresses are not routed across the public Internet, unlike public IP addresses. Private Ip addresses assigned by IANA are below:-
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
Any Organization can allocate these Private Ip addresses for their Internal use.
What is NOS?
A network operating system (NOS) is used only for network devices such as a router, switch, or firewall. For example, Cisco IOS is a NOS.

What is DoS?
The main goal of a DoS, or Denial-of-Service attack, is to disrupt the network services provided to a large group of people at the same time. The impact of a DoS attack is often measured by the number of users who cannot use the service and the time required to restore it. A DoS attack usually takes place with the help of bots that a hacker or a malicious individual controls. The goal of a DoS attack is to cause a service to crash or to make it unavailable. It is usually done by flooding the service with too many requests for information or requests for service. These requests use up the server or network resources and can make it difficult or unable to provide the service.
What is OSI, and why is it important in computer networks?
Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) was created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and it is a seven-layer international standard for communicating data through networks and telecommunications systems. This model divides a network into seven layers, each defining a specific function within the network. The bottom two layers, the Physical and Data-Link layers, form the foundation for the rest of the layers. The top five layers, the Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application layers, are concerned with applications that use the network.
What is the purpose of shielded and twisted pair cables?
The basic function of shielded and twisted pair wires is to eliminate crosstalk. Crosstalk is a term that refers to electromagnetic interference or noise that can disrupt the transmission of data across cables.
What are the benefits of address sharing?
Address sharing is done through NAT (Network Address Translation), and it allows multiple inside hosts to share the same Public IP address. You need a special device capable of doing NAT, for example, a router or a firewall. Address translation not only saves Public IP addresses but also has an inherent security benefit compared to routing. That’s because servers on the Internet can only see the public IP address of the external interface of the firewall, not the host’s private IP address behind it. The firewall has an inbuilt NAT table for address translation which maps public ip addresses and ports with Private IP addresses and ports of every connection.
What are MAC addresses?
MAC, or Media Access Control address or an Ethernet Address is a unique 6-byte (48 bit) identifier assigned to network devices by the manufacturer. Every computer, printer, router, etc., has a unique MAC address or physical address that is automatically assigned at the point of manufacture. It is typically not changeable by the end-user. This allows for the tracking of devices on a local area network (LAN).
What are the equivalent layers of the TCP/IP with the OSI reference model?
- The TCP/IP Application layer is mapped to Session Layer, Presentation Layer, and Application Layer of OSI model.
- The TCP/IP Transport layer is mapped to the Transport Layer of the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP Internet layer is mapped to the Network Layer of the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP Network, Access layer, is mapped to the Data Link Layer and Physical Layer of OSI model.
How to determine the IP class associated with a specific IP address?
You can determine the class of an IP address by looking at the first octet. If the first octet of the address begins with a 0, it is a Class A address. If the address starts with bit 10, it is a Class B address. If it starts with 110, it is a Class C network.
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
What is the main objective of OSPF?
OSPF, or Open Shortest Path First, is a link-state dynamic routing protocol. In OSPF, every device on the network advertises its topology to other devices on the network by flooding information about its links and subnets. The devices on the network then use this information to calculate the best possible path or shortest path to any given destination.
What is a firewall?
A firewall is a software program or a hardware device that secures an Inside network from outside. It has a range of rules to block unauthorized user access, such as hackers accessing internal servers while permitting safe passage to authorized users.
What is a star topology?
A star network has one central node – called a Hub, which connects to all other nodes (computers, terminals, printers, etc.). Star networks are advantageous because they are easy to set up, troubleshoot, modify and have a central management point. Therefore, they are the most popular topology for small wiring networks. However, it has drawbacks, like if the hub fails, everything connected to it will fail. Moreover, it is costly and unsuitable for heavy network traffic as it slows down the entire network.
What is a gateway?
A gateway is a router or layer3 device that handles all network traffic between two networks. For example, if you are connected to the Internet through your home modem, that modem is your network gateway. A gateway can provide services like routing, network translation, DHCP, DNS, VPN, firewall, web server, etc..
What are the disadvantages of a star topology?
Disadvantages of star topology include:-
- It has a single point of failure; if the central hub fails, everything connected to it will fail.
- It is costly to manage, as you need a high-end hub to cater to all traffic from the slave nodes.
- It is not suitable for heavy network traffic. Because everything is connected to the hub, and if the hub is not working properly, it slows down the entire network.
What is SLIP?
SLIP or Serial Line Interface Protocol is a computer networking protocol used by most dial-up Internet service providers (ISP) before the popularization of Ethernet technologies. Though no longer used, SLIP can still find it running on most operating systems for remote access.
Give some examples of private ip addresses.
These are private ip addresses.
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
What is tracert?
The “tracert” or “traceroute” utility is a standard tool for network troubleshooting. It is used to monitor the route that a packet takes between a sender and a recipient. It is a command-line tool available on almost all network devices and operating systems (Windows/Mac/Linux).
What does a network administrator do?
An effective network administrator knows how to design a network, configure a network, troubleshoot a network, and maintain a network.

What is the main disadvantage of a peer-to-peer network?
The most significant disadvantage of a peer-to-peer network is the lack of selective service. This means that if one of the nodes is not currently receiving data, no one will be able to.
Another problem with peer-to-peer networks is that there is always the possibility of malicious users sharing or attempting to distribute pirated software or copyrighted material. And Peer-to-peer networks typically do not try to prevent this.
What is a Hybrid Network?
A hybrid network combines features of both client-server and peer-to-peer networks. As a result, it is more flexible than a pure client-server network while maintaining a pure peer-to-peer network’s simplicity and low cost.
In this type of setup, the server is connected to clients via a hub, and the clients are connected via a group of routers. The main advantage of this type of network is that it allows for sharing data, resources, and files between different users.
What is DHCP?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns unused IP addresses from a pre-allocated ip pool to network devices. It can also provide other critical network information to clients like subnet mask, DNS, default gateway, and other network-related config parameters.
What is the primary function of the ARP?
ARP or Address Resolution Protocol is used for mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses. This process is typically used to determine which device is connected to the network.
What is TCP/IP?
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) is a set of protocol layers and a standard way to transfer data across the Internet and other computer networks.
The TCP layer is responsible for getting the data to the correct destination and ensuring it reaches the destination in the right order. The IP layer is responsible for routing the packet to the correct computer.
How to use a router to manage networks?
Routers are layer3 devices, and their main task is to provide routing between two networks or two network segments. However, they are smart enough to provide other network services, including DHCP, DNS, default gateway, logging, firewall, etc. In addition, most of the home modems have inbuilt routers and firewalls, and you can use them to restrict/allow computers for certain websites at a particular time of day, event and data logging, and much more.
What protocol can be applied when you transfer files between different platforms, such as UNIX systems and Windows servers?
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a platform-independent protocol, so it is the best option for transferring files between different server platforms.
Why do we use a default gateway?
Default Gateways are devices that connect the internal network to the external network. A default gateway is often called a “default” gateway because all packets coming in on the LAN are routed through it. In this way, it acts as a default option for routing. You can check your default gateway on your windows computer by doing “ipconfig.”

What can be considered good passwords?
A good password must be more than six characters long and a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. It must not be guessed easily, like your date of birth or your pet’s name, etc.
When it comes to UTP cables, what is the proper termination rate?
Unshielded twisted-pair network cable should be terminated with a 100-ohm resistor.
What is the netstat command?
Netstat is a command-line utility. It is used to display the status of TCP connections, including the state of the connection, the amount of data transmitted, the host’s address, the port number, and the protocol. Netstat has lots of information to offer; you can do “netstat help” on the windows command prompt to get the list of all helpful netstat commands.
What are the number of network IDs and Host IDs in a Class C network?
Class C networks have a Network ID of 21 bits (Bits 22, 23, and 24 are fixed and cannot be changed) and a Host ID of 8 bits, which means that each network can have up to ‘2 to the power of 21’ = 2,097,152 Networks and ‘2 to the power of 8 minus 2’ = 254 Hosts in each network. We subtracted two from the Hosts formula because one is the Network Address, and the other is the Network Broadcast Address and cannot be used.
What happens when cables are used that are longer than the specified length?
Excessively long cables will result in signal loss. This happens because data transmission and reception degrade, and the signal becomes weak as we extend the length beyond the specified point.

What common software issues can result in network failures?
The list is endless, but I have listed some of the common software related issues:
- Outdated network devices and other components
- Application Malfunction
- Client-server issues
- Any Misconfiguration in the network
- A virus and malware issue
- The server is not properly patched
- Virus infections
- Misconfigured or missing User policy and rights issues
- DDoS or webserver attacks
- Overloaded CPU
- Missing or corrupt software updates
- Backup failures
What is ICMP?
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a network layer protocol used by network tools such as PING by network devices to diagnose network communication problems. ICMP is mainly used to check if data is arriving at its intended destination on time. ICMP is frequently used on network devices like routers. While ICMP is necessary for error reporting and testing, ICMP can also be used by hackers to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
What is Ping?
Ping is a command-line application that can be found on practically any operating system or network device with network connectivity and is used to determine whether a device on the network is reachable or not.
The ping command sends a request to a specific device using its IP address or device name over the network. A successful ping results in a response from the device to which the ping was sent.
What’s a peer-to-peer network?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks are networks that do not rely on a central server for their operation. All of the computers connected to this network function as individual workstations.
What is DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) is like a phone directory used to translate user-friendly domain names (www.abc.com) into numerical IP addresses (191.3.4.5) and vice versa. Translation to IP addresses is required to identify and contact computers and other resources on the Internet.

What are the advantages of fiber optics over other transmission media?
Below are the advantages of fiber optics over other media:-
- Fiber is faster and has less data loss rate over long distances (up to 40 km with single-mode fiber).
- Fiber supports higher bandwidth, meaning you can send more data in one go.
- Fiber is thinner and lighter in weight, making it easier to fit/distribute, consuming less power.
- Fiber has no twisted copper wires, and it is immune to EMI/RFI and lightning damage.
- Fiber is entirely safe to work with because there are no electric sparks or shock concerns.
- Fiber has a longer lifespan than copper.
- Fiber is hard to tap or hack.
When comparing a hub with a switch, what are the main differences?
Below are the significant difference between hub and switch:
Difference between a Hub and a Switch
| Hub | Switch |
|---|---|
| Hub works on Physical Layer. | Switch works on Data Link Layer. |
| Hub supports only broadcast type transmission. | Switch supports all type of transmissions whether it is unicast, multicast or broadcast. |
| Hub usually has less ports , 4 or 5 ports maximum. | Switch has more ports 24, 48 ports. Or multi-chassis switches have more than 200 ports. |
| Hub has only one Collision domain. | Each port in a switch has its own collision domain. |
| Hubs do not supports VLAN. | Switch supports VLANs. |
| Hub supports only half duplex. | Switch supports half and full duplex both. |
| Hubs do not support packet filtering. | Switches support packet filtering. |
| Hubs sends/replicates packet to all ports and it is not an intelligent device. It is relatively affordable in comparison to switch. | On the other hand , switches are Intelligent devices and only send packets to selected ports. It is expensive compared to a Hub. |
| Hubs are obsolete these days and are not used in networks. | Switches are Intelligent and complicated devices that are commonly used in the networks. |
| A hub cannot be utilized as a repeater in any way. | A switch can be used as a repeater in certain situations. |
What are the various network protocols that Windows RRAS services support??
RRAS (Routing and Remote Access Service) is a Windows Server feature that enhances the server’s TCP/IP internetworking capability. Windows RRAS supports the following network protocols: NetBEUI, TCP/IP, and IPX.
What are the maximum networks and hosts in class A, B, and C networks?
| Class | Number of Networks | Number of Hosts per Network |
|---|---|---|
| A | 126 | 16,777,214 |
| B | 16,384 | 65,534 |
| C | 2,097,152 | 254 |
Maximum networks and hosts in class A, B, and C networks
What is a straight-through cable’s standard color sequence?
- Orange/white
- orange
- green/white
- blue
- blue/white
- green
- brown/white
- brown
More details on the color-coding of straight-through and cross-over cables.
In the TCP/IP stack, which protocols are part of the Application layer?
Application layer protocols are: Telnet, FTP, TFTP, NFS, SMTP, HTTP, HTTPs.
How can two PCs be connected for file sharing without the use of a hub or a router?
Yes, you can connect two computers back to back using a crossover cable for file sharing. Cross over cable’s one end of data transmit pin is connected to the other end data receive pin and vice versa.
What is ipconfig?
“Ipconfig” is a Windows utility used to check the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway information of a windows computer’s NIC (Network Interface Card). With “ipconfig/all,” you can get more details, including Physical address, ipv6 address, DHCP, etc.
You can further use “ipconfig help” to get a list of everything “ipconfig” has to offer.
How does a straight-through cable vary from a crossover cable?
A straight-through cable has an identical pin connection at both ends. And that is the reason it used to connect two different devices—for example, a computer with a switch or a hub.
On the other hand, a crossover cable has the pin connection reversed between the two ends, and it is mainly used to connect two similar devices, for example, two computers.
What is the client-server network?
In a client-server network, end-users, referred to as clients, connect to a central computer, referred to as a server, to access a centralized repository of resources such as files, songs, videos, or any other data or service. The main goal of a server is to serve its clients.

Networks
What is networking?
Networking is the implementation of the physical connections (wired or wireless), devices, and logical links that connect multiple computers and support data communication between them.
Is the MAC address transferred when moving NIC cards across PCs?
Yes, it does, as MAC addresses are encoded into the NIC hardware, not the PC. This also means that a PC’s MAC address may change if a new NIC card is installed.
What is clustering support?
A network operating system’s capacity to connect several servers in a fault-tolerant group is called Clustering Support. The key benefit is that the cluster will continue processing on the next server if one server dies.
Where is the best location for an anti-virus program to be installed?
Individuals can access any workstation or can use their USB drives to install a virus. So to be fully protected, all servers and workstations must have antivirus software installed.
Describe Ethernet.
Ethernet is based on IEEE 803 standard. It is a local area network (LAN) technology that enables network services, such as data, voice, and video, among networked devices over shared media.
What are the disadvantages of ring topology?
Disadvantages of Ring topology:
- Only one path – With a ring network, there is only one path between two nodes, and therefore if the path goes down, the whole network goes down.
- Limited number of nodes – The number of nodes and devices attached to any single network device is limited.
- Larger diameter – Ring topologies do take up quite a large area, and it’s not ideal if you need to build an extensive network.
- Not easier to Manage: You need to take down the entire network to reattach or reconfigure a node.
What are the main differences between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA?
CSMA/CD, or Collision Detect, retransmits data frames whenever a collision occurs. CSMA/CA, or Collision Avoidance, will first broadcast intent to send before data transmission.
Difference between CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
| CSMA/CA | CSMA/CD |
|---|---|
| CSMA / CA is effective Before a collision. | CSMA / CD is effective After a collision. |
| CSMA / CA is widely used in wireless networks. | CSMA / CD is used in wired networks. |
| As the name suggests "Collision Avoidance", CSMA/CA reduces the likelihood of a collision. | As the name suggests " Collision Detection" , CSMA/CD only minimizes the recovery time. |
| CSMA / CA is used in 802.11 standard. | CSMA / CD is used in 802.3 standard. |
| CSMA/CA conveys the sender's intent to send data; upon receipt of an acknowledgment, the sender then sends the data. | On the other hand , Whenever a conflict occurs, CSMA / CD resends the data frame. |
| CSMA/CA is approximately as efficient as CSMA. | CSMA/CD is better and powerful than CSMA. |

What is SMTP?
SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol used to send and receive email messages.
What is multicast routing?
Multicast routing is the routing of packets sent to a multicast address (224.0.0.1) rather than to a single host (192.168.0.1) or a broadcast address(255.255.255.255). This is similar to how unicast routing works, except that hosts within a multicast group have a single multicast address that many hosts can share instead of every host having its own unicast address. Multicast routing is helpful in cases where messages are sent from a source to multiple receivers.

What is the significance of network encryption?
Encryption is scrambling a data string into a format that a receiver can only interpret with access to the encryption key. Encryption ensures that information captured halfway remains unreadable. Without encryption, anyone on the network could read everything.
How are IP addresses organized and displayed?
IP addresses (192.168.1.100) are represented as a string of four decimal numbers separated by a period or a dot. This layout is also referred to as the dotted-decimal format.
What is the importance of authentication?
Authentication refers to the process of verifying that a user of a service is who they claim to be. A username and password are the most common authentication methods, but other methods like two-factor authentication, certificates, and biometrics are available. This provides a secure way of restricting access to the network from hackers and intruders.
What is IPSec tunnel mode?
IPSec has two modes of operation: Tunnel and Transport. IPSEC Tunnel Mode transmits data over the Internet that encrypts both the data and the original IP address. The ESP operates in Transport or Tunnel Mode. In Tunnel Mode, ESP encrypts both data and IP headers.
When it comes to building WAN networks, what are the various technologies that are used?
- Analog connections – those made via standard telephone lines
- Digital connections – made possible by the use of digital-grade telephone lines
- Switched connections – data is transferred utilizing multiple sets of links between the source and receiver.

Mesh Topology
What is Mesh Topology?
A mesh network is a network topology where each node is connected to every other node directly (physically or virtually). Mesh networks are self-healing and highly redundant; if one of the primary paths is lost, data can reroute using other available paths.
There are different types of mesh networks, and the most common ones are partial mesh and full mesh.
In Partial Mesh topology, most of the devices are connected with each other, but few devices are connected with just two or three devices.
In Full Mesh topology, every device is connected directly with every other device.
What are some of the most typical hardware-related issues that might happen when troubleshooting computer network problems?
Hardware components tend to fail over time, and there are many ways that this can happen. For example, a device can age and stop working. Even a hard drive or storage device can malfunction, NIC (Network Interface Card) can be broken, and a computer or network device can overheat and burn chips inside. Sometimes hardware misconfiguration can also cause trouble; for example, you forgot to enable a second power supply or accidentally switched off the Core device.
How to fix signal attenuation problems?
First, you should check the cable or signal length limitations; for example, a copper cable length must not exceed 90-100 meters. If the length exceeds the allowed limit, use repeaters and hubs to regenerate the signal and prevent signal loss. Lastly, you can also check whether the cables are correctly seated and connected at both ends.
How does DHCP help in network administration?
DHCP is a protocol for network computers to automatically request and receive IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateway, and other IP configuration information from a DHCP server. This eliminates the need for the network administrator to individually visit and configure the network settings statically on each computer.
What is a profile in terms of networking concepts?
Profiles are the configuration settings that are created for each user. For example, you can create a profile in Microsoft active directory that automatically places a user in a group.
What is sneakernet?
Sneakernet is a term used for computer file transfer in which files (usually large) are copied from one machine to another via floppy disk, USB flash drive, or other portable media device rather than transferring the data directly over a wired or wireless network.
What is the IEEE’s role in computer networking?
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) is a professional electronic and electrical engineering society founded in 1963. It is an engineering organization that develops and oversees standards for electrical and electronic equipment. In addition, they build new networking concepts for computer networking, maintain and update existing Network related RFCs (Request for Change), build and maintain standards for Networking equipment vendors, etc.
What protocols are included in the TCP/IP Internet Layer?
The TCP/IP Internet layer is equivalent to the network layer in the OSI model and manages four protocols. These protocols include ICMP, IGMP, IP, and ARP.
What are rights in networking?
The term “rights” in networking refers to the authorization provided to an individual user by the network administrator/manager to carry out specific actions. For example, an Administrator can assign individual privileges to each network user based on what they can accomplish on network devices. You can use AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) concepts to maintain “rights” within your organization.
What is one basic requirement for building VLANs?
Without VLANs (Virtual LAN), a network switch has a single broadcast domain. This also means you can use only one subnet through that switch. By building VLANs, you can break a single broadcast domain into multiple broadcast domains and use multiple subnets through a single switch.
VLANs also enhance security because you can isolate or restrict certain communication between hosts on different network segments.
VLANs divide a big broadcast domain into smaller, manageable, more secure domains.
What is IPv6?
The IPv6 protocol is designed to address the problem of the exhaustion of IPv4 Public IP addresses. IPv6 is an evolution of IPv4, the protocol currently used to define Internet addresses and define how computers and other devices worldwide can communicate. IPv6 has been deliberately designed to not be backward-compatible with IPv4, as IPv6 has many additional capabilities not present in IPv4.
IPv6 has 128-bit (2128) addresses and provides 3.4 x 1038 unique IP addresses. This is equal to 340 trillion trillion trillion IP addresses.
What is the RSA algorithm?
RSA stands for Rivest-Shamir-Adleman. It is one of the most widely used public-key cryptography algorithms. The RSA algorithm is used for both encryption and digital signatures.
What is 100Base FX?
The number “100” in 100BaseFX indicates a data transfer rate of 100 megabits per second or 100Mbps. The term “Base” refers to digital transmission over baseband. The letter F means that the segment is of the Optical Fiber variety.
What is the 5-4-3 rule, and how is it utilized in network architecture?
The 5-4-3 rule applies to 10Base2 and 10Base5 Ethernet topologies. A network with four repeaters can have a maximum of five segments. Only three of the five segments can include nodes.
What are the differences between TCP and UDP?
The following are some of the most significant differences between the TCP and UDP protocols:
| TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
|---|---|
| TCP handles connections, and it is a connection-oriented protocol. Connection-orientated indicates that devices should establish a connection before sending data and disconnect thereafter. | UDP is a datagram oriented protocol. This is because opening, maintaining, and closing connections has no overhead. UDP is good for broadcast and multicast networks. |
| TCP is reliable because it ensures data delivery to the destination. | UDP does not guarantee data delivery to the intended destination. |
| TCP has numerous inbuilt error-checking techniques. This is due to the fact that it enables data flow control and acknowledgment. | UDP only uses checksums for minimal error checking. |
| TCP has an Acknowledgement segment. | UDP has no Acknowledgement segment. |
| TCP does Sequencing of data. This simply means that packets will always arrive in order at the receiver's end. | UDP does not do any sequencing of data. And If it is required by the application then it has to be managed by the application itself. |
| Because TCP does error-checking, sequencing, etc to make sure data is delivered at the destination, it is SLOW by design. | Because UDP does not guarantee delivery of the data at the destination, it is FASTER compared to TCP. |
| TCP can retransmit data if data is lost in transmission. | There is no possibility of retransmission in UDP. If some data is lost it is lost for ever. |
| TCP has a variable-length header of (20-60) bytes. | UDP always have a fixed header length of 8 bytes. |
| TCP is heavier than UDP. | UDP is lighter when compared to TCP. |
| TCP uses a three-way handshake such as SYN, ACK, SYN-ACK. | Since UDP is connectionless, it does not need any handshakes. |
| TCP does not support Broadcasting. | UDP does support Broadcasting. |
| TCP is most commonly used by HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP and Telnet. | UDP on the other hand is mostly used by DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. |
Difference between TCP and UDP
What are the most critical components of the protocol?
Three most important elements of the protocol to remember:
- Syntax: The syntax of the data is the format in which it is presented. It determines the order in which the data is shown.
- Semantics: The semantics of each part specify the meaning of the bits contained inside it.
- Timing: Timing refers to When the data is to be sent and how quickly it is sent.
What is the maximum length of a segment in a 100Base-FX network?
A 100Base-FX network segment can be up to 412 meters long.

Decoder
What is a Decoder?
A decoder is a circuit or computer program that restores the original data format by translating/converting codes or ciphertext into readable data. It also converts the digital signal into analog. Thus, the decoder is the opposite of an encoder.
What is Brouter?
Brouter or a Bridge router is a device that links two networks. A bridge router can operate as a Bridge (a layer2 device) and a Router (a layer3 device) when a Brouter acts as a bridge in the network when configured in transparent mode and not operating in Layer 3 mode. When a Brouter is in Layer 3 mode, it routes data between two networks.
How to use VPN?
A VPN makes you become almost anonymous and can make it appear as if you are located in another place or country. For example, you are based out in Canada and want to enjoy Netflix from the US; you can use VPN to accomplish that.
To use a VPN service. First, select a VPN service (for example, NordVPN, Expressvpn, etc.) and install the app on your device. Once installed, run the app and log in using your username and password (you selected when signing up for the service). When logged in, you’ll typically notice a large ‘connect’ button and the ability to automatically select a server depending on its proximity to you or the one that offers the fastest connection. Hit that button after choosing the correct country. That’s all; you’re now connected to the Internet via VPN and can pretend to be in another country or place rather than your home country.
Why the standard OSI model is known as 802. xx?
In February 1980, the OSI model was created. So in 802.XX, 1980 is denoted by ’80,’ while February is denoted by ‘2.’
What is NVT in a computer network?
In its simplest form, a Network Virtual Terminal (NVT) is a dumb terminal that communicates to a central server to start a Telnet session. The NVT is also known as a client-server architecture in the client/server computing model.
What is the source route?
The source route is a series of IP addresses that identify the path taken by a datagram. The source route can be included in the IP datagram header.
Explain the term Pipelining
Pipelining is a term used to describe the sequence in which processes are carried out. Sequencing is the term used to describe the process of starting a new task before completing an existing job.
Ethernet transmission speed is measured in which unit?
Ethernet transmission speed is usually measured in Mbps.
How long is the thinnest cable?
The Thinnet cable is 185 meters long.
What is the RG8 cable?
RG8 cable is a thicknet cable.
Is coaxial cable still widely used in computer networks today?
No, coaxial cable is not used in modern computer networks anymore.
An RJ11 connector can be found on which cable?
RJ11 connectors are used in a telephone cable.
What is Multi-homed Host?
A multi-homed host is a computer with multiple network interfaces and is topologically capable of having more than one network address.
What is EGP?
EGP stands for Exterior Gateway Protocol and is a network protocol used to exchange routing information between Autonomous Systems. EGP is the predecessor of BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) and is not used anymore.
What is Passive Topology?
When a computer device in a network only listens for and receives a signal, it is a passive node. And that network topology is called Passive Topology.
What purpose does a Pseudo TTY serve?
It’s a fake terminal that lets you connect through Telnet or log in. No connection can be made without it. The pseudo TTY is a pseudo-terminal emulator, and it is used for running daemons and user services in the background to provide security to a running process.
What is Redirector?
A network redirector is a set of software components installed on a client computer that allows access to remote files and resources (such as printers and plotters). The network redirector transmits file operation requests from local client programs to a remote server for processing. Responses from the distant server are returned to the local application. The network redirector program makes remote files and resources appear as local files and resources on the client machine, allowing them to be used and handled similarly.
What is a TCP three-way handshake?
A TCP three-way handshake process allows a client and server to open a reliable connection before the actual data communication process starts. In a three-way handshake, the client sends an SYN (synchronization) packet, which is replied to by a server through SYN-ACK, and then finally client sends back an ACK (Acknowledgment) packet.

Hamming Code
What is a Hamming code?
Hamming code is used to detect and fix bit errors that can arise when moving or storing computer data. R. W. Hamming of Bell Labs named this code.
Like other error-correction codes, Hamming code uses parity and parity bits, which are added to data to ensure validity when read or received in data transmission. An error-correction algorithm may identify and locate a single bit defect in a data unit using several parity bits.
What is the use of the Hamming code?
Hamming codes are utilized in various applications that frequently encounter errors, including DRAM memory chips, satellite communication hardware, PlasmaCAM, open connectors, shielded wires, and embedded processors.
What are the potential benefits of the Hamming code?
For single-bit errors, Hamming codes are the most cost-effective solution.
Error detection and rectification are both possible with this technology.
Hamming codes are the best choice for computer memory and single-bit error correction and detection because they are simple to utilize.
Why Use MAC Address?
The following are some of the important reasons for using MAC addresses:
- First, it provides a secure way to find senders or receivers in the network.
- The MAC address is useful in preventing unauthorized network access.
- MAC address is a unique number and can be used to track the device.
- Wi-Fi networks at the airport use the MAC address of a specific device to identify it.
What are the different kinds of MAC addresses?
MAC addresses are classified into three types: Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast. Simply examine the first byte to determine the sort of address you are viewing. The initial byte of a unicast address will be even, such as 02, 04, 06, and so on. A multicast address’s first byte is odd, such as 01, 03, or 05. The broadcast address is all 1s binary or entirely hexadecimal FF.
What are the important differences between MAC addresses and IP addresses?
Here are some differences between MAC and IP address:
| MAC Address | IP Address |
|---|---|
| MAC Address is an abbreviation for Media Access Control Address. | IP Address is an abbreviation for Internet Protocol Address. |
| MAC works on Layer 2 (Data Link layer) of OSI model. | IP works on Layer 3 (Network layer) of OSI model. |
| MAC addresses ensure that each machine has a Unique physical address on the LAN (Local Area Network). | The IP Address is a computer's logical address, and it is used to identify a computer that is connected to the Network. |
| MAC Address is a six byte hexadecimal address. | IP Address is a 4 bytes (ipv4) or of 16 bytes (ipv6). |
| One can find MAC address by using ARP. " Show arp " in cisco devices. | RARP (Reverse ARP) is required to derive IP Address from MAC address. |
| Because MAC address is burnt inside the Network Interface Cards, It is hard to change a MAC address of an Device. | IP addresses are relatively easier to change than MAC addresses. You can change IP address by simply going inside your computer's Network settings. |
| MAC addresses does not have any classes. | On the other hand , there are six classes of IP addresses in IPv4: A, B, C, D and E. |
Difference between MAC Address and IP Address
What is an Analog Signal?
An analog signal is a continuously variable signal that varies in proportion to the value of the quantity being measured, i.e., the signal is directly proportional to the quantity being measured. Examples include sound, light, temperature, and pressure.
What is a Digital Signal?
Digital signals are binary signals, meaning that they can exist in either of two states. A single bit can be either on or off or high or low. The values that the signal can take on are the most elementary binary values.
What are the differences between analog and digital signals?
Below is a list of the most significant distinctions between analog and digital signal transmission:
| Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|
| The analog signal is continuous and varies in time. | A digital signal has two or more states and is binary in form. |
| An analog signal is represented in the form of sine wave. | A digital signal is represented in the form of square wave. |
| An analog signal is Easily affected by the noise. | On the other hand , Digital signals are more stable and less prone to noise. |
| Analog signals can be impacted during transmission. | Digital signals are more robust and cannot be affected during data transmission. |
| Analog signals consumes more power. | While Digital signals consumes less power. |
| Example of Analog Signals are : Temperature, Pressure, Flow measurements, etc. | Examples of Digital signals are : Valve Feedback, Motor Start, Trip, etc. |
| Troubleshooting Analog signals are a bit difficult. | Digital signals are easier to troubleshoot compared to Analog signals. |
| Analog circuits utilize components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes. | Digital circuits use components such as transistors, logic gates, and microcontrollers. |
Difference between Analog and Digital signals
What is MAN?
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that connects nodes in a metro area such as extended public transportation, universities, and corporate campuses. You may also use a MAN to connect two or more separate LANs (Local Area Networks) such as individual buildings. A MAN or WAN aims to cover a relatively large geographical area while keeping costs low and providing high performance and reliability.

Modem
What is Modem?
The modern modem is a device that offers a digital connection for voice, video, and data.
The modem is an abbreviation of MOdulator DEModulator.
The purpose of a modem is to modulate a digital signal to an analog signal and demodulate an analog signal to a digital signal.
Telecom companies use practically many modems, which are the specialized hardware that they use for exchanging data over a telephone line, satellite link, or a cable network with another computer.
What are the benefits of using a modem?
Benefits of using the Modem:
- Modems are devices that allow two computers to communicate with each other.
- Most modems come with a built-in router and firewall.
- Modems mostly come free with the Internet service you take at home.
- The modem is widely used in homes and small offices, and it is the simplest way to connect to the Internet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you can ace the Interview of a network engineer even without a formal college degree. The basic concepts and terminology are easy to understand. Network engineers must have a thorough understanding of networking protocols and a keen eye for detail. They must be able to perform their job efficiently and effectively. To be a good network engineer, you need to be self-motivated and capable of working long hours. You need to know how to troubleshoot problems and how to implement solutions. Please make sure you go through the Interview Questions of Network Engineer provided in the blog post before the interview. Best of luck with your preparations, and please share this post so that it reaches out to all aspiring future network engineers.
- Telecom Network Infrastructure: Complete Guide to Components & Design - January 6, 2026
- TP-Link TL-SG108E vs Netgear GS308E: Budget Smart Switches - January 5, 2026
- MikroTik CRS305-1G-4S+ Review: The Ultimate Budget SFP+ Switch Guide - December 25, 2025